Briefly about education in Malaysia
- Education in Malaysia is developing as fast as the country's economy. Currently, the University of Malaya ranks 59th in the QS Top Universities Ranking, but 8 years ago it was 156th.
- Cost of training in English is much lower than in neighboring Singapore: prices start at 6,000 USD/year when studying in English.
- Language. Malaysia has a large number of programs in English for both bachelor's and master's programs. The country is affected by its historical connection with the British education system, economic growth, and favorable location.
- Branches. More than a dozen branches of British, Australian, Irish universities also operate in the country. The cost of studying in them is higher than in public universities in Malaysia but lower than in Britain and Australia. Training is conducted entirely in English, and after graduation, you can get a diploma of a renowned European university.
- Requirements. Admission after graduating from 11 years of school is impossible, students will have to go through one of the Foundation/IB/A-levels or study a year at a university in their home country. For admission, you do not need to pass additional exams, except for English (IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 550).
- Visa. A student visa is issued after arrival in the country. Prior to arrival, you need to obtain the Visa approval letter (VAL) from the Immigration Department of Malaysia. The visa is issued for a year and then extended.
- Work while studying. It is possible, but only on holidays and for no more than 20 hours a week. To work, you will have to obtain a permit from the Immigration Department.
- Scholarships. There are both public and private scholarships for foreigners. Most of them are for master’s and doctoral students.
- Employment. The Malaysian government does not give foreigners time to look for work after graduation. You can stay in the country only with a work permit. It is issued only if an invitation from the employer has already been received.
Advantages of education in Malaysia
- You can study in English. Universities in Malaysia offer about 2000 bachelor’s programs in English. There are especially many of them in IT, mathematics and related fields. Most of the available master's and doctoral studies are also in English. 60% of the country's population speaks English[1].
- Multinationality. Malaysia has 130 thousand international students[2]. According to this indicator, the country ranks 11th in the world[3]. The majority of students come from Bangladesh, China, Nigeria, Yemen, Indonesia, and Pakistan. By 2025, the government plans to double this number, so it is attracting students from other Asian and European countries.
- Affordable prices. There are world-famous universities in Malaysia, and education there is much cheaper than in Western universities. For example, to become an engineer in the branch of a British university will cost 17,000 USD. A diploma from the same university in the UK will cost 3 times more — 54,000 USD. With a fairly high standard of living in large cities, prices in Malaysia are lower than in developed neighboring countries. Even in the capital city of Kuala Lumpur, you will have to spend about 500 USD per month on living, while in neighboring Singapore it can easily double that.
- Security. According to the report of the Institute for Economics and Peace[4], with its stable political regime — Malaysia is one of the most peaceful countries in the world. The report takes into account the level of crime and violence, military and political conflicts, environmental safety. Malaysia is included in the group of countries with a very high human development index (0.804), which is rather unusual for Asia: out of 62 Asian countries, this group includes only 20[5].
Disadvantages of education in Malaysia
- Cramming. Many foreign students note that the educational process in Malaysia is built on mindless memorization and preparation for exams. Teachers have little interaction with students, because of this, fluency in the topic and class morale suffer.
- Work while studying. It is difficult to combine studies and work in Malaysia. The law states that a foreign student can work up to 20 hours a week only during holidays. If you are caught violating this law, the authorities will take away your student visa and deport you.
- It is difficult to stay in the country after graduating from university. The Migration Service of Malaysia has high requirements for those wishing to obtain a work permit. It is necessary not only to find an employer in advance and receive an invitation but also to have relevant work experience of at least three years. Therefore, graduate students with extensive qualifications will have better chances of staying in the country.
- The climate in Malaysia can be both an advantage and a disadvantage. High humidity and 35 Co heat are not suitable for everyone.
