Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Article score: 4.7 out of 5 (10 reviews)
Admission in the Netherlands is possible after the 11th grade, but not at all universities. For some, a high school diploma is sufficient, while others require foundation courses or one year of bachelor’s studies at home. Continue reading for information on prices, scholarships, visas, and other requirements.
Free consultation





Admission in the Netherlands is possible after the 11th grade, but not at all universities. For some, a high school diploma is sufficient, while others require foundation courses or one year of bachelor’s studies at home. Continue reading for information on prices, scholarships, visas, and other requirements.
Read our separate articles on the higher education system, universities, as well as bachelor's and master's programs in the Netherlands.
| Program | Age | Duration | Min. cost per year | Avg. cost per year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | 17+ | 1 year | 9,040 USD | 15,820 USD |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 3-4 years | 10,130 USD | 15,820 USD |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-3 years | 10,170 USD | 15,820 USD |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 13,560 USD | 39,550 USD |
| Doctorate | 21+ | 4-5 years | Free | Free |
| Expense | Average cost |
|---|---|
| Registration fee | 113 USD |
| Visa | 197 USD |
| Rent | 1,017 USD/month |
| Insurance | 181 USD/year |
| Food | 203 USD/month |
| Public transportation | 68 USD/month |
| Bicycle rental | 11 USD/day |
Please specify all prices and requirements on the website of your chosen university.
The Netherlands has a binary education system. Universities are divided into applied (hoger beroepsonderwijs, HBO) and research (wetenschappelijk onderwijs, WO) categories. Both options are available to foreign students.
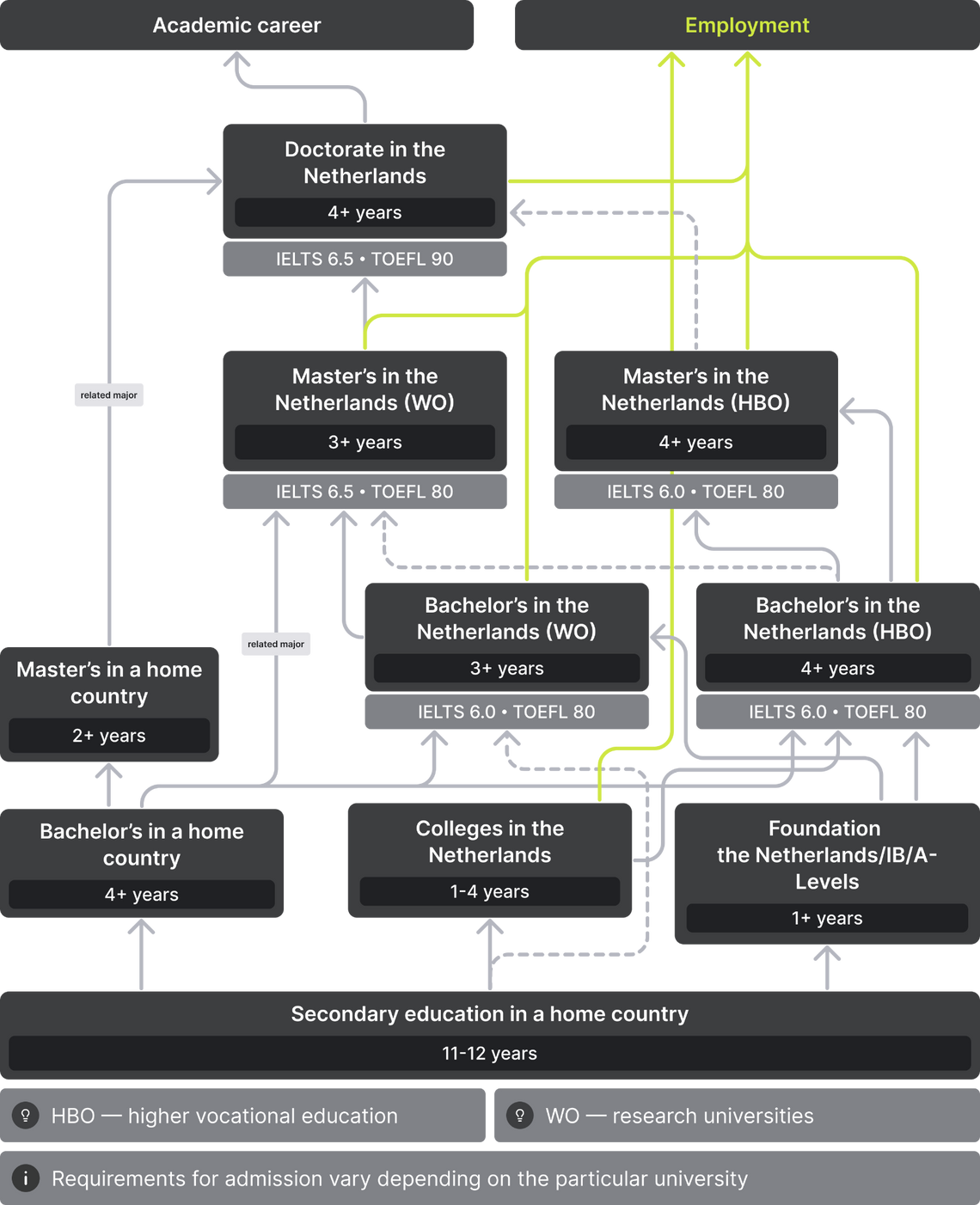

