Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Article score: 4 out of 5 (12 reviews)
Read about how to enroll at a Canadian university: admission process for foundation, bachelor's, master's and PhD programs, requirements and deadlines.
Free consultation





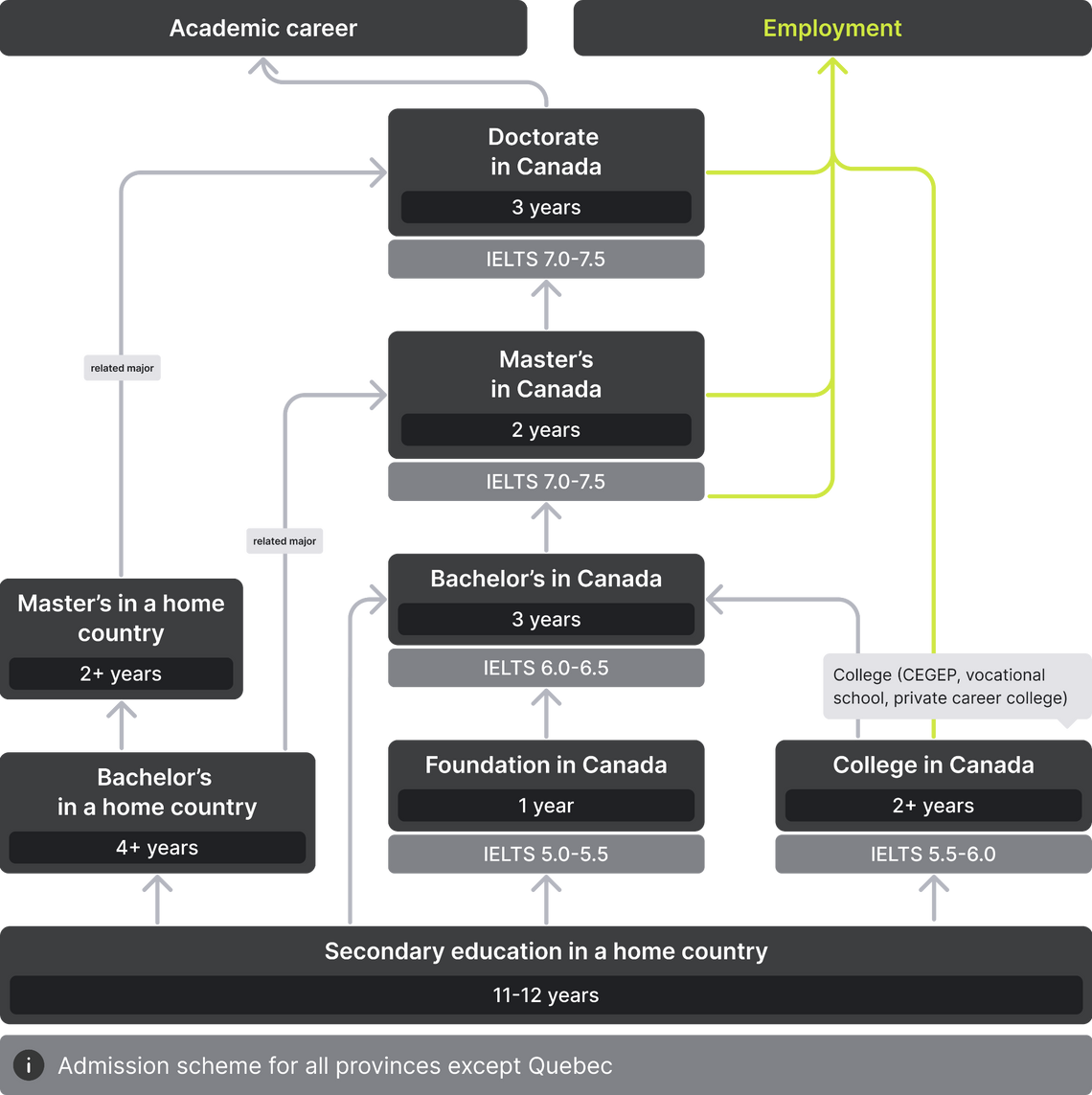
It is not difficult to enroll at a Canadian university, but there are some nuances and subtleties. Universities in all provinces, except Quebec, accept students after the 11th grade. You will need a high school diploma with a good GPA and an IELTS, TOEFL, or DELF certificate. Also, some universities require standardized tests and a motivation letter.
In the article, we discuss the admission process in Canada, requirements for bachelor's and master’s programs, as well as information on applied colleges and CÉGEP.
