Students can enroll at Turkish universities after the 11th grade, but there are several nuances. First, there are entrance exams. Most universities in Turkey accept international SAT, GRE and GMAT results. However, some require applicants to take their own standardized tests — YÖS for bachelor’s and ALES for master’s and PhD students. Secondly, the language is a big factor. While there are many English-language programs in Turkey, there are still many more programs in Turkish. In addition, it will be more difficult to get used to the country without knowing the local language.
Of course, there are many other requirements. Continue reading to learn more about them, as well as about the cost of study and scholarships.
We talk about higher education in Turkey in another, equally detailed article.
Cost of education in Turkey
In Turkish
| Program | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language level | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language courses | 6+ | 1-52 weeks | 160 USD/week | 400 USD/week | Temel 1 (A0) | School test |
| Language courses at a university | 16+ | 2 weeks - 2 years | 1,200 USD/year | 1,600 USD/year | - | - |
| University preparation | 16+ | 1-2 years | 100 USD/month | 200 USD/month | Orta (B1) | Placement test |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 4-6 years | 300 USD/year | 5,000 USD/year | Yüksek 1 (B2) | TÖMER/TYS |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-3 years | 300 USD/year | 5,000 USD/year | Yüksek 2 (C1) | TÖMER/TYS |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 4,000 USD/year | 18,000 USD/year | Yüksek 2 (C1) | TÖMER/TYS |
| PhD | 20+ | 2-4 years | 300 USD/year | 500 USD/year | Yüksek 2 (C1) | TÖMER/TYS |
In English
| Program | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language level | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language courses | 6+ | 1-14 weeks | 200 USD/week | 600 USD/week | A1 | School test |
| University preparation | 16+ | 1-2 years | Free | 8,100 USD/month | A1 | Placement exams |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 4-6 years | 252 USD/year | 7,000 USD/year | B2 | TOEFL IBT 75 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-3 years | 600 USD/year | 11,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL IBT 92 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 2,000 USD/year | 15,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL IBT 92 |
| PhD | 20+ | 2-4 years | 500 USD/year | 9,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL IBT 92 |
Additional expenses
| Expense | Average cost |
|---|---|
| Registration fee | 120 USD |
| Visa | 100 USD |
| Accommodation | 2,400 USD/year |
| Insurance | 50 USD/year |
| Meals | 2,200 USD/year |
| Transportation | 500 USD/year |
