Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Article score: 4.56 out of 5 (9 reviews)
Instruction on how to apply to a Japanese university — documents, requirements, application process, deadlines and cost of undergraduate, graduate and doctoral programs.
Free consultation




For admission to a Japanese university, foreigner students need to pass the unified EJU exam and confirm their Japanese proficiency. A motivation letter, academic essay, and recommendations will also come in handy. However, this can be done only after a year of bachelor's study in their home country or a Japanese preparatory program — it is impossible to enroll at a Japanese university after the 11th grade. Read more about the admission process and requirements of Japanese universities below.
For more information on higher education and universities in Japan, read our separate articles.
| Program | Min. age | Duration | Min. cost per year | Avg. cost per year | Min. language level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| University preparation | 18+ | 1-2 years | 4,544 USD/course | 5,593 USD/course | N5-N1 / A1-C1 |
| College | 15+ | 2-3 years | 1,640 USD | 2,237 USD | N2-N1 / B2 |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 4-6 years | 3,746 USD | 6,502 USD | N2-N1 / B2 |
| Master's | 22+ | 2 years | 5,900 USD | 7,600 USD | N1 / С1 |
| MBA | 22+ | 1-2 years | 3,746 USD | 31,460 USD | N1 / С1 |
| Law school | 18+ | 4-6 years | 3,746 USD | 8,389 USD | N2-N1 / В2 |
| PhD | 24+ | 3 years | 3,746 USD | 5,002 USD | N1 / С1 |
| Expense | Average cost |
|---|---|
| JLPT language exam | 16-28 USD |
| EJU exam | 200 USD |
| Registration fee | 119-210 USD |
| Student fee | 1,972 USD |
| Translation of documents into Japanese | 35 USD |
| Rent | 825 USD/month |
| Dormitory | 229 USD/month |
| Utilities | 154 USD/month |
| Internet | 33 USD/month |
| Travel | 64 USD/month |
| Meals | 419 USD/month |
| Insurance | 24 USD/month |
| Study materials | 161 USD/year |
The prices listed in the table are given for reference. For exact amounts, visit the official website of your chosen university.

When choosing a university in Japan, you should pay attention to several main criteria.
Your decision should highly depend on your specialty. Japan is one of the best destinations to study engineering and technology. For example, the University of Tokyo is ranked 17th in the world in this area[1]. Moreover, there are many international companies in Japan that specialize in technology, innovation, and robotics — Sony, Mitsubishi, Canon, Casio, Toshiba. Students of Japanese universities have an opportunity to intern at these companies and get a permanent job after graduation.
Of course, these are far from all of the areas in which Japanese universities lead. For example, Kyoto University is ranked 25th in the world in the field of natural sciences. Japan is also the third largest economy in the world and a dominant trading power[2]. The areas of economics, business, and maritime trade are well developed at Japanese universities.
When choosing a university, refer to subject rankings. They will help determine how strong your specialty is at a particular university. QS and THE offer such ranking lists.
Japanese universities are annually ranked high in world rankings. According to QS, the University of Tokyo is 23rd in the top 100 best universities in the world, Kyoto University is 33rd, and Osaka University is 71[3].
However, you should not blindly trust international rankings. Most often, these are dry statistics and survey results that do not objectively reflect reality. Moreover, the position of universities differs from ranking to ranking because they are based on different criteria. For example, QS pays more attention to the reputation of the university and opinion of students and professors, while ARWU evaluates scientific achievements and research activities.
Moreover, regional universities rarely make it into the rankings. This is due to the small number of international students, a relatively short history, and other factors. However, even regional universities in Japan receive good funding from the state. Therefore, they have developed infrastructure no worse than top universities, and foreign specialists teach their programs.
More about: international rankingsIt is a lot cheaper to study at national universities, given that they are fully funded by the state. The University of Tokyo and Kyoto University are the most popular national universities in Japan. On average, the cost of studying here is 5,733 USD per year.
State universities are under the control of prefectures. As an example, these include Hokkaido University, Okayama University, Nara Prefectural University, and others. The average tuition cost for international students is about 6,502 USD per year.
The most expensive place to study are private universities. The average tuition cost is 7,690 USD per year, with some programs reaching 55,930 USD / year. The most popular are Keio University, Waseda University, and Sophia University.
If Japanese is not your forte or you are unsure as to whether your language level is sufficient for admission, look for universities that offer English-language programs. In total, Japan offers about 500 programs in English. They are more common among master's and PhD programs, but options can also be found in bachelor’s programs. For example, Waseda University has 5 bachelor’s and 10 master's programs in English. But, the University of Tokyo is better to consider for those who are fluent in Japanese. There are only two English-language bachelor’s programs offered here.