You can read more about the Canadian higher education system in our separate article.
| Program | Age | Duration | Min. cost per year | Avg. cost per year | Min. language level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | 16+ | 1 year | 7,169 USD | 10,754 USD | B1 |
| College | 17+ | 1-4 years | 2,294 USD | 7,886 USD | B2 |
| Bachelor's | 17+ | 3-4 years | 7,169 USD | 12,905 USD | B2 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-3 years | 2,151 USD | 17,923 USD | C1 |
| MBA | 20 + | 2 years | 14,338 USD | 21,508 USD | C1 |
| PhD | 20+ | 3-6 years | 1,792 USD | 12,188 USD | C1 |
| Expense | Average cost | |
| Registration fee | 61 USD | 104 USD |
| Document legalization | 84-179 USD | |
| Visa fee | 108 USD | |
| Rent | 1,371 USD/month | |
| Groceries | 62 USD/month | |
| Internet | 59 USD/month | |
| Transportation | 72 USD/month | |
| Utilities | 123 USD/month | |
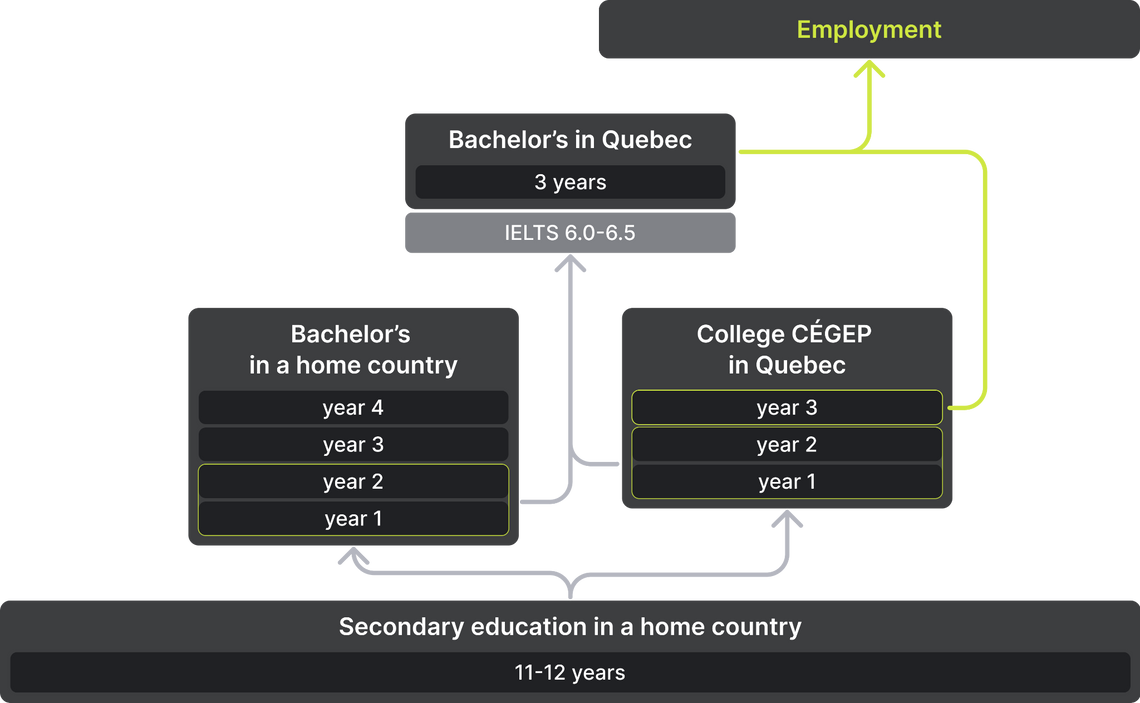

Choosing a university is one of the most important stages of the admission process. Canada consists of 10 provinces and 3 territories — each one differs in the language of instruction, deadlines, costs, admission requirements, and scholarship programs at universities. For example, you cannot enter a university in Quebec after finishing the 11th grade — applicants must study for 2 years at a CÉGEP, where programs are predominantly in French.
Other criteria for choosing a Canadian university:
UniPage employs professionals with extensive experience in admission to Dutch universities, including the University of Toronto, the University of Alberta, and the University of Waterloo. They will help you:
Items 1-6 of 419
Advanced search
Admission in Canada is possible after graduating from the 11th grade.
Higher education in Canada can be obtained at universities and vocational colleges. In both cases, you must have a diploma of complete secondary education. Moreover, be sure that the university or college is accredited, otherwise you may be denied a visa.
