
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
What do you want to know about higher education in the UK? We'll tell you everything: how much does it cost, what type of institution to choose, how to apply and get accepted.
Free consultation









In this article, we explain how higher education in the UK is arranged: what types of programs exist and what their differences are. The process of admission to English universities and the education system as a whole are described in other articles.
Admission to the UK UK universities Education system
Vocational education in Britain is obtained at FE colleges. They assign the following qualifications:
These programs are intended for applicants over 16 years of age. Students receive practical skills and after graduation can immediately get a job. According to statistics, most certificates are issued to specialists in the fields of health, arts, media, business, law, information technology, trade, tourism, and engineering[4]. FE graduates have the opportunity to move on to the next level of undergraduate studies.
Qualifications are considered to be a special category of education in Britain, known as apprenticeships. This is an internship in which most of the training takes place on the job — a minimum of 30 hours per week and 30 weeks per year. The student, called an apprentice, receives a salary for his work, enjoying all of the rights of an employee of the company. Only 20% of his time is devoted to classes at a college or university. Higher/degree level qualifications are equivalent to academic bachelor's or master's degrees in higher education. For admission to an apprenticeship program, GCSE/A-Level exams or an Advanced Apprenticeship diploma may be required.
The cost of training is fully covered by the government and employer. However, it is not so easy for foreign students to take advantage of internship opportunities: this requires a work visa. Internship levels, requirements, standards, and governing bodies vary by region[5]. To find out all the details, you need to contact the college, university, or employer.

Undergraduate (bachelor's degree) is the first stage of higher education in Britain. In England, Wales, and Northern Ireland, almost all undergraduate programs, with the exception of medicine and architecture, last 3 years. The basic knowledge that forms the basis of the first year of European and American universities, British students receive in preparatory courses. However, training can last 4 years in Scotland.
Undergraduate students conduct both independent and group research. Teachers involve students in discussions, and this contributes to the development of critical thinking. Such education is largely focused on practice that meets the needs of the modern labor market.
At the end of a bachelor's program in the UK, students, depending on the direction of study, receive various qualifications: BA (Bachelor of Arts), BSc (Bachelor of Science), BEd (Bachelor of Education), BEng (Bachelor of Engineering) or LLB (Bachelor of Laws). In addition, all of these degrees are divided into ordinary degrees and degrees with honours. The difference between them lies in the average score of the diploma and the number of teaching hours. For example, to get an ordinary degree, you need to score 150 ECTS, and for a degree with honours you need 180 ECTS. The type of degree will not affect the graduate's employment, but will play a role in the transition to the next level of education. At some universities, a student who completes a bachelor's degree with honours can enter a doctoral program without having a master's degree.
ECTS is the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System. For each course completed, students earn points called credits. The number of credits depends on the number of academic hours required to complete the program. One academic year (60 ECTS points) corresponds to 1500-1800 academic hours. Without gaining the required number of credits, a student will not be able to complete his studies at a university.
Britain has its own analogue of the system — CATS. CATS credits are converted to ECTS very simply: 2 CATS = 1 ECTS. Because they are more common, in this article we present ECTS.

