
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Let’s take a look at American higher education: study degrees one can earn there and learn about costs, scholarships, student visa and other useful insights.
Free consultation








Education in the USA is the most popular choice among those who go to study abroad. Today, there are more international students in the United States than in any other country. Over the past year, their number has exceeded one million, despite the lack of free education and the requirement of SAT or ACT. That is primarily due to the academic prestige and effectiveness of US universities. In addition, graduates of American universities often achieve brilliant results in business, science, and politics.
The education system of the USA has the same model as many other countries. Students are required to attend school until the age of 16, in some states — 18. Most students receive K-12 education (from kindergarten to grade 12), but there is an optional Preschool stage, including the last preparatory year before school as well, called Pre-K:
| School-level | Grades | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Preschool (pre-kindergarten) education | Pre-K | 4-5 |
| Primary (elementary) school | K-5/6 | 5-11/12 |
| Middle (junior high) school | 6/7-8 | 11/12-14 |
| Secondary (high) school | 9-12 | 14-18 |
Primary school includes studying basic subjects within the confines of one classroom with some additional classes, such as physical education, music, and art. Then, at the middle school level, students are given more freedom by being offered elective courses. However, unlike in the UK, schools in the United States remain comprehensive until the 12th grade, with the exception of vocational schools.
High school students are referred to differently each year, similarly to undergraduate students: freshmen (9), sophomores (10), juniors (11) and seniors (12). Admission to higher education institutions is only possible after completing all 12 years of study and receiving a high school diploma.
Most children go to public schools, and only 10% prefer fee-paying private schools. The latter include schools for gifted students, for children with disabilities and specialized schools (including those with religious affiliation). Elite private schools are highly selective and, unlike public schools, won’t hesitate to expel unruly students.
It should be noted that, according to US law, foreign citizens may enter a public school only at the high school level and for a maximum period of 12 months, while paying the full cost of tuition[1]. There are no restrictions on attending private schools for foreigners[2].
| Type of study | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language level | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer Camp | 6-18 | 1-10 weeks | 700 USD/week | 1,000 USD/week | A1 | - |
| Language courses | 16+ | 1-16 weeks | 350 USD/week | 650 USD/week | A1 | - |
| Secondary education | 11-18 | 6-7 years | 13,000 USD/year | 30,000 USD/year | B1 | - |
| Pathway / Pre-Master's | 16+ | 1 year | 15,000 USD/year | 30,000 USD/year | B1 | TOEFL iBT 55 |
| Two-year college | 16+ | 2 years | 4,000 USD/year | 12,000 USD/year | B1 | TOEFL iBT 55 |
| 17+ | 4 years | 18,000 USD/year | 30,000 USD/year | B2 | TOEFL iBT 61, SAT / ACT | |
| Master's | 20+ | 2 years | 18,000 USD/year | 25,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL iBT 78, GRE / GMAT |
| Medical school | 20+ | 4 years | 25,000 USD/year | 40,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL iBT 78, MCAT |
| Law school | 20+ | 1-4 years | 22,000 USD/year | 45,000 USD/year | С1 | TOEFL iBT 100, LSAT |
| Doctorate | 20+ | 4-6 years | 18,000 USD/year | 25,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL iBT 78, GRE / GMAT |
| Expenses | Average cost |
| Language test | 260 USD |
| Application fee | 50-100 USD |
| Foreign credential evaluation | 160 USD |
| SEVIS I-901 fee | 350 USD |
| Student visa F-1 | 360 USD |
| Flight | 380 USD |
| Study supplies | 800-1,200 USD |
| Accommodation and meals | 6,000-14,000 USD/year |
| Health insurance | 1,000-1,500 USD/year |
| Public transport | 900-1,300 USD/year |
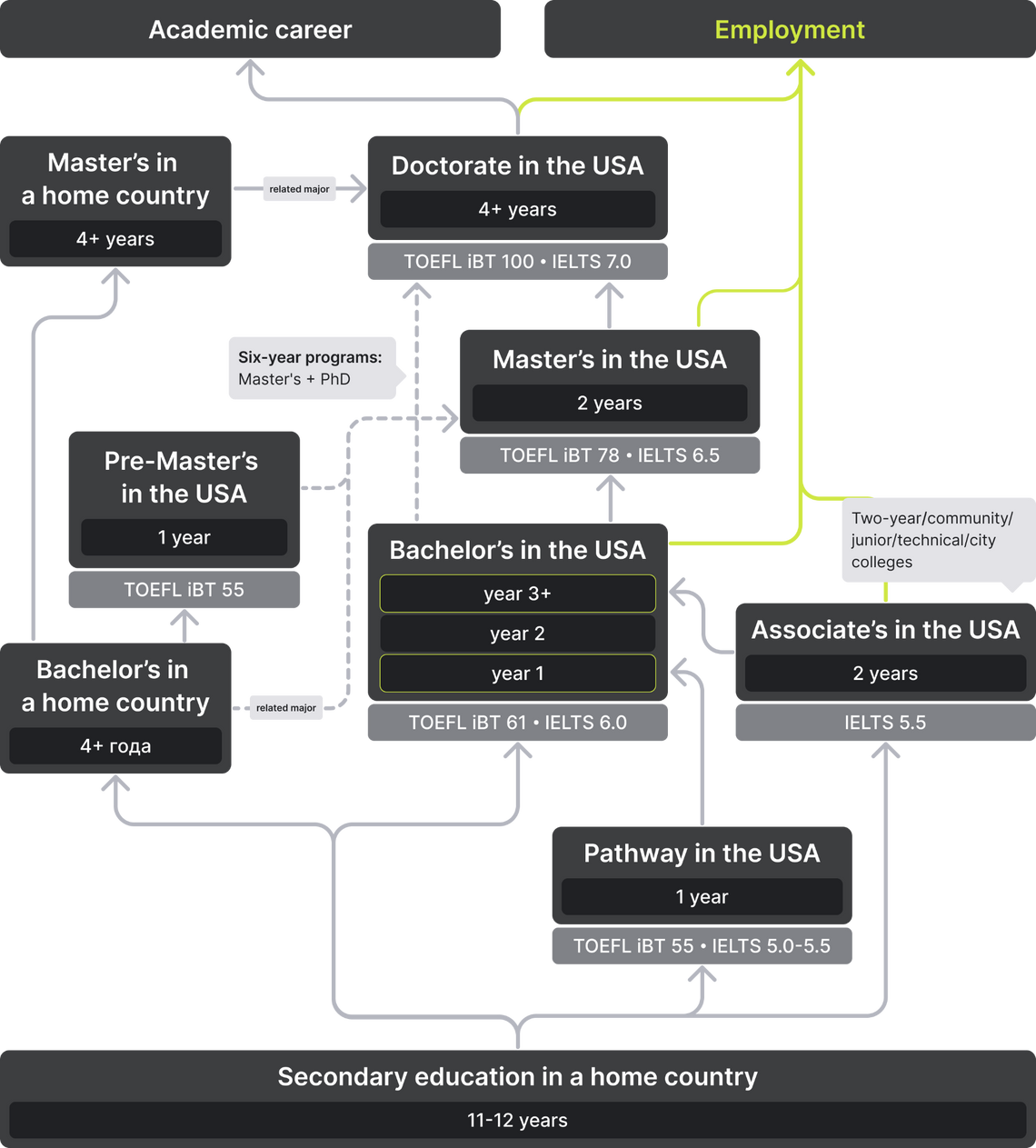