In addition to educational documents, you will also need:
Additional requirements:
In many ways, the education system in Quebec differs from the rest of Canada. For example, this is the only province where children go to school not for twelve, but eleven years. However, completion of the 11th grade is not enough to enter a university in Quebec. The province has its own kind of bridge between secondary and higher education — CÉGEP. Depending on the program, education at the college lasts 2-3 years. The two-year educational program paves the way for higher education in Quebec, while the three-year programs are designed for students who plan to get a job straight out of college.
Foreign applicants who wish to enter a university in Quebec need to have at least 12 years of study behind them. To do so, you can go to a Canadian college or pursue one year of bachelor’s studies in your home country.
Most foreign documents in Canada must undergo consular legalization. However, in the case of a diploma, an apostille and notarized translation are sufficient.
Universities handle document evaluation on their own. If they do not have the right to independently assess the qualifications of a candidate, they request certificates from independent credential evaluation services.
Canadian universities and employers recognize the assessment of the six major organizations that make up the Alliance of Credential Evaluation Services of Canada (ACESC). World Education Services (WES) is one such popular service. If desired, the student can contact one of them in advance, but this is not necessary. Canadian universities take into account the judgment of these organizations, but still reserve the right to make a final decision on the recognition of qualifications.
In the event that a student does not have sufficient language proficiency or knowledge of other subjects to enter a college or university, he can pursue a one-year Foundation program. Such programs help students adapt to the country and learn the language. Some universities offer their own preparatory courses for foreigners, but there are also independent programs at language schools.
Read more about language courses in Canada
The requirements for Foundation programs are lower than those for admission to a college or university. The minimum required level of English or French is B1 (Intermediate / Intermédiaire). However, some universities impose GPA requirements — at least 3.0 on a 4-point scale. Check the exact requirements on the website of the chosen preparatory program.
A list of available Foundation courses in Canada can be found on the official websites of universities or on specific aggregators for finding study programs.

You can pursue a bachelor’s program at a Canadian university upon graduation from the 11th grade, with the exception of some provinces. For example, universities in Quebec only accept foreign applicants who have done one year of bachelor’s studies in their home country, or two years at a CÉGEP.
In Canada, there is no uniform system for university admission. However, there are similar services in some provinces, such as Ontario — this is a website where you can apply to several universities at the same time. Moreover, prospective students can apply to an unlimited amount of programs. That being said, you can only apply to three programs within one university[3]. Such a procedure entails application fees — 112 USD for three programs, and 36 USD for each additional program.
Enrollment at Canadian universities takes place during the fall and winter semesters. Deadlines for document submission are in December-March and September-November, respectively. Some universities have an additional intake for the spring semester, which ends in February.
Document submission begins a year before the expected start of the program, and official acceptance decisions from educational institutions come a month after the deadline. Often, admissions committees consider applications as they are received and within a certain quota, and therefore, early submission of documents significantly increases the enrollment chances of a candidate.
Universities set their application deadlines independently. This information should be specified on the website of the selected program.
| University | Application deadline |
|---|---|
| University of Toronto | January 13 |
| McGill University | January 15 |
| University of British Columbia | January 15 |
| University of Montreal | February 1 / September 1 |
| University of Alberta | March 1 |
| University of Waterloo | January 13 |
| Queen's University | February 1 |
| University of Calgary | March 1 |
You may also need:
As a rule, you do not need to take additional entrance tests when applying for Canadian bachelor's programs. However, each university establishes its own list of requirements. Clarify this information on the official website of the chosen university.
You can enroll in a Canadian master’s program upon completion of a bachelor's degree.
Applications are sent directly to the chosen university. It is advisable to start preparing for the admission process at least a year in advance, namely to have time to pass the standardized GRE and GMAT exams. These exams test the English proficiency and analytical skills of the applicant.
Also, an academic resume, motivation letter, and 1-2 recommendations from professors are required for master’s programs.
An MBA is a master's degree in business administration. Requirements for admission include a bachelor’s degree with a high GPA (3.6 out of 4), a motivation letter, GMAT scores of 550-750, and an IELTS score of at least 7.0. Also, a frequent requirement is work experience of at least 2 years and letters of recommendation from colleagues and managers.
MBA programs are offered at 47 Canadian universities. Application deadlines vary depending on the specific program, but are usually set in March.
The admission period for master’s programs is similar to that of bachelor's programs — 2-3 times a year.