Cost and structure of education in Malaysia
| Type of education | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer Camp | 5-17 | 1-12 weeks | 63 USD/week | 105 USD/week | - |
| Language courses | 18+ | 2-48 weeks | 67 USD/week | 105 USD/week | - |
| Secondary education | 12-19 | 7 years | 52 USD/year | 6,273 USD/year | - |
| Foundation | 17+ | 1-2 years | 1,882 USD/year | 4,182 USD/year | IELTS 4.0 |
| Vocational education | 17+ | 2-3 years | 314 USD/year | 4,600 USD/year | IELTS 4.0 |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 3-5 years | 766 USD/year | 5,227 USD/year | IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 550 |
| Master's | 21+ | 1-3 years | 2,105 USD/year | 5,645 USD/year | IELTS 6.0+ / TOEFL 550+ |
| Doctoral | 21+ | 3-5 years | 2,063 USD/year | 7,318 USD/year | IELTS 6.0+ / TOEFL 550+ |
Additional expenses
| Item | Average cost |
|---|---|
| Registration fee | 13 USD |
| Student Pass | 8 USD/year |
| University deposit (Personal bond) | 314 USD |
| Exams | 199 USD |
| Accommodation | 121 USD/month |
| Food | 138 USD/month |
| Study materials | 21 USD/month |
| Medical insurance | 10 USD/month |
| Communication | 10 USD/month |
| Internet | 33 USD/month |
| Transport | 25 USD/month |
| Flight | 627 USD |
Scheme for admission to universities in Malaysia
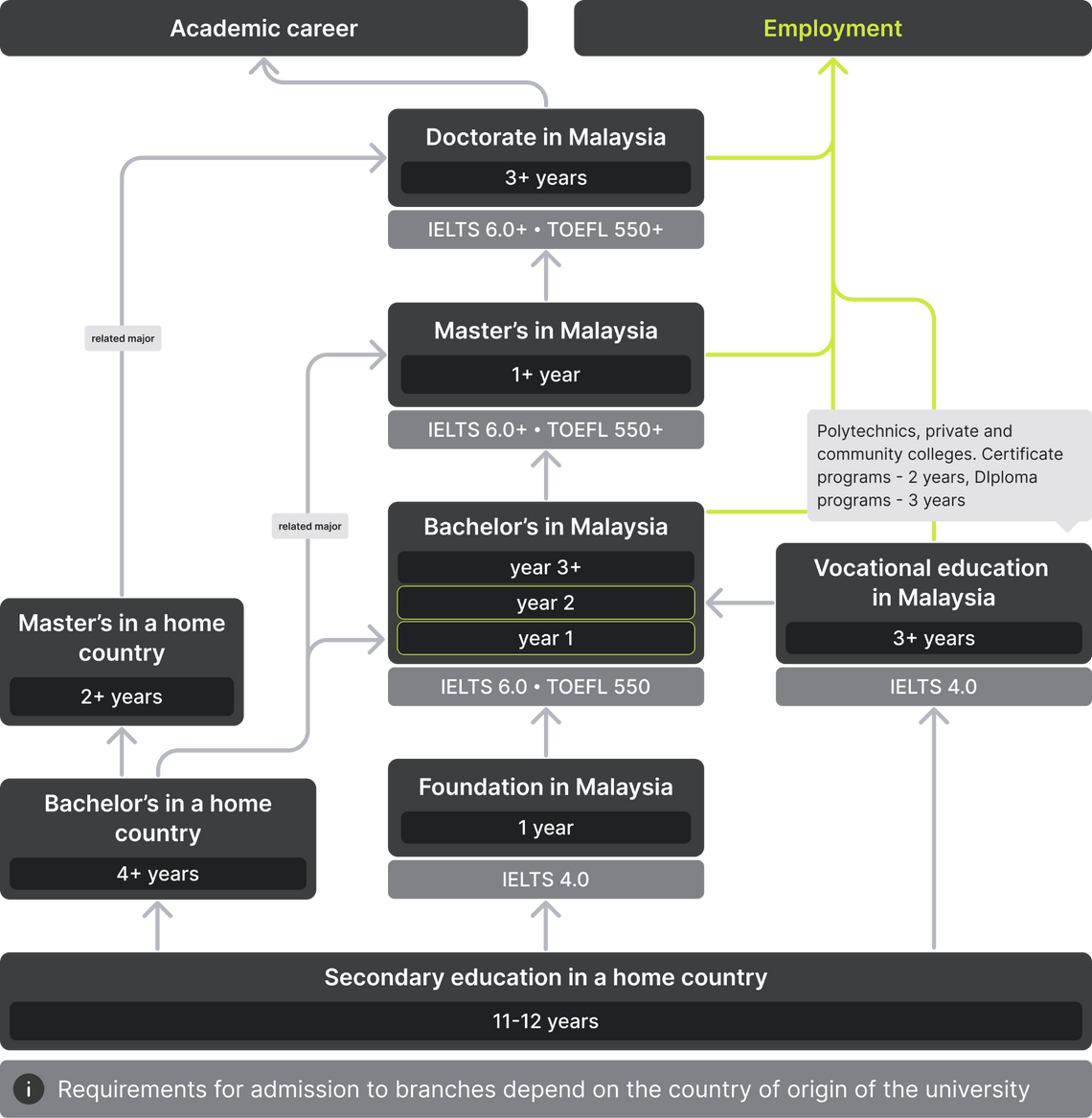

Admission requirements at universities in Malaysia
To enter a university in Malaysia, a student must complete at least 12 years of secondary education. There are several ways to cover the academic difference in case your country has an 11-year secondary education system:
- Complete a Foundation program;
- Enroll in a college or polytechnic in Malaysia for a Diploma program (an analogue of an Associate’s degree). Training lasts three years, after graduation students can enter the second year of a bachelor’s program. There are also programs in English;
- Complete a year of bachelor’s studies in your country and then apply to a Malaysian university;
- Complete an A-Level or IB program.