Most US universities do not require entrance exams (except for SAT / ACT and GRE / GMAT). Students apply online through university websites. There are normally three intakes per year, i.e. fall, spring, and summer. Students are to prepare at least one year before the expected start of training. In some cases, the whole process takes a few months. There are three admission plans at US universities:
One of the requirements may be evaluation of academic credentials. An official report can be issued and then sent to the chosen institutions by special independent organisations, such as WES, EСE. It should be noted that for some of these organisations, including the most popular WES, documents must be verified by apostille. Others require only certified translations. The fee is 100-205 USD depending on the educational level and service package.
If accepted, an applicant is enrolled in the Student and Exchange Visitor Information System (SEVIS). Most students are required to pay an additional fee of 350 USD (the SEVIS I-901 fee). For some students it can be reduced to 35 USD, for others it may not be the case.
In America, preparatory programs are called Pathways, or Pathway programs. They are designed for foreign students who need to improve their language proficiency, as well as acquire knowledge and skills for further undergraduate (Undergraduate pathway) or graduate (Pre-Master's) studies. Within the program, students study English as a second language (ESL) and some courses for credits.
Pathway programs are provided by both universities and language schools that have agreements with universities. Most of them offer conditional acceptance. This means that in case of successful completion (with a sufficient language level and a high GPA), a student can be automatically enrolled in a partnering institution (first or even second year) without taking SAT or TOEFL.
Depending on the level of English proficiency, Pathways can last from 4 to 12 months. In case a student does not meet basic requirements (TOEFL iBT 55 / IELTS 5.0 — 5.5), he can choose an intensive English language program (1-2 semesters) with further transition to a Pathway (2 semesters).
Finishing a preparatory program is not compulsory for admission, but for many students, it is an opportunity to adjust to a new academic environment, try oneself in different courses and make an informed decision on one’s major. If a student is sure that some differences between the education systems of his home country and the USA will not prevent him from succeeding in studies, but he still doubts his level of English, he can take language courses in the USA. They are much more effective here in the English-speaking country.