All prices and requirements must be specified on the official websites of universities.
Admission to universities in Turkey
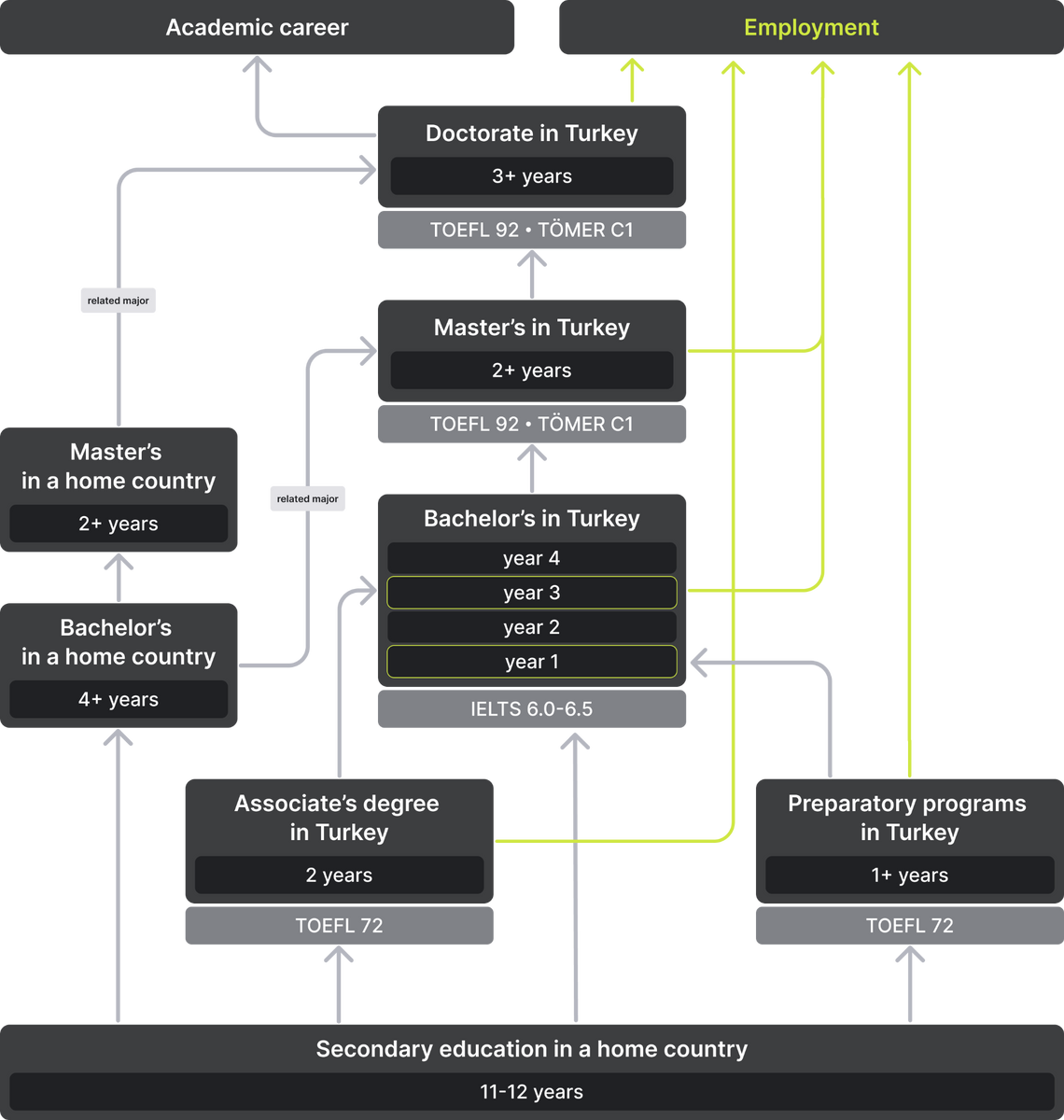
How to choose a university
There are more than 200 universities in Turkey. Most of them are young, being no more than 20-30 years old. Because of this, major international ratings do not tend to notice them. Therefore, higher rankings are occupied by universities founded 100-200 years ago: Istanbul University, Istanbul Technical University, Yıldız Technical University, and Bogazici University.
Prestigious universities are well-known, which means they are more in demand among employers. However, high-quality and relevant education can be obtained at other Turkish universities. Moreover, tuition at these institutions is much less.
Pay more attention to the rankings of Turkish universities in particular subjects. QS, THE, and ARWU conduct subject rankings. For example, Hacettepe University is ranked 272 in the world and the first in Turkey in the direction of medicine[1]. But in the general list of the best global universities, its position is much lower — 801-1000[2].
There are other criteria that can help you choose a university.
Education in Turkish or English
In Turkey, there are about 800-1000 English-language programs. Therefore, it is not necessary to master a second foreign language. You can find universities with English programs on several aggregators: StudyPortals, TopUniversities, or FindAMasters. They can help with the initial search.
But first check out studyinturkey.gov, which is an official source from the Turkish government. It contains more up-to-date prices and programs. However, you will have to put up with a complicated interface and login problems.
Studying in Turkish should not be an obstacle for you either. You can learn this language in the country itself. That is, first enter a Turkish university, but spend the first year of study in language courses. Find out if the university offers this opportunity.
Requirements
In Turkey, most universities require standardized examinations. Some accept SAT, GRE, and GMAT results, while others cannot be entered without YÖS and ALES. These are exams that are valid only in Turkey. Most often, they are required at prestigious universities and in the fields of medicine, law, architecture, and IT.
There are universities that do not have any entrance tests. Some accept standardized tests of foreign countries, while at others a high school diploma is enough. It is worth looking into such options because it can save you a lot of time, effort, and peace of mind.
The rest of the requirements do not differ much from those of other countries. Some universities ask for a motivation letter, recommendations, high grades, video interviews, while others only ask for a high school diploma.