The Japanese government actively attracts foreign students to the country through generous scholarships. Most options are available for bachelor’s and PhD students.
You can check the availability of scholarships and grants on the official website of universities in the Scholarships and Financial Aid sections. You can also refer to the Ministry of Education of Japan list, or the website of the JASSO international student assistance organization.
It is also worth paying attention to less obvious, but important factors:
This criteria list can be endless. When choosing a university, think about what is most important to you. Based on your preferences, narrow down the options until you find the ideal university.
Items 1-6 of 1,091
Advanced search
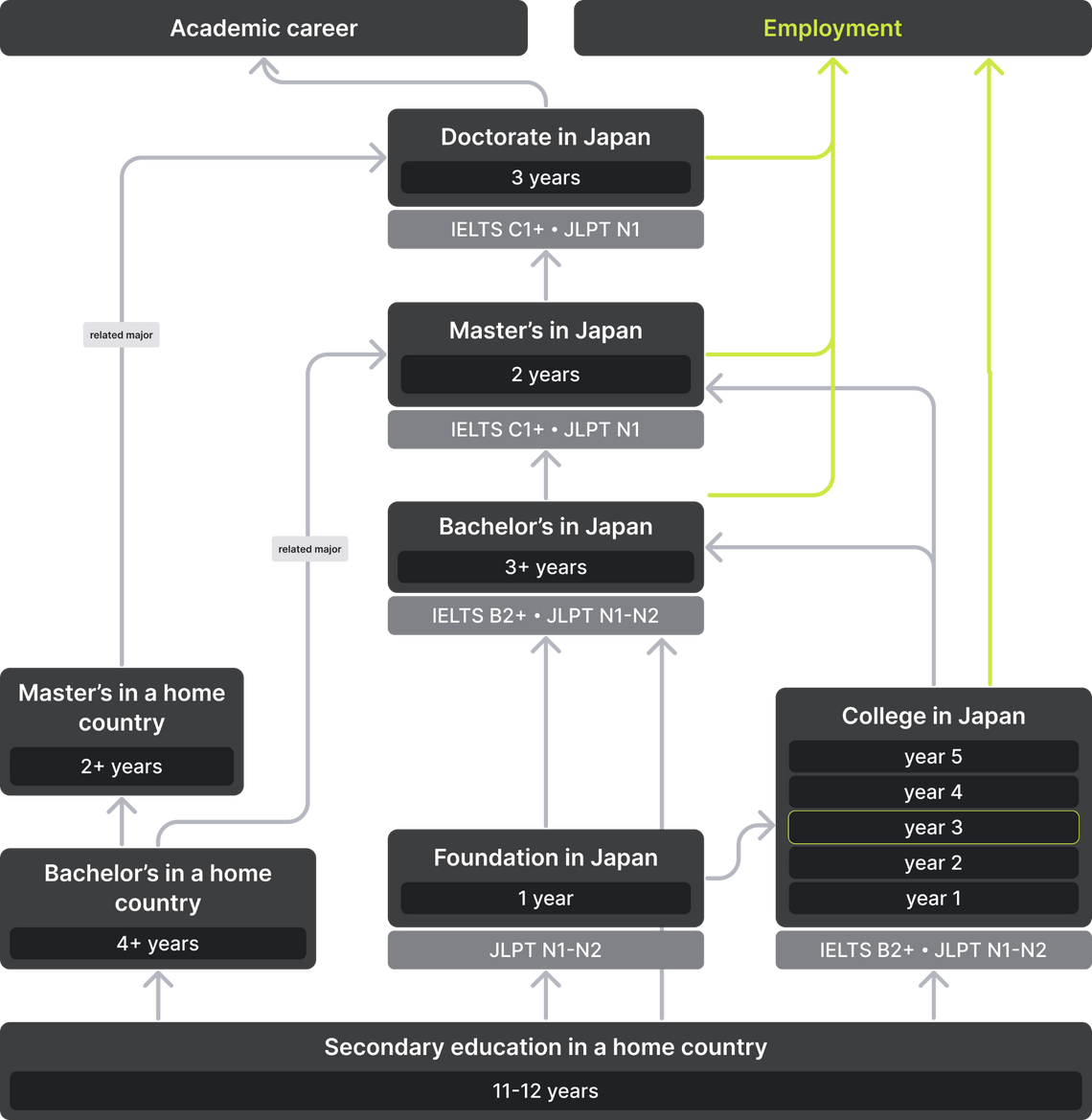
It is impossible to enter a Japanese university after the 11th grade. In this case, you have the choice to:
In most cases, foreign students entering a Japanese university must pass a unified exam — EJU (Examination for Japanese University Admission for International Students) and / or JLPT (Japanese Language Proficiency Test).