This is a key point when looking for a university, and our career guidance article is here to help. The most popular fields for international students in the Netherlands are economics and business, humanities and social sciences, and engineering. Each university has its own top study programs and faculties. For example:
You can evaluate a particular university faculty through subject ratings and reviews written by graduates and lecturers.
The level of education can also significantly differ from one university to another. For example, the University of Amsterdam offers strong master's and doctorate programs, while its bachelor's programs do not stand out from that of other Dutch universities.
Rankings should be used as a reference point in the initial stages of the search. Not all of them are objective or suitable for your personal goals. By all means, some excellent universities are not included in rankings. For example, there is not a single university of applied sciences, given that their students are career-oriented and publish less research.
In the QS ranking, the most significant criterion (40%) is the university’s reputation based on the opinion of students and lecturers. This is a good indicator for the quality of education. But if you plan on pursuing an academic career, then the ARWU ranking is better for you — it evaluates the quantity and quality of the university’s scientific publications.
For example, the University of Amsterdam ranks 54th and 1st in the country according to the QS Ranking. However, it ranks 101st in the ARWU, while Utrecht University boasts 50th place[1].
You can learn more about ranking systems in this article.
Education in the Netherlands is one of the most expensive options in Europe, but cheaper than that of the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. On average, annual tuition will cost you 15,820-20,340 USD.
However, you can sometimes come across programs that are cheap for the Netherlands. For example, the Erasmus University Rotterdam has a Research Master in Philosophy and Economics that costs 4,859 USD per year. Also, do not forget about the universities of applied sciences (HBO) — they are cheaper, averaging at 12,430-13,560 USD per year.
There are fewer private universities in the Netherlands than public ones. Usually these are medical schools, business schools, or international affiliates of other universities. As a rule, their programs are more expensive. For example, at Saba University School of Medicine, the Clinical Medicine program costs 23,300 USD per semester[2].
Choose a university and program according to your budget. Be sure to consider living costs along with tuition. In the Netherlands, expect to spend about 1,130 USD per month on day-to-day expenses. That being said, keep an eye out for scholarship opportunities — we will discuss them a bit later.
As you might assume, the admission requirements of popular universities tend to be more rigorous than those of their less known counterparts.
But more importantly, many programs (mainly architecture, law, and medicine) have a numerus fixus — a limit on the number of students. They also have different application deadlines (usually January 15) and higher requirements. All this should be taken into account when choosing a university — be sure to have a plan B.
Some universities do not accept high school diplomas received after the 11th grade. It is advisable to contact the admissions committee of the chosen university and clarify the possible nuances.
Consider your own individual values. While we discussed the main criteria addressed during the selection process, your case may be different.
Identify and make a list of what else might be important to you while studying at a Dutch university — for example, housing, foreigner student ratios, and food costs.
Items 1-6 of 202
Advanced search
Some universities accept high school diplomas received after the 11th grade. However, some research universities may require you to take a preparatory course, choose another university, or study for one year in your home country.
For each program, you need to confirm your language level unless you are a native speaker.
What other requirements do you need to be prepared for?
At almost every Dutch university, admission consists of three stages:
In the Netherlands, the school year starts during the first week of September. Application deadlines for most universities are in May and April. But, there is an exception — numerus fixus. Such programs have a separate deadline — January 15th. It is easy to tell these programs apart — on Studielink, a warning about limited placements and dates is put on the relevant programs. Most often, these include those in the law, medicine, engineering, and architecture fields.
Diplomas and certificates from the CIS countries are recognized in the Netherlands without an apostille. Depending on the program, only a translation into English or Dutch is required.
Preparatory courses, known as the Foundation year, are usually chosen by applicants who hesitate about their language level or grades. Such courses last from 2 to 12 months. Students get used to the Dutch education system, improve their knowledge in the chosen direction, and prepare for standardized language tests (IELTS, TOEFL, or NT2).
The Foundation year is an excellent choice for applicants who were denied admission due to academic differences. Not all research universities accept students from the 11th grade, so the Foundation year can be a good alternative to another year of study.
For admission, you need an IELTS 5.0 or TOEFL iBT 70 certificate, along with high grades in core subjects.