Vocational education in the United States is provided by two-year colleges (community / junior / technical / city colleges). Upon completion, students are awarded certificates, diplomas and associate's degrees. The latter can be also earned in four-year colleges, but those mostly focus on bachelor’s degrees.
Similarly to a bachelor's degree, an associate's degree may have the titles Associate of Arts (AA), Associate of Science (AS) and Associate of Applied Science (AAS), as well as AAB, AAT, ABA, AE, AEng, AIT, AN, AOS, AT and other specialized varieties. The first year of study involves general subjects; the second year focuses on specific areas of discipline. The program is normally 60 credits.
The admission process in two-year colleges is much easier than in four-year educational institutions, as it is based on open admissions policy. Requirements are often limited to a high school diploma. In some cases, demonstrating one’s ability to benefit from receiving education is enough.
The basic English proficiency is TOEFL iBT 55-61 / IELTS 5.5. However, in many colleges, it is subject to change. Students with a lower level can be enrolled as well. So, they will take language courses as part of their educational program. SAT results are generally not required when applying to community colleges.
After two years, graduates can already move on to employment, although most students prefer to continue their studies towards a bachelor’s degree. Many community colleges have partnerships with four-year colleges and universities, where students can be automatically enrolled in the 3rd course, followed by a bachelor's degree. Such a transfer admission is becoming increasingly popular among both American and international students. Firstly, it saves a lot of money. Studying at a two-year college is many times cheaper. Secondly, it is characterized by better chances of admission. An applicant does not have to participate in a difficult competition to get to the 1st year of university.
Bachelor's degree in the USA can be obtained at four-year educational institutions — colleges and universities. Each year spent here has its own name: freshman, sophomore, junior and senior years. After two years of general education courses, a student focuses on his major. Upon completion, students can be awarded the common titles of Bachelor of Arts (BA) or Bachelor of Science (BS), as well as a number of specialized BFA, BSW, BEng, BSPA, BSN, BPhil, BArch, BDes.
It should be noted that in the USA there are no Bachelor’s degrees in Medicine or Law. These are advanced professional programs offered by graduate schools. However, a person will still have to take a set of courses before entering a medical school. At this point, they are usually referred to as pre-med.
Courses in American universities are based on seminars, with small groups of students discussing particular topics. However, there are also traditional lectures, especially for disciplines studied by many students (computer science, medicine, business). The content of the courses varies depending on the program: "liberal arts" programs usually include a large number of elective subjects, while specialized and technical courses are more structured and highly specialized.
Requirements for admission to undergraduate programs in the United States:
The list of documents may include:
The latter is very significant for American universities. Students can use it to demonstrate their commitment to a particular college, explain their choice of program and thereby set themselves apart from the other candidates.
Four years is only an approximate period for which a student is to earn a certain number of credits (120-128). Depending on the number of courses taken, one may exceed the plan in three years or complete the program or "on-time" within six years.

While most countries refer to master's and doctoral studies as postgraduate programs, in the USA this term is almost never used. After receiving bachelor’s, students can continue their education in graduate (grad) schools that are part of the universities. The term postgraduate in America is usually understood as someone who has completed a graduate program and plans to pursue an academic career.
Thus, American universities typically set up both colleges and schools. The latter grant master's degrees (MA, MS, MSW, MFA), professional degrees (MBA, JD, MD) and doctorates (PhD).There are also professional schools that offer advanced training for a particular profession. These include, for example, medical, law and business schools.
Master's degree in the United States is the first step of higher education within graduate schools. Unlike in the UK, there are no purely research master's programs in America. Instead, they are much more structured and involve taught courses and continuous assessment. For two years, students complete various tasks, take exams, write coursework essays, receive grades, later converted into GPA.
Master’s degrees in America are divided into two types:
The common requirements are the following:
To apply, you will need a number of documents:
Interviews (in person or over Skype) can be introduced as an additional selection stage for successful applications.

Doctorate is the final stage of higher education in the US. Doctoral degrees, like Master’s, are not based purely on research. Full-time programs last from 4 to 6 years on average and include:
Most graduate schools grant traditional PhDs. Some offer professional DBA, EdD, JD, MD. American doctoral degrees in medicine and jurisprudence are quite specific and, as a rule, are not recognized in other countries. International students do not usually consider these degrees unless they plan to live and work in the United States after graduation.
A master's degree is not always a basic requirement for a PhD in the US. The reason is that master's and doctoral programs are often merged into one graduate program. In some cases, students are awarded a Master's degree at the end of the coursework stage. For those who already have one, universities can transfer credits and shorten the duration of PhD studies. A Grade Point Average (or its equivalent) from the previous levels of education may be also taken into account: a GPA of 3.0 or its equivalent is considered a good result.
The main requirements of the university may include:
The university may request the following documents:
In some cases, a student will need a research proposal or its simplified version — a research statement. As a rule, students decide on their dissertation topic within the program, so at this stage, they are only supposed to indicate their scientific interests and possible research areas.
To begin with, some assistantships can be obtained by graduate students. Employees in the following positions receive either a salary or a fee waiver:
A traditional academic career involves the following steps after earning a doctorate:
There are also a number of temporary academic positions:
Although America is considered one of the most expensive countries to study, most students here receive financial aid in the form of scholarships or grants. These are usually awarded to those who do not have sufficient funds to pay for training (need-based) and / or have significant academic achievements and talents (merit-based).
The most generous offers can be often found in the most prestigious universities. For example, the 5 largest US universities accept students (local and foreign) on a need-blind basis. This means that any promising candidate who has been selected at Harvard, Amherst, Princeton or MIT, can get some funding, regardless of the financial situation.