Tuition
The cost of studying in Turkey is one of the lowest in the world. For example, bachelor’s programs at Middle East Technical University start at 252 USD/year. At Bogazici University, annual tuition starts from 1,087 USD. If your goal is to save money, you can easily find a good option for yourself. But there are still some nuances.
The cost of tuition is higher in areas of medicine and engineering — even at public universities. At private universities, expect to pay an average of 21,351 USD/year. These include universities with high rankings, such as Koç University and Sabancı University.
Read more about universities in Turkey in a separate article.
UniPage specialists have been working with Turkish universities for many years. We help with the selection of universities and programs based on the capabilities and interests of our clients. We know everything about foreign education and do not miss a single detail when preparing documents and writing a motivation letter.

Best universities in Turkey
Items 1-6 of 242
Advanced searchfrom14,468USD Middle East Technical University
Boğaziçi University
Sabancı University
Koç University
Istanbul Technical University
Requirements for admission to Turkey
Students can enroll at Turkish universities after the 11th grade. You will need to go through the recognition process of a high school diploma (Denklik) and pass either the Turkish YÖS or the American SAT. Master’s and PhD programs also conduct their own testing — ALES is often taken instead of GRE and GMAT. Each university has different entrance exams. Some accept only YÖS / ALES, while others have a selection of its international counterparts.
At the same time, many regional universities also accept the results of standardized tests of other countries or do not require any exams at all. There are such exceptions even at the best Turkish universities in, which occupy high places in international rankings:
- Koç University accepts SAT and UNT[3]
- Sabanci University by GPA or SAT scores[4]
- Middle East Technical University accept USE scores[5]
YÖS entrance exam
YÖS (Yabancı Uyruklu Öğrenci Sınavı) is a standardized exam for foreigners who enter Turkey for a bachelor's or associate's degree. Usually, its results are required at leading universities with a highly competitive selection process, as well as for programs in medicine, law, architecture, or mechanical engineering.
It consists of 80 questions. 45 of them test abstract thinking and logic, and the remaining 35 test knowledge of mathematics and geometry. If you are applying for a Turkish-language program, there may also be language proficiency questions. The test lasts 90 minutes. You can pass it in English and many other languages.
Each university conducts its own YÖS examination. Therefore, the questions in each test can either coincide or differ. As such, not every university accepts certificates from other institutions.
YÖS can be taken not only in Turkey. Many universities have their own exam centers in different countries.
The application fee for the exam costs 20 USD. YÖS usually takes place from mid-March to May. However, the terms at each university are different, so be sure to check them on the official website of your selected university[6].
ALES entrance exam
MSc and PhD applicants have to take the ALES (Akademik Personel ve Lisansüstü Eğitim Giriş Sınavı). It consists of 2 parts, 4 sections and 200 questions. The first part tests knowledge of the Turkish language, while the second part focuses on mathematics. You are given 180 minutes to complete the test. The exam is evaluated at each faculty in different ways. In the humanities, more points are given to the language part, and technical fields will pay more attention to mathematics.
You can take the ALES twice a year — in spring and autumn[7].
In addition to entrance exams, there are other requirements:
- Language. English-language programs accept applicants with a TOEFL score of 79 points, but many universities prefer local exams — YDS, YOKDIL. Sometimes, they may conduct language testing on their own. The SAT also has language test tasks, and can thus be sufficient for admission at some universities. Turkish proficiency can be confirmed through TÖMER, YKS and TYS exams — these are the most common language proficiency tests in Turkey. A C1 level is desirable for admission, but in rare cases B2 may also pass. If your language ability seems weak to the admissions committee, but you fulfill all of the other requirements, you may be sent to a language course at the university. Afterwards, you can immediately begin the first year of your bachelor’s study.
- Motivation letter. This is an essay in which you must introduce yourself to the admissions committee. It can be written in different formats. An unstructured format is the most common, as it allows you to freely talk about your achievements, personal qualities, interests, experience, and learning goals. Each university has its own requirements for volume and structure.
- GPA. The minimum score for admission to a Turkish university is 2.7 points out of 4.0.
- Resume. This is a document with a brief description of your achievements, education, and work experience.