You can apply for admission and send documents via the university website. Each university establishes the list of required documents itself. As a rule, these are:
- Scan of a certificate or a diploma;
- Transcript with grades;
- Scan of all pages of the passport and/or birth certificate;
- Entrance exam results (if necessary);
- Language certificate (TOEFL / IELTS / PTE-A / CAE / CPE / MUET);
- Scholarship certificate or other proof of funds;
- Letters of recommendation;
- CV;
- Motivation letter;
- Portfolio.
Documents must be submitted with a certified translation into English or Malay.
The academic year in Malaysia runs from January to November. Most universities admit students in three periods:
| Preparation of documents | Applications deadline | University response | Start of studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| May-June | October | November | February |
| November-December | March | April | July |
| February-March | June | July | October |
The exact dates of admission should be checked on the websites of the universities.
After arriving in Malaysia, the applicant must undergo a medical examination within seven days. You do not need to do this in advance.
Legalization and recognition of a diploma in Malaysia
Malaysia has not signed the 1961 Hague Convention[6], therefore consular legalization is required to use foreign documents from most countries. Refer to the university websites for the details.
There is no single system for the recognition of foreign diplomas in the country, so the decision is made by universities. Recognition through special agencies may be required when applying for a job as a civil servant, teacher, or doctor. The information should be checked for each individual case on the Government of Malaysia website.
Foundation — Preparatory programs in Malaysia
If a student's qualifications are not enough for admission, Malaysian universities offer Foundation programs. Their duration is 12 months. The disciplines studied depend on the chosen direction in the bachelor's degree and are often tied to the programs of specific universities. Therefore, a Foundation graduate in Management won’t be able to enroll in a Bachelor's Program in Architecture. Moreover, universities often do not accept Foundation certificates from other universities.
To complete a Foundation, a student must pass the midterm certification, earn 50 credits, and pass the final exam. For admission to preparatory programs, a certificate of complete secondary education is required. Other requirements for applicants should be specified on the websites of universities.

Vocational education in Malaysia
Vocational programs are implemented in polytechnics, private, and community colleges. They combine practical (75%) and theoretical (25%) training. Upon completion, the graduate receives a diploma or a certificate. To get a certificate, you will have to study for two years and collect 60 credits. To get a diploma, you need to study for two or more often three years and collect 90 credits. Formally, the diplomas of polytechnics and colleges are equal, but entering a polytechnic is usually more difficult.
Then the student can continue their studies in the second year of the Bachelor's program or Advanced Diploma programs. The latter requires an additional 40 credits, including compulsory practice, and designed to develop managerial skills.
Colleges have programs in English. For admission, you will need a certificate of completed secondary education and a language certificate. At the same time, graduates of 11-year schools do not need to take preparatory courses (Foundation), as when entering a university.
Bachelor’s in Malaysia — Undergraduate
To obtain a bachelor's degree, you need to study at least 3 years full-time and collect 120 credits (1 credit = 40 hours ≈ 1.77 ECTS), however, the duration varies depending on the university. Programs in accounting, dentistry, engineering, and law typically take four years. And to become an architect or a doctor, you have to study for five years. Students usually spend the first year studying general and fundamental subjects, and only after that focus on the compulsory specialized disciplines and electives.
You can get a bachelor's degree in Malaysia at public and private universities, branches of foreign universities, private and university colleges. At the same time, private colleges in Malaysia, as a rule, are eligible to award an academic degree only through partnership agreements with universities in the UK, Australia, and the USA. Programs in all types of institutions are accredited by the Malaysian Qualifications Agency. Bachelor’s studies are mostly in Malay, but there are many programs in English (about 250 at public universities), Chinese, and even Arabic.
Among the requirements for admission are usually indicated:
- Certificate of complete secondary education (average score of 2.0 out of 4 and above);
- Certificate of completion of the preparatory program (Foundation, IB, A-Level) or equivalent;
- Language certificate (TOEFL 500 / IELTS 6.0 / PTE-A / CAE / CPE / MUET);
- The university can schedule an interview as an additional entrance test;
- Letters of recommendation;
- Motivation letter.