Studielink is used to apply to most universities. Register, verify your passport information, and indicate information regarding your previous education. You can then select universities and apply for one or more programs. After that, you will be contacted by email and invited to upload documents on the university system — this is usually a website or app.
Some research universities may not accept an 11th grade high school diploma, because secondary education lasts 12 years in the Netherlands. In this case, the student needs to:
Before admission, it is advisable to contact the admissions committee to clarify questions regarding your diploma.
As with bachelor’s programs, master’s applications start with registration and passport verification on Studielink. There, you need to select a university, program, and describe your previous education.
If your application for Studielink is approved, the admission process will move to the university website. The university may ask for additional documents, such as a motivation letter, language certificates, recommendations, resumes, and a list of achievements. Prestigious universities and programs with a high competition usually conduct an additional interview.
Your bachelor's degree must be in the same subject area as the chosen program. Often, universities lay out a list with the required subjects, according to which the applicant can check. If you want to change your profession and enroll in another program, you can take preparatory courses at universities.
Some research institutions do not accept bachelor’s degrees from universities of applied sciences. As such, students enroll in pre-master's programs and receive 30-60 credits.
To apply for an MBA, you will need a bachelor's degree and language exam certificates. Many universities require a GMAT score of 600 points. Checkpoints at prestigious schools — 620-640. Additionally, universities may request recommendations, motivation letters, and a resume. You can apply through the university/business school website. Basic requirements for admission include:
Also, depending on the university:

Doctorate studies in the Netherlands are most correctly classified as work, not study. Most of the programs here are paid jobs. The university hires you to conduct a specific study, assigns a supervisor, and awards you with a doctorate degree after completing your dissertation.
At the university, you will be a full-fledged employee. You will conduct research, teach, and perform some of the duties of a research assistant.
The approximate salary for doctorate positions is 2,260-3,390 USD per month. Vacancies can be found in scientific journals, on university websites, and through specialized resources such as AcademicTransfer.
If you have your own topic or idea for research, but there is no suitable vacancy for it, you can contact the university and propose it yourself.
For admission, you usually need knowledge of Dutch or English, a good academic portfolio, and high grades throughout your master's program. Teaching experience will also be helpful.
Scholarships are available at all major Dutch universities. Most often, they are designed for talented and motivated students — for example, the Amsterdam Excellence Scholarship from the University of Amsterdam is offered to master’s students from non-EU countries. It covers 28,250 USD of tuition and living costs per year. Similar scholarships are offered by:
There are also many government scholarship programs. All of them are listed on the Study Holland website. It lists current opportunities by country, degree, and area of study. Of these, there are two popular grants — Orange Tulip Scholarship and Holland Scholarship.
| Title | Applicant requirements | Size | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| One-time grant from 5,650 USD | The university must be a participant in the scholarship program. The application is submitted directly to the university. | |
| Orange Tulip Scholarship | Depending on the university, from 25% to 100% of the study costs | You can only apply after enrolling at a university. The university must be a participant in the scholarship program |
You can apply for both grants at the same time.

To enter the country, you will need a long-term MVV (Machtiging tot Voorlopig Verblijf) visa. A residence permit for study (VVR) is simultaneously issued. The visa application is carried out jointly with the university:
The entire process does not usually take more than a month, but may be delayed in case of an error with the documents. The cost of obtaining a visa is about 249 USD.
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got