Each university independently chooses the format for entrance examinations. In addition to EJU and JLPT, this can be:
Additional documents may be required:
All foreign students entering Japanese universities must pass the EJU Unified Examination (Ryugaku shiken), the purpose of which is to assess the Japanese proficiency and academic abilities of the applicant.
The exam consists of four sections. Students choose one or more sections, depending on the requirements of the university:
| Section | Subjects | Max. score | Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese as a foreign language | - | 450 | Japanese |
| Natural sciences | Physics / Chemistry / Biology | 200 | Japanese or English |
| Japan and the world | Critical thinking, General knowledge | 200 | Japanese or English |
| Mathematics | Basic / Advanced | 200 | Japanese or English |
EJU centers are located not only in Japan, but also abroad.
Examinations are held twice a year: in June and November. Registration is required two to three months in advance.
Some universities, such as Kobe University, accept foreign students without the EJU, instead conducting internal examinations. Clarify whether or not you must take the EJU on the official website of your chosen university.
Also, you need to pass the JLPT (Nihongo Nōryoku Shiken) for admission to Japanese programs. The minimum level for admission is N2-N1.
The exam takes place twice a year: in July and December. Applications must be submitted two to three months in advance. Applicants can take it at any of the centers located around the world.
Japan is a member of the 1961 Hague Convention. Therefore, you must obtain an apostille for your educational documents.
In addition, all documents must be translated into Japanese or English and notarized.
The enrollment period at Japanese universities takes place three times a year — for the autumn, spring, and summer semesters.
Application deadlines for most universities in Japan:
| Semester | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Spring semester | October-November |
| Summer semester | February-April |
| Fall semester | June-July |
Exact deadlines may vary depending on the program and level of study. Verify them on the official website of your chosen university.

Secondary education in Japan lasts 12 years. Foreign applicants who have finished the 11th grade can make up for the missing year through the Foundation preparatory program. They are offered by universities, private language schools, and academies of additional education.
For admission, you will need a high school diploma with a transcript, and sometimes a motivation letter or academic essay. The language requirements for Foundation programs are lower than those for universities — it is enough to speak Japanese at the N5 level (Elementary).
Courses begin in April and October. The application deadline is November and April, respectively.
A full list of available Foundation programs at Japanese universities and colleges can be viewed here.
Documents for admission:
| Stage | Spring semester | Summer semester |
|---|---|---|
| Submit documents and pay the administrative fee | August-November | February-April |
| Receive acceptance letters and make an enrollment decision | November-December | May-June |
| Verification of immigration documents by the university | December | June |
| Receive an eligibility certificate from a university to stay in Japan | Beginning of March (following year) | Beginning of September (following year) |
It is not possible to enter a Japanese bachelor's program after the 11th grade, given that the Japanese go to school for 12 years. To resolve the academic difference, you can complete one year of bachelor’s study in your home country or enroll in a preparatory program at the chosen university.
In Japan, there is no unified application system for entering universities. Therefore, documents must be submitted directly to the university. This can be done online on the university’s official website or by post.
Foreign applicants need to pass the unified EJU exam and JLPT N2-N1. Also, some universities may require confirmation of English proficiency — IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 80-90.
Additional documents, depending on the university:
Depending on the chosen university and program, requirements may vary. Verify them on the official website.
Documents must be translated into Japanese or English and notarized. They must also have an apostille.
Foreigner students who have completed the 11th grade in their home country can enter a Japanese college of technology — kosen. These institutions specialize in applied education. Programs last 5 years, but, as a rule, foreigners immediately enter the 3rd year. Upon graduation, they receive an associate's degree.
The main condition for admission to a kosen is at least 11 years of education. In addition, foreigner students must pass the unified EJU exam and JLPT N2. Many colleges also require you to write an essay or pass an oral exam in Japanese.
Documents must be translated into Japanese and notarized. They must also have an apostille.

To enroll in a Japanese master's program, you need to pass the EJU, JLPT, or university entrance exams. In addition, some programs require standardized test results — GMAT or GRE. Specify the admission requirements on the official website of your chosen program.
One of the most important requirements for enrollment is a plan for a future master's thesis. The applicant must decide on a research topic and choose a supervisor among the program faculty. He needs to submit a research proposal and get consent from the supervisor to work on it.