Master’s in Malaysia — Postgraduate
Course content and assessment methods for master's programs vary. There are three types of programs:
- International standard. For several semesters the student learns, takes exams and then makes an individual research project.
- Focused programs. They do not imply writing a thesis, but they expand the number of disciplines taught. These programs include both self-study and group work on projects, making them attractive to students looking to focus on their careers.
- Research programs. These almost fully focus on research.
To obtain a master's qualification, you must collect at least 42 credits, regardless of the type of program. Each credit is equal to 20-30 hours of study. 6 credits are awarded for writing a thesis. Programs last 1-3 years.
The academic year in Malaysian universities consists of two semesters: from January to May, and from June to November. Master's degree studies last from one to three years, depending on the specific course and subject area. Part-time and distance learning programs may take a little longer.
Documents required for admission to the master’s program:
- Bachelor's degree in a similar field (average score above 2.5 out of 4);
- Motivation letter;
- Letters of recommendation;
- CV;
- Transcript;
- List of publications.
To apply to the management and business programs it is often required to pass the GRE or GMAT entrance exam.

Doctoral studies in Malaysia — Postgraduate
Doctoral studies are implemented at public and private universities and last from three to five years. There are more courses for three years, as the majority of scholarships cover this term of study. A list of doctoral studies can be viewed on the official website of education in Malaysia.
Most PhD programs in Malaysia are not as clearly structured as in other countries. The main requirement is to conduct your own independent research and provide reports at the seminars. Some universities also require the study of disciplines within the selected modules and the publication of research results in peer-reviewed journals. At the end of the studies, a doctoral student writes a thesis in their research project and defends it in front of the commission. The PhD applicant must demonstrate knowledge in the subject area and prove the originality and relevance of the work within the research field.
PhD programs in Malaysia can start all year round, however, most institutions accept admissions twice a year — in July and February. The application can be submitted through the websites of the universities. In addition to a master's degree in a similar field, universities also request a letter of motivation, resume, and research proposal. In addition, knowledge of English, previous publications, participation in research projects, conferences, etc. are taken into account. Some programs will require additional study of the Malay language.
Academic career in Malaysia
An academic career in Malaysia is broken down into six stages: tutor, lecturer, senior lecturer, associate professor, professor, distinguished professor. The Professor's position, in turn, also has three levels: Professor Grade C, Professor Grade B, and Professor Grade A. The highest position, distinguished professor, includes the duties of all previous ones. Each university independently establishes the duties of a professor, but the core responsibilities are teaching and research. Often the position of a professor is combined with an administrative position.
The positions of a tutor or a lecturer can be obtained only after receiving a PhD. On rare occasions, a junior teaching position is offered to doctoral and even graduate students. Employment also may require research / teaching experience and 3-4 publications. Further career advancement takes place within the university. The decision on promotion is made by a specially appointed person holding a higher position in the university hierarchy. The candidate is assessed on five criteria: teaching, research, consultation, publications, service to the community, and the university. For the position of a lecturer, it is more important to have teaching experience, and for an associate professor, you should have research experience. The title of a distinguished professor is awarded only by the Ministry of Higher Education of Malaysia.
The average salary of a professor in Malaysia is 26,345 USD per year[7], and a junior lecturer can earn 13,590 USD per year[8].
Scholarships and grants at Malay universities
The government and universities in Malaysia fund primarily graduate and doctoral students. Unfortunately, bachelor's scholarships are far less common. At the state level, there are none at all.
Malaysian International Scholarship (MIS) is the most famous scholarship from the Government of Malaysia. The scholarship is only available to master’s and doctoral students. The scholarship covers tuition, flights, accommodation, textbooks, medical insurance. PhD students are also paid to conduct research and publish results. To get a scholarship, you will have to submit documents and participate in a competition.
The main criteria for receiving a scholarship:
- Age up to 45 years;
- GPA in CGPA diploma 3.5 / 4.0;
- Research plan;
- English proficiency at level B2 or above.
Research should be in the interests of the development of Malaysian society.
Documents for MIS
- Copy of the passport;
- Copy of the diploma;
- Copy of the transcript;
- CV;
- Two letters of recommendation from teachers;
- Language certificate (IELTS from 6.5 and TOEFL from 580;
- Research plan;
- Confirmation of admission to a Malaysian university;
- Medical examination certificate
All documents must be translated into English and notarized. More information can be found on the website of the Ministry of Higher Education of Malaysia.
Another famous scholarship from the Malaysian government is the Malaysian Technical Cooperation Program (MTCP). The scholarship is only available to master’s and PhD candidates in mainly technical specialties. The requirements for MTCP applicants are similar to those of the MIS; details can be found on the website of the Malaysian government.
