
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Education in Canada is one of the highest quality and most prestigious in the world. Find out more about the Canadian education system: universities, fees, accommodation costs, admission, visa requirements.
Free consultation





By law, secondary education in Canada is compulsory. There is no single national system: education is overseen by provincial and territorial governments. Schools within a certain area are also managed by local school boards.
Students in every Canadian province must attend school up to the age of 16, except for Manitoba, Ontario and New Brunswick, where the compulsory age is 18, or until a high school diploma has been achieved.
| Stage of Education | Grades | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-elementary | Kindergarten | 4-5 |
| Elementary / Primary | 1-8 | 6-14 |
| Secondary / High school | 9-12 | 15-18 |
Students can choose to study in English, French or two official languages. Both public and private schools now accept international students. The curriculum in these institutions is the same within a certain province or territory. But in private ones, the class sizes are usually smaller.
There are private boarding schools (with on-site accommodation), IB-schools, alternative and specialized sports programs or schools for students with learning disabilities.
Please note that special rules apply to minor children studying in Canada[1].
Education in Canada is one of the highest quality and most prestigious in the world. While studying students are given unique opportunities to gain practical experience in Canadian companies, which significantly enhances their further employment in any country. Upon successful completion of the program, a talented graduate has every chance to immigrate to Canada without major obstacles from the government.
| Type of study | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language level | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer Camp | 6-17 | 1-4 weeks | 108 USD/week | 1,792 USD/week | A1 | - |
| Language School | 16+ | 2-24 weeks | 108 USD/week | 2,868 USD/week | A1 | - |
| Secondary education | 6-18 | 11-12 years | 5,735 USD/year | 7,886 USD/year | B1 | IELTS 5.0-5.5 / DELF B1 |
| Foundation | 16+ | 1 year | 7,169 USD/year | 17,923 USD/year | B1 | IELTS 5.0-5.5 / DELF B1 |
| Colleges | 17+ | 1-4 years | 1,434 USD/year | 7,169 USD/year | B2 | IELTS 6.0-6.5 / DELF B2 |
| Bachelor’s | 17 + | 3-4 years | 14,338 USD/year | 1,936 USD/year | B2 | IELTS 6.0-6.5 / DELF B2 |
| Master’s | 20+ | 1-3 years | 7,169 USD/year | 12,690 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 7.0-7.5 / DALF C1 |
| MBA | 20+ | 2 years | 27,960 USD/year | 37,854 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 7.0-7.5 / DALF C1 |
| Doctoral | 20+ | 3-6 years | 7,169 USD/year | 10,754 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 7.0-7.5 / DALF C1 |
| Expenses | Average cost |
|---|---|
| Language test | 140 USD |
| Evaluation Service | 108 USD |
| Study permit | 108 USD |
| Flight from Mumbai / Beijing / Los Angeles | 1180 / 1440 / 194 USD |
| Accommodation | 3,585 USD per year |
| Health insurance | 502 USD per year |
| Food | 251 USD per month |
| Public transport | 72 USD per month |
| Study materials | 860 USD |
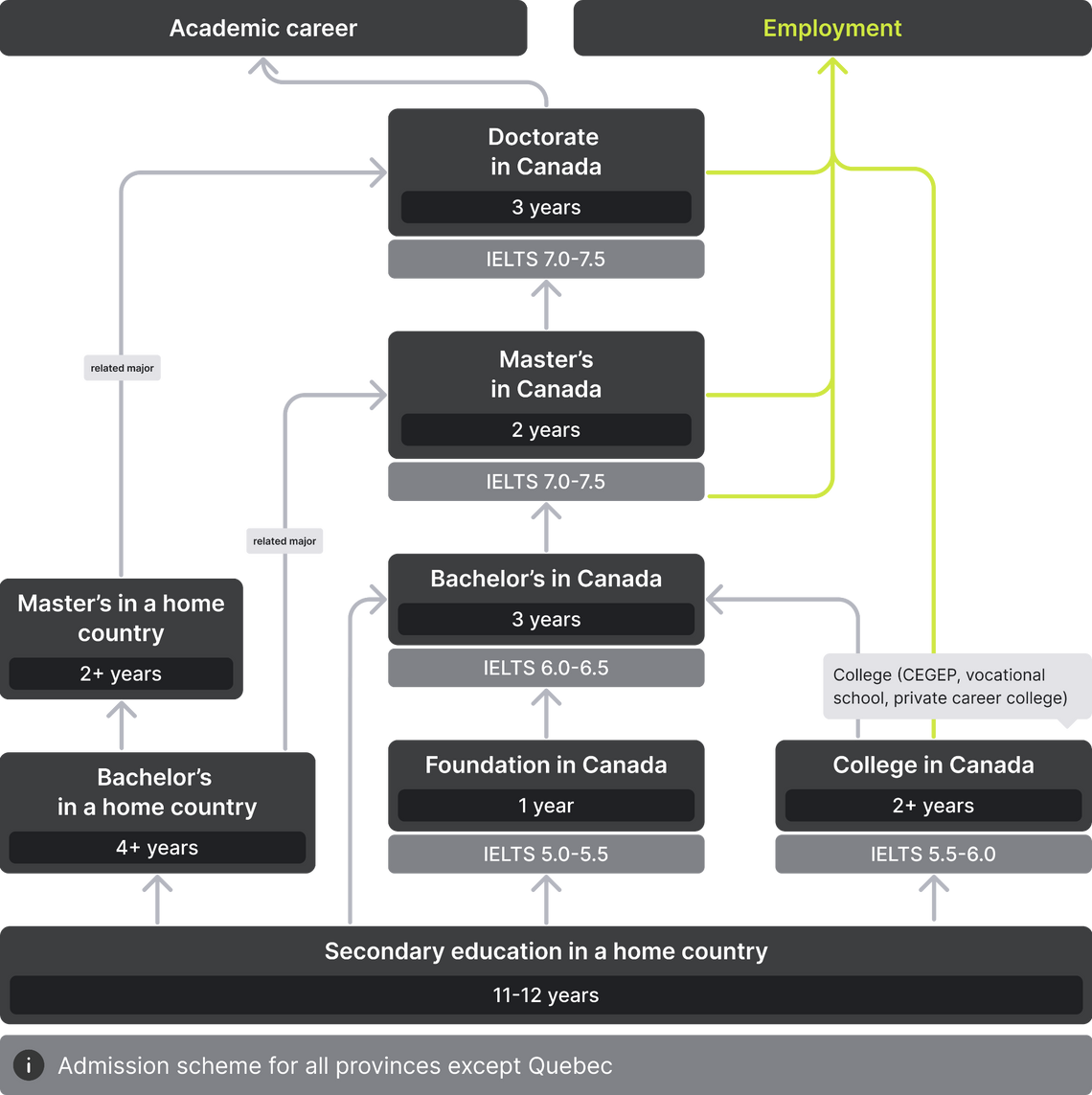