International students may be eligible for the following US visa types:
To obtain a visa (M or F), a student must, first of all, be accepted by one of the US approved educational institutions — SEVP-certified schools. It should be noted that the process can be delayed for various reasons, so it is better to submit documents at least six months before the course starts. As soon as the student is enrolled in SEVIS system and has paid the SEVIS I-901 fee (200 USD), the university issues Form I-20 which is necessary to apply and schedule an interview.
List of documents for a student visa to the United States:
Additionally, a student may need:
Please, check the complete list of requirements on the website of a particular US Embassy or Consulate[9].
A student visa can be issued up to 120 days before the date indicated on the Form I-20. It should be noted that obtaining a visa does not guarantee entry into the United States. Final permission is given by the customs official at the US port-o-entry (usually an airport) after showing a passport, visa and I-20 form.
Upon completion of the educational program, students with F or M visas must depart the country within 60 and 30 days (grace period), respectively. A student can apply for a student visa extension only at the US Consulate or Embassy in a home country.
During their studies in the USA, F-1 students are allowed to work on the university campus, having previously obtained permission from a designated school official (DSO). Typically, foreigners can work up to 20 hours a week (part-time) during the academic semester and up to 40 hours (full-time) during holidays.
Work off-campus is available to F-1 visa holders only in special circumstances[10].
Some off-campus employment opportunities are still possible after the first year of study:
A prerequisite for any work is to obtain a Social Security number (SSN).
Graduate students can also take an assistantship position so that to receive a salary or a fee waiver while working at the university. But it should be noted that the recruitment process is highly competitive, and not everyone succeeds. Financial aid covers from 70% to 100% of tuition and accommodation costs. Depending on the university, the following positions may be available: Graduate teaching assistant, Research assistant, Administrative assistant, Research fellow.

The most common ways to stay in the United States after completing your studies are to obtain an Employment Authorization Document (EAD) or switch to a temporary work visa H-1B. A student can apply for both in turn.
EAD is a work permit which allows one to work in the US for 1 year after graduation within post-completion OPT. First of all, a student consults the designated school official (DSO) about the OPT position. They update the I-20 Form in SEVIS. After that, a student is to submit the other documents with USCIS. One can start applying for EAD 3 months before and 2 months after completing the program). The fee is 410 USD. At the same time, a student is only eligible if he:
The H-1B visa allows students to work in the USA in specialty occupations for 3 years with the right to extend it for up to 6 years. To obtain H-1B a graduate student must find a certified employer who will file the Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker, Form I-129 with the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
The application deadline is 6 months before F-1 visa expires or OPT comes to an end. The fee is 460 USD. The only requirement for a candidate is a bachelor's degree from an accredited American university or its international equivalent. Having OPT experience can increase one’s chances of getting an H-1B.
While being an H-1B temporary worker, there is an opportunity to get a US green card (American permanent resident card), and then, after 3-5 years of continuous residence in the country, apply for US citizenship through naturalization.
Education in the USA is closely connected to the economic situation in the country: educational institutions are supposed to meet the labor market demands. In addition, US universities and colleges are motivated to ensure that their graduates land jobs as soon as possible since employment statistics are an important indicator of their efficiency.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the unemployment rate among the population aged 25 and older is extremely low: 3.5% for those who hold an associate degree and 2.1% for those with a bachelor's degree and above[11]. Moreover, according to OECD statistics, the foreign-born unemployment rate does not exceed 3.5%, which is several times lower than in the EU — 15.2%[4]. This proves that foreigners who want to start a career in the United States have almost the same opportunities as the local population.
The most popular industries in the US today are aerospace, consumer goods, electronics, food processing, healthcare, and motor vehicles. Also, the media sector and IT entrepreneurship continue to actively develop. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the following list of the most sought-after professions of the coming years: healthcare professionals, cooks, accountants, software developers, retail workers, customer service representatives, office clerks, market research analysts, and marketing specialists[12].
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got