The language requirements for master's programs are higher than those for bachelor's programs. You need to know Japanese at the N1 (Advanced) level. For admission to English-language programs, you will need IELTS 7.0 or TOEFL 90-100 results.
Some universities require you to write an academic essay and pass an oral interview in Japanese. These tests determine the language level and education of the applicant — whether or not it corresponds to the level of Japanese bachelors.
Pre-Master’s are common programs in Japan. They prepare applicants for graduate study. Admission requirements are lower than those for regular master’s programs. You need a bachelor's degree and Japanese proficiency at the N3 level (in some cases — N4).
Admission takes place in April and October.
Documents must be translated into Japanese or English and notarized. They must also have an apostille.
For admission to MBA programs in Japan, you will need a bachelor's degree and proof of English proficiency, given that most programs are instructed in this language.
Documents for admission:
Admission takes place twice a year: in April and September.
For admission to a PhD program, you must provide a research proposal and find a future supervisor. The admissions committee and future supervisor may request an academic resume and list of scientific publications. In addition, many universities conduct interviews with PhD applicants.
Applicants must also pass the EJU or internal entrance exams of the university. GRE results may also be required. For English-language programs, you need IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 100+. To study in Japanese — JLPT N1.
Some universities may require:
Documents must be translated into Japanese or English and notarized. They must also have an apostille.

Education in Japan is tuition-based for both local and foreigner students. However, students may be exempted from tuition fees if they experience financial difficulties — for example, in the event of parental death or a natural disaster.
In addition, there are many scholarship programs available to students in Japan.
The Japanese Ministry of Education annually offers 7 types of scholarships to students of Japanese universities. They fully cover the cost of tuition, registration, and other university fees, along with a one-way flight and sometimes Japanese courses. MEXT scholarship recipients receive monthly payments.
You can apply for a government scholarship through your university or embassy. Applicants are interviewed and take written exams in Japanese, English, and the subjects of their chosen specialty.
| Type of scholarship | Age | General requirements | Monthly payment | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young Leaders Program | Up to 40 | Complete a bachelor's or college degree in administration or business | 1,692 USD | 1 year |
| For bachelor’s students | Up to 25 | Enroll in a bachelor’s program at a Japanese university | 818 USD | 5 years |
| For vocational college students | Finish 12 years of high school and go to a vocational college in Japan | 3 years | ||
| For kosen students | Complete 11 years or more of school and enroll in a Japanese college of technology | 4 years | ||
| For master’s and PhD students | Up to 35 | Continue studying in the same field | 1,007 USD | 2 years |
View the complete list here.
JASSO (Japan Student Services Organization) — a non-profit organization that annually provides scholarships to foreign students of Japanese universities, colleges, language schools, and preparatory courses. Funding is available for all levels of education.
Scholarship amount — from 30000 to 336 USD.
General requirements:
Governments and international organizations of various Japanese prefectures also establish their own scholarships for students of local universities and colleges. The main requirement is residence in the territory of a particular city or region. Additionally, recommendation letters from the university, an interview, or a written exam may be required.
| Type of scholarship | Level of education | Payment | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kitami scholarship for international students | Bachelor’s, master’s, PhD | 1,398 USD/year | 1 year |
| Otawara scholarship for international students | Bachelor’s | 70 USD/month | 1 year |
| Shinjuku scholarship for international students | Bachelor’s, master’s, PhD | 1,678 USD/year | 1 year |
View all of the options in this brochure.
Many organizations also set up private foundations to provide financial assistance to foreign students. Most often they can be found through special aggregators, such as the JASSO organization website.
| Scholarship | Level of education | General requirements | Quota | Monthly payment | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iizuka Takeshi Scholarship Foundation | Bachelor’s, master’s, PhD | Enroll at a university in the Tochigi prefecture | 5 | 350 USD | For the entire period of study |
| Kajima Ikueikai | Master’s | Study architecture or construction at the University of Tokyo, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Osaka University, and others. | 16 | 699 USD | 2 years |
| Atsumi International Foundation | PhD | Attend a university in Tokyo or the Kanto region | 16 | 1,748 USD | 1 year |
To study in Japan for more than 90 days, you need to apply for a student visa. It is valid for the entire period of study. If you wish to pursue graduate study after finishing a bachelor’s program, you must extend your visa through the migration service.
Registration is carried out jointly with the chosen educational institution. To get a Japanese student visa, you need to:
Japanese student visas are issued 4 times a year: in April, July, October, and January. Registration is free and takes from 3 to 4 months.
Required documents:
The list of documents may vary depending on the university. Additional documents may include a motivation letter, copies of educational documents, and proof of Japanese proficiency.
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got