Unlike degree-granting universities, colleges grant mainly diplomas, certificates and in some cases, bachelor’s degrees. Colleges focus more on specific employment skills, career training, and trades. They provide students with practical learning in a variety of technical and professional fields such as agriculture, business, engineering, information and communication technology, health, hospitality management, language, social services, and arts and design.
University colleges also offer degree programs where a student can take courses and earn credits that can be later transferred to a university. However, college-level education is already enough to get a job that does not require an in-depth four-year study.
Bachelor's degree is the first stage of classical university education, which takes 3-4 years to complete, depending on the province. Students can get here directly after graduating from school (11 years) or Canadian college. For foreign applicants, it is also possible to spend the first year of study in a separate institution — an international college — followed by admission to the second year of undergraduate studies.
An academic year usually runs from September to May, divided into two semesters, some universities also offer a summer one. In addition to compulsory subjects, bachelor students have the opportunity to choose additional courses that are not related to the program. In the learning process, the main emphasis is on seminars and independent study of the subject, which requires a student to have a high degree of interest in the chosen program. In order to graduate from a Canadian university, you need to get a certain amount of credits, which is individual for each university.
Most universities in Canada provide students with practice (1-2 months) in a Canadian company, which usually becomes a significant advantage for further employment.
Several universities in Canada offer cooperative education options. Co-op students combine study with work, for which they can get up to 50 percent of credits. Such programs usually take about 4.5 years to complete.