- Letters of recommendation. A brief description of your academic or work performance with a signature from a teacher, professor, or employer. For some universities, the recommendation letter must be sent by the recommender himself to the e-mail of the admissions committee.
- Achievements. This is an optional requirement that not all universities have. This includes certificates, letters of thanks, medals, and diplomas for achievements in sports, olympiads, internships, or volunteering.
Legalization and recognition of a diploma in Turkey
Fortunately, Turkey is a member of the Hague Convention on the legalization of documents[8]. First you will need to put an apostille on the original diploma. Then, it will need to be translated into Turkish or English. Finally, the translation must be notarized at the Turkish Consulate.
After the legalization procedure, you will need to go through the process for recognizing education — Denklik Belgesi. You can do this at the Turkish consulate in your own country, or at the regional Ministry of National Education (İl Milli Eğitim Müdürlüğü) in Turkey. You can apply online and preferably in advance, as the process can take several weeks. Many universities allow students to begin their study without having a diploma recognized.
Deadlines at Turkish universities
The general deadline for submitting applications and documents to Turkish universities is August 1. However, dates may vary depending on the university and the specific program. Check the information on the official website of your selected university.
For example, the application deadline is July 29 at Sabanci University, while Koç University requires applicants to submit their application by January 4.
How to apply for a bachelor's degree
Before enrolling, you need to translate your high school diploma into Turkish or English. It will also need to be notarized and go through the recognition process — Denklik Belgesi. This can be done at the consulate or the Ministry of Education in any Turkish city.
Turkey does not have a single admission system. Therefore, you need to apply directly to your selected university.
Prestigious universities require applicants to pass YÖS — a standardized exam for foreigners who enter Turkey. The same requirement applies to programs in medicine, law, architecture, and some technical and IT areas. Each university conducts its own exam. Therefore, if you apply to three universities, you will have to take YÖS all three times separately. You can register for the exam on the website of the selected university.
Most universities still accept students with an analogue of this exam — the SAT. And some regional ones even accept students with other standardized test results or even on the basis of their high school GPA.
Language proficiency influences admission results less than high school grades or entrance examinations, but certificates are still needed. For English-language programs, almost all universities accept a TOEFL score of 79. Be prepared for the fact that you may be asked to take a local English exam — YDS or YOKDIL. Or, universities may conduct their own testing.
To study in Turkish, you will need a C1 level according to TÖMER results, but some universities accept B2 as well.
After enrolling at a university, you may be assigned preparatory language courses if your language level is low. Classes will be held at the university to which you applied. As soon as your language level is high enough, you can begin the first year of your bachelor’s study.
List of required documents
- High school diploma and transcript
- SAT / ACT (or YÖS) results
- Proof of English language proficiency (TOEFL / CAE) or Turkish — TÖMER
- Motivation and recommendation letters
- Passport copy
- 2 photos

How to apply for a master’s degree
You can enter a master's program with a bachelor's degree — preferably, in the same field for which you are applying. You can submit an application on the website of your selected university.
Most universities require you to take the ALES exam, especially if you are applying to a prestigious university or to a program in medicine, law, architecture, and IT. Sometimes, they may require GMAT or GRE scores instead. Universities can also conduct interviews.
Some programs, especially research ones, require you to meet with a future supervisor before applying and receive a letter from him with a recommendation and a topic for future research.
English can be confirmed with a TOEFL 92 certificate, and Turkish with a TÖMER score of 60 or TYS at the C1 level.
Full-time master's programs most often begin in October.
List of required documents
- ALES Exam Results — 70, or GMAT / GRE — 720/156
- Motivation letter
- Resume
- Bachelor's degree
- Grade transcript, preferably with an average score of 2.8 out of 4.0 or 70%
- TOEFL results for English programs
- TÖMER or TYS results for Turkish programs
- 2 letters of recommendation
- Other documents, depending on the program
How to apply for a PhD
For admission to PhD programs, students must choose a suitable program, apply online, and pass all of the required exams and interviews.
In some programs, applicants should find a supervisor for their future dissertation even before enrolling at the university. You will need to independently contact someone at the department of your interest and discuss your research plans with him. This is mainly needed for candidates of engineering and health care programs.