In most cases, applications for undergraduate programs are accepted from the beginning of September to the end of January. For admission to universities in the UK, a student will need a:
| Ordinary degree | Degree with honors | GPA |
|---|---|---|
| Distinction | First Class Honours (1st / 1 / I) | 70-100% |
| Merit | Upper Second Class Honours (2:1 / 2i / II-1) | 60-69% |
| Pass | Lower Second Class Honours (2:2 / 2ii / II-2) | 50-59% |
| Pass | Third Class Honours ( 3rd / 3 / III) | 40–49% |
| Fail | — | <40% |
In many countries, undergraduate education is limited to a bachelor's degree. In Britain, this includes a number of other qualifications:
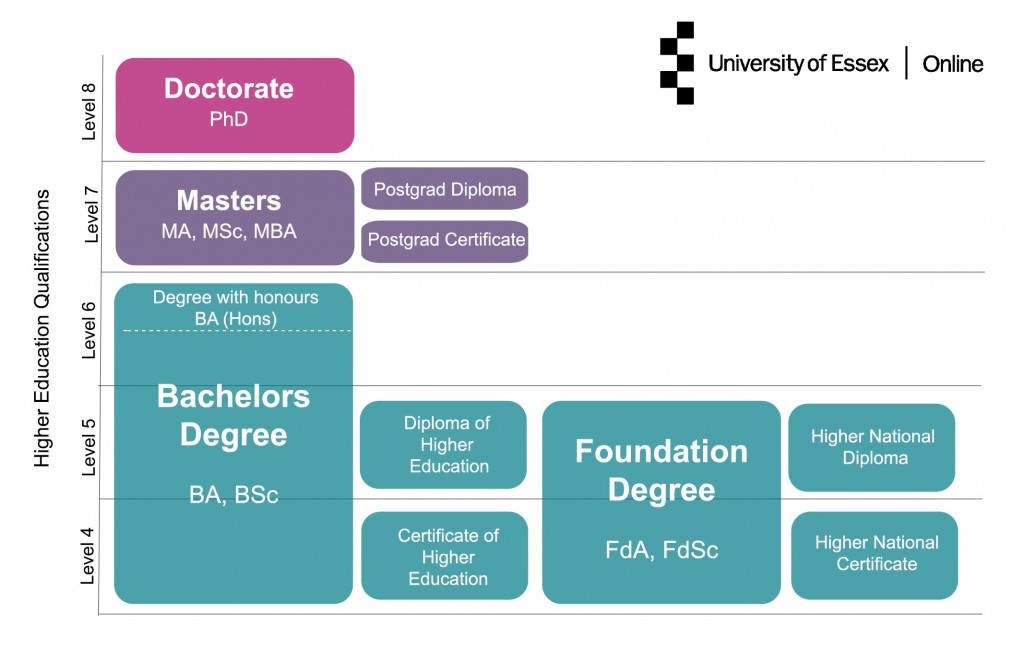
Master's degrees at UK universities represent academic programs and practice-oriented postgraduate courses. Most of them will require 1 year of study (90 ECTS).
Types of master's qualifications:
There are also two varieties of the Academic master's:

Many universities accept applications all year round, but some have deadlines in June and January. The list of documents for admission includes:
Additionally, the university can conduct an entrance test or an interview with the candidate (in person or via Skype). If he does not speak English at the proper level, private educational institutions, as a rule, offer a Pre-Master's preparatory program to the student.
| Degree | Full title | Type | Length of study | Subject area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA | Master of Arts | Taught | 1-2 years | Arts, Humanities, and Social Sciences |
| MSc | Master of Science | Taught | 1-2 years | Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics, and some Social Sciences |
| MRes | Master of Research | Taught /Research | 1-2 years | All subjects |
| MPhil | Master of Philosophy | Research | 2 years | All subjects |
| MFA | Master of Fine Arts | Practical/Professional | 1-2 years | Arts |
| MLitt | Master of Letters | Taught/Research | 1-2 years | Arts and Humanities |
| LLM | Master of Laws | Taught / Research | 1-2 years | Law |
| LPC | Legal Practice Course | Professional | 1-2 years | Law |
| GDL | Graduate Diploma in Law | Professional | 1 year | Law |
| MBA | Master of Business Administration | Professional | 1-2 years | Business and Management |
| MIM | Master in Management | Professional | 1 year | Business and Management |
| MEng | Master of Engineering | Taught/Professional | 4 years | Engineering and Technology |
| MSW | Master of Social Work | Taught/Professional | 2 years | Social Work |
| PGCert | Postgraduate Certificate | Taught / Professional | 1 semester | All subjects |
| PGDip | Postgraduate Diploma | Taught / Professional | 2 terms | All subjects |
| PGCE | Postgraduate Certificate in Education | Professional | 1-2 years | Education |
| PGDE | Professional Diploma in Education | Professional | 1-2 years | Education |
In the UK, there are a large number of specific programs that can be difficult to distinguish from each other:
Retraining courses are designed to introduce you to a new profession. There are 4 main types of conversion courses:
At British universities, the most common courses are in the following subject areas:
In most cases, the requirements for admission to retraining courses coincide with those for a regular master's program.