Master’s degree, in contrast to undergraduate studies, involves a narrower subject focus. An applicant can choose between two types of master's degrees. Research-based master’s programs emphasize conducting original scientific research, while professional master’s programs focus more on applied education, offering a set of courses in a particular subject area. Duration varies from 1 to 3 years.
Most programs include a dissertation that makes up a large proportion of the course’s credits. Upon completion of training, students can also take a comprehensive examination, including both written and oral parts. Each of them is assessed on a pass/fail basis. Due to its size, the exam can be administered in several days.
Some Canadian universities offer co-op programs which enable students to gain hands-on, paid internships related to their field of study. They are usually between 2 and 4 months long. They are often used by employers for getting to know potential employees.
As in many other countries, the highest level of academic qualification a student can achieve in Canada is doctorate. In addition to the traditional academic PhD, professional doctorates are also available. Those include DBA and EdD. Most programs require 3 years of full-time study, but some may be extended up to 6 years.
Unlike the United States, doctoral studies in Canada are research-based from the outset. In the first year of study, students complete general courses focusing on techniques and methodology of research, teaching, presentation or publication, sit a comprehensive exam, and then move on to write their thesis. As for professional programs, they include a lot of practice and case studies also ending with doctoral thesis.
Some Canadian universities offer a collaborative route to PhD involving students studying for some time at another international institution within cotutelle programs. Unlike other joint PhDs with ongoing partnerships between universities, cotutelle arrangement is usually specific to each student’s project.
In most cases, a master’s degree is required in order to gain admission to a PhD program. However, some universities offer doctoral stream Master’s routes for those holding a bachelor's degree. Such programs begin with one or two years of additional training, making up for the lack of master's education.
You can start your academic career in Canada already at the stage of obtaining a doctorate as a graduate teaching assistant, or instructor. Holding this position assumes a certain amount of teaching (usually at the undergraduate level) and significantly enhances a CV. In return, a PhD student either gets paid a salary or has some of his doctoral fees waived by the university.
Those who have already earned their PhD can be considered for the positions of Graduate Research Associate, Postdoctoral Instructor, or Junior Researcher. It is also possible to become an Assistant Professor. Unlike European countries, there is no limit to the number of people holding higher academic ranks within a university in Canada. Therefore, competition is much lower. The most important criterion affecting career advancement is scientific research. Besides, almost all academic staff typically spend from 6 to 20 hours a week teaching.
After a probation period (usually 6-7 years), the Assistant Professor may be promoted to Associate Professor and receives tenure. And after another 5 years, based on continuing accomplishments in the areas of teaching and research, the candidate may be promoted to Full Professor.
Salaries typically depend on the budget of the university itself. On average they would be 5,735 USD for Assistant Professor, 7,384 USD for Associate Professor, and 9,392 USD for Full Professor. At the same time, the average wage in the country is much lower — about 2,868 USD.

According to a study permit, an international full-time student may be able to work on- or off-campus, without a work permit, which can significantly reduce the cost of staying in the country. During regular school semesters, a student is allowed to work up to 20 hours per week, during winter and summer holidays — full time. It is also necessary to get a Social Insurance Number (SIN), which provides students with a right to work and get government benefits and services.
The minimum wage of an international student depends on the province and can be 8-11 USD.
Upon graduation, international students have the right to temporarily work in Canada with a Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP). It can be valid for 3 years, provided that the training program was more than 2 years. In other cases, a PGWP is issued for up to the same length as a study program completed. The cost of a PGWP is 183 USD.
To be eligible for this opportunity, a student must have completed a PGWP-eligible program:
A student is strongly advised to apply before his study permit expires. The processing time is about 3.5 months. During this period, applicants can work full time if they:
The experience gained with PGWP can help you qualify when applying for immigration through Express Entry. Both federal and provincial programs are available. To participate, you will need to submit your profile in the online system. Then you will be ranked in a pool of candidates using a points-based system. Those with the highest scores will get an invite to apply for permanent residence within 90 days.

60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got