Universities can also fund their students. Therefore, when looking for a scholarship, the information should be checked with specific universities.
Student visa to Malaysia
To study in Malaysia, you need a Student Pass, which is issued after arrival in the country. Foreign citizens may be required to make a single entry visa. You can apply for it online.
Before getting a Student Pass, you must obtain a Visa approval letter (VAL) from the Immigration Department of Malaysia. An application for VAL can be submitted both through the university and online, the process takes 14 business days. After receiving your VAL, the student can travel to Malaysia.
Upon arrival, you will need to undergo a mandatory medical examination within a week; without it, the Student Pass cannot be issued. After that, the migration service will request your passport from the university to issue a student visa. After 10 business days, the student will be able to collect their Student Pass. A student visa is issued for 1 year, then extended in the country of residence of the student or directly in Malaysia.
Required documents for obtaining a VAL
- 1 photo 3.5 x 4.5 cm;
- Copy of the passport (must be valid for at least another 12 months);
- Invitation from the university;
- Personal bond of 314 USD;
- Health declaration form;
- Copies of diplomas and transcripts;
- Copy of the certificate of complete secondary education;
- Language certificate (TOEFL 500 / IELTS 6.0 / PTE-A / CAE / CPE / MUET)
The current list must be checked on the official website of education in Malaysia.

Ability to work while studying
Students are allowed to work up to 20 hours a week and only during breaks and holidays that are longer than 7 days. You can get a job in restaurants, gas stations, mini-markets, and hotels, while you cannot hold the position of a cashier. In addition, in the hospitality sector, students are prohibited from working as singers, massage therapists, musicians, and other activities that may be considered immoral[9]. An application for a part-time job is submitted through the educational institution in which the student is studying. The minimum hourly rate in Malaysia is 1 USD.
Required documents for a work permit
- Letter indicating the reasons for needing a job;
- Copy of your passport;
- Residence address, email, phone number;
- Invitation from a future employer indicating the place of work, position, rate;
- Schedule of classes and study breaks;
- Copy of the certificate of secondary general education;
- Letter of permission from the head of the faculty.
Opportunity to stay and immigration to Malaysia
To stay in Malaysia after graduation and get an Employment Pass, you first need to get an invitation from your employer. In this case, he will provide all the necessary documents.
A work permit is issued for a period of two to five years. It is important that the passport is valid for at least another 18 months from the moment the employer made you an offer.
To obtain a work permit, a candidate must:
- Have the qualifications required for the job;
- Have three years of relevant work experience;
- Work in a managerial or technical position that requires specialized skills;
- Meet salary requirements: from 627 USD to 2,091 USD depending on the type of Employment Pass.
Due to the strict requirements to stay in Malaysia, it is likely that only established specialists will succeed after receiving a master's degree.
It is quite difficult to obtain citizenship in Malaysia. To do this, you need to:
- Be over 21;
- Live in Malaysia for 10 years in a 12-year period, including 12 months before applying;
- Possess “adequate knowledge of the Malay language”.
You can also get citizenship by marrying a Malay, but this option is only available to women. If the marriage falls apart in less than 2 years, citizenship will be revoked.
Malaysia does not recognize dual citizenship.
Employment prospects and opportunities
In Malaysia. Malaysia's economy is growing at 4.8% per year[10] and ranks third in Southeast Asia, behind only Indonesia and Thailand[11]. A developing economy requires skilled workers, so the Malaysian government is investing in education and attracting foreigners. However, this is only true for highly qualified specialists with work experience. If the graduate has no experience, it will be difficult for them to get a job.
There are many promising employment sectors in Malaysia. Thus, the financial sector is actively developing here: the country has already become the world center of Islamic banking[12]. Natural resources are one of the main productions of Malaysia: the oil, gas, and energy sectors account for 20-30% of GDP, Malaysia accounts for 39% of the world production of palm oil[13]. High-tech production is developing. World-famous giants work in the country: Intel, AMD, ASE, Texas Instruments. Local brands such as Globetronics and Green Packet are also growing. Another key sector of the Malaysian economy is the automotive industry. Thanks to 27 manufacturing companies, the country exports its own brands to foreign markets.
In other countries. Graduates of Malaysian universities will be able to find work outside Malaysia. Local universities rank high in world rankings. For example, the University of Malaya is ranked 59th in the QS rankings. The country also has branches of British, Australian, and American universities. At the same time, the diploma received at the Malaysian branch is no different from the diploma issued in London or Melbourne.
Want to study at a foreign university but don't know where to start? We can help!
Our specialists will find a university, arrange your documents, fill out the applications, and stay in touch until you receive an offer.