Application period for select Canadian universities:
| University | Application period |
|---|---|
| University of Toronto | September-March |
| University of British Columbia | November-January / January-March |
| University of Montreal | 1 February / September 1st |
| University of Alberta | January-June / September-November |
| McMaster University | October-January |
| University of Waterloo | September-December / January-April / May-August |
| University of Calgary | January-May |

Doctoral studies in Canada are designed for future researchers and teachers and are aimed at conducting independent research. Therefore, already at the stage of admission, the student needs to decide on the topic of his dissertation and agree with the supervisor. An important document for admission is a research proposal, where you should describe your research topic, its relevance, and generally demonstrate your potential for independent analysis.
Some universities appoint a supervisor based on the research topic, while others invite students to choose from a database of professors. In this case, the applicant needs to contact the future supervisor, send him a research proposal, and discuss a plan for further work.
For admission, you will need a master's degree with a GPA of at least 3.6 out of 4, IELTS 7.5 or TOEFL scores from 107, DELF / DALF for French-language programs, a motivation letter, and 2-3 recommendation letters from professors or managers.
Some Canadian doctoral programs allow students to enroll directly after bachelor’s studies. Education in this case lasts 6 years and combines the master's and doctoral stages. The first 1-2 years of study are equivalent to a master's degree, and students devote the rest of their time to research.
That being said, the admission requirements for such programs are high — excellent grades for the last two years of bachelor’s studies (GPA not lower than 3.6 out of 4), as well as existing scientific publications and a convincing research proposal.
Admission deadlines depend on the university, program, and even future supervisor. Most universities close the admission period in December-January. As a rule, studies begin one year after enrollment[4].
Higher education in Canada can be obtained at an applied college. College programs last from several months to four years. Upon completion, students receive a certificate or diploma. There are also programs that pave the way towards a bachelor's degree — you can go straight into the 2nd or 3rd year, and the credits received while studying in college are counted towards the degree.
The admission process for Canadian colleges is similar to that of bachelor’s programs at universities. You will need a high school diploma with a transcript and a certificate confirming English or French proficiency.
GPA requirements and minimum language exam scores for colleges are generally lower than for universities. For example, 6.0 on the IELTS and 70 points on the TOEFL exam are deemed sufficient. Check the exact requirements on the official website of the selected college.
If you are planning to pursue higher education in Quebec, you cannot do without a preparatory college. Here, they are called Collèges D'enseignement Général et Professionnel or CÉGEP. High school graduates must study at a CÉGEP for 2 years before entering a university in the province. They also offer career programs that last 3 years and allow graduates to immediately enter the labor market. Upon graduation from a CÉGEP, students receive a Diploma of College Studies.
A list of available CÉGEPs can be found here.
For admission to a CÉGEP, students must complete 11 years of high school. Some programs have specific requirements, such as having high grades in core high school subjects.
In Quebec, there are three centralized services for applying to a CÉGEP: SPAM (metropolitan Montreal), SRASL (administrative region of Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean), and SRACQ (the rest of Quebec). Depending on the college location, students apply to one of these services.
The admission period takes place twice a year — for the fall and winter semesters. The application deadlines are February 1 and May 15, respectively. Clarify the exact dates on the official website of the selected college.
Documents for admission:


Talented students of all educational levels can receive material support in the form of scholarships and grants for academic performance, sports, or professional achievements. They are called merit-based scholarships. Many Canadian universities award them automatically at the stage of enrollment[5]. View a selection of available scholarships here.
As a rule, scholarships can cover up to 50% of tuition costs. But there are also more generous grants that fully cover tuition, along with accommodation, food, and other expenses. The number of scholarship holders is always limited, and the competition is unusually high. Therefore, it is important to apply as early as possible.
Scholarships are also offered by provincial governments and private organizations. For example, the government of Quebec offers French-speaking students from other countries a discount on tuition at public universities and colleges in the province[6].
To study in Canada for more than 6 months, potential students need to obtain a Canadian study permit. The visa fee is 108 USD. Applications must be submitted before leaving for Canada. A study permit covers the entire period of study in a particular program plus 90 days to decide on further actions. The permit must be renewed if the student plans to move on to the next level of education. This can be done within the country.
A study permit is not a visa. To cross the border, the student will additionally need a tourist visa (visitor visa) or an electronic travel authorization (eTA). One of these documents will be issued along with the study permit.
Required documents:
To study in Quebec, you need to obtain additional permission from the provincial government — a Certificat d'acceptation du Québec (CAQ — Québec Acceptance Certificate).
Besides this, each Canadian province has its own age of majority. A student who has not reached it at the time of admission is considered a minor, and therefore must either arrive in the country with a parent, or have a guardian in Canada. The guardianship process may delay the visa application for an additional two months.
| Alberta, Manitoba, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, Saskatchewan | 18 |
| British Columbia, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Northwest Territories, Nova Scotia, Nanavut, Yukon | 19 |
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got