Doctorate degrees (PhD, DPhil) are the third and final step in the UK higher education system, equivalent to a PhD. There are PhD programs in all subjects. The duration of most of them is 3 years, during which students do their own research, consult with a supervisor, publish articles, participate in conferences, and sometimes teach bachelor’s students. At the final stage, they write a dissertation followed by an oral defense. In some cases (New Route PhD scheme, Wellcome Trust Four year PhD scheme) doctorate programs are supplemented by training courses, increasing the duration of study to up to 4 years.
Most often, a master's degree is required for admission to a PhD program, however, some universities offer programs that are available to students immediately after their bachelor's studies. This mainly applies to graduates of STEM areas.
Doctorate programs usually begin in September-October, and applications are accepted all year round. However, early submission of documents can increase the candidate's chances for acceptance. The list of requirements for admission to doctorate studies includes:
The competition for doctorate programs is quite high in the UK — the success or failure of a candidate largely depends on his research experience, academic achievements, number of publications, and extracurricular activities.
Compared to other countries, academic careers in the UK are quite open to foreigners: 31% of the teaching staff comes from abroad[7]. This figure grows with every year, largely due to the prevalence of the English language.
A PhD is required to start an academic career. In some cases, an MPhil can open doors to various academic positions, such as a research assistant, lab technician, project manager, or teaching fellow.
One of the shortcomings of the British system is the widespread use of temporary fixed-term contracts. They make it difficult to find stable employment in the academic field. The chances of obtaining a permanent position depend on the requirements of the Research Excellence Framework (REF), which emphasizes the need for research and publications.
The main academic positions at British universities are:
Admission to a British university is multi-stage, and because of this is fairly difficult. First, you need to enter a preparatory program (A-levels, Foundation, or International Year One), undergo training, pass the final exams, and only then apply to a university.
During a free consultation, UniPage experts will explain in detail the requirements that apply to an applicant. We fully supervise the admission process — selecting a university and program, collecting a package of documents, and submitting applications. All so that you have free time for the most important thing — studying and preparing for exams.

For foreign students studying full-time, a student visa allows them to work according to the following rules: up to 20 hours per week during the semester and up to 40 hours per week during the holidays. The exception is persons 16-17 years old, who can work up to 10 hours a week throughout the year.
Full employment is only possible if the internship or practice is part of an educational program and is assessed by credits. At the same time, the work time should not exceed 50% (sometimes 30%) of the total duration of training.
Restrictions also apply to several areas of employment: students are prohibited from engaging in entrepreneurial ventures, having their own business, and being a professional athlete, coach, doctor, or artist[8].
After receiving a job offer, the student must obtain a National Insurance number.
An exception is Apprenticeship programs that offer formal employment with periodic attendance at classroom classes. This opportunity is available to foreign students, but in order to use it, the candidate must apply for a work visa. Check with the college, university, or employer for details.
The UK has a minimum wage that applies to foreign students. The National Minimum Wage rises every year and is based on age.
| Age | Minimum wage per hour |
|---|---|
| 23+ | 12 USD |
| 21-22 | 11 USD |
| 18-20 | 9 USD |
| <18 | 6 USD |
| Apprentice <19 | 6 USD |
Britain is one of the most complex countries for immigration. From the summer of 2021, a graduate with a student visa has 2 years to switch to a Skilled Worker visa, intended for skilled workers. To obtain such a visa, you need to get a job in a company with a sponsorship license. However, the student does not have to wait until the end of his studies, given that most of the available vacancies may already be filled by this time. To increase your chances of finding a job, start looking for employment about a year before graduation.
Criteria for obtaining a Skilled Worker visa:
Additionally, you may need a five-year travel history, a certificate of the absence of tuberculosis, and a certificate of no criminal record. The cost of a visa depends on the validity period[9]. A Skilled Worker visa allows you to work in the country for up to five years. It can be extended, but the total stay should not exceed six years. The visa also allows you to find a second part-time job (up to 20 hours per week)[10].
Another option to stay in the UK is to get a Start-up visa. To do this, the candidate must have an innovative business idea approved by an educational institution or a company from the list of authorized organizations, known as endorsing bodies. The visa is issued for only two years and is not renewable, but gives access to the Tier 1 (Entrepreneur) visa and Innovator visa.
After 10 years of legal residence in the country on any visa (including student), an immigrant is granted the right to permanent residence, and after another year — to citizenship. This method is called long residence and is one of the few options for immigration to the country for foreign students.

60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got