Colleges of faculties evaluate the applications of each student. If necessary, universities may conduct interviews.
List of required documents
- ALES 80 exam results or GMAT / GRE
- English language proficiency — TOEFL / CAE / PAE
- Master's degree
- Grade transcript, preferably with an average score of 3.0 out of 4.0 or 75%
- Motivation letter
- 3 letters of recommendation
- Resume
- Research plan
Turkiye Burslari and other Turkish scholarships
Turkiye Burslari is the largest scholarship program in Turkey. It is designed for bachelor’s, master’s and PhD students with a high GPA and outstanding academic achievement.
Turkiye Burslari covers:
- Tuition
- Accommodation
- Monthly payments of 31 USD at the bachelor’s level, 43 USD at the master's level, and 55 USD at the PhD level
- One-year Turkish language course
- Medical insurance
- One-way airplane ticket
Scholarships are awarded on a competitive basis and are not easy to obtain. Each year, the commission receives more than 100000 applications and awards about 5000 scholarships[9]. Selected candidates are interviewed in their countries of residence, either online or by phone.
| Degree | Scholarship/month | Duration | Performance criterion | Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bachelor’s | 25 USD | 1 year lang. course + 4-6 years | 70% | Under 21 |
| Master’s | 34 USD | 1 year lang. course + 2 years | 75% | Under 30 |
| PhD | 49 USD | 1 year lang. course + 4 years | 75% (for medicine — 90%) | Under 35 |
Detailed information and a list of universities can be found on the scholarship website.
Scholarship for prize-winners of international scientific olympiads. The Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK) provides scholarships for international students who win international science olympiads in:
- Mathematics (IMO)
- Physics (IPhO)
- Chemistry (IChO)
- Biology (IBO)
- Informatics (IOI)
Financial assistance is provided for bachelor’s programs related to the theme of the Olympiad. The grant provides a monthly stipend of 31 USD and covers tuition fees up to 62 USD. The scholarship is given for 4-6 years, throughout the entire duration of study. A nice bonus is an extension of the grant for further education — this happens if the scholarship holder successfully completes his bachelor's degree and enters a master's / PhD program at a Turkish university. You can apply for a grant and find out detailed information on the TÜBİTAK website.
University aid. Turkish universities receive financial support from large corporations, which allows them to provide scholarships to students. However, this is not the easiest option for foreigners.
- Academic scholarships. Foundations and some public universities help outstanding students financially. Scholarships are usually awarded for 4-5 years. Students are selected based on grades, scores, and rankings. The grant covers tuition, accommodation, and monthly stipends.
- Partial scholarships. Universities also offer partial scholarships. For example, the Academic Success Scholarship covers 30-50% of tuition fees. Quotas for partial scholarships exist for international students. Candidates may be interviewed by phone or email.

Student visa to Turkey
Student visas are issued at the Turkish Consulate in the student’s country of residence. It usually takes about 2 weeks from the time you apply to receive your visa. Therefore, it is necessary to apply for a student visa as soon as the university sends an acceptance letter. The earliest submission date is 60 days before the start of the program. You can schedule an interview for the submission of documents on the website of the consular services of Turkey.
Required documents for a visa depend on the country. Usually, they include:
- Complete application
- Passport + copy
- Printout from the website confirming the appointment date for the visa application
- Purchased or booked airplane ticket to Turkey
- Invitation letter from a university
- Confirmation of tuition payment
- Proof of financial solvency in the form of a bank account statement
- Medical insurance
- 2 photographs
- Proof of accommodation booking in Turkey
The application and detailed information can be found on the website of the Turkish Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The cost of a visa depends on the candidate’s country of residence, the average being 200 USD.
Upon arrival in Turkey, students must register at the local police station and apply for a residence permit at the Migration Office within 30 days. To do this, you need to fill out a form on their website.
After obtaining a residence permit (ikamet), you can live in Turkey, open a bank account, and use the ikamet card when entering or leaving the country. The residence permit must be renewed 6 weeks before the expiration date.
Want to study at a foreign university but don't know where to start? We can help!
Our specialists will find a university, arrange your documents, fill out the applications, and stay in touch until you receive an offer.













