
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Singapore is an ideal place to acquire knowledge in the fields of science, business, finance, and management. The prestige of the Singaporean diploma will allow graduates to choose a job not only in their native country, but also around the world. Find out more reasons to study in Singapore (or not) in our article
Free consultation





Thanks to the economic breakthroughs of the past 30 years, Singapore has been able to combine the cultural values of the East and the high standard of living of the West. Education is the main priority in the development of the country. This is confirmed by the top places of universities in international rankings and the rapid development of research and innovation. Today, Singapore has become one of the most important economic centers in Asia and the world. The state spares no funding for universities and students, because it believes that the country's wealth lies in people. For a foreign student, Singapore is an ideal place to acquire knowledge in the fields of science, business, finance, and management. The prestige of the Singaporean diploma will allow graduates to choose a job not only in their native country, but also around the world.
| Type of education | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language level | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer camp | 7+ | 1-2 weeks. | 577 USD/wk | 1,062 USD/wk | A1 | - |
| Language Schools | 9+ | 1-12 weeks. | 190 USD/wk | 1,517 USD/month | A1 | - |
| Language courses at the university | 16+ | 3 months - 12 months | 759 USD/month | 2,276 USD/wk | B1 | - |
| Secondary education | 12+ | 4-5 years | 1,062 USD/month | 22,759 USD/year | B1 | - |
| Foundation | 16+ | 1 academic. year | 3,035 USD/year | 7,586 USD/year | B1 | IELTS 5.5 / TOEFL 66 |
| College | 17+ | 1-3 years | 8,193 USD/year | 11,380 USD/year | B2 | IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 79 |
| Bachelor's | 17+ | 3-4 years | 9,104 USD/year | 45,518 USD/year | B2 | IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 85 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-2 years | 22,759 USD/year | 68,278 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 / TOEFL 85 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 30,346 USD/year | 60,691 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 / TOEFL 85 |
| Doctoral | 20+ | 2-5 years | 10,621 USD/year | 27,311 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 / TOEFL 85 |
| Expenses | Average cost/month |
|---|---|
| Rental housing | 1,138 USD |
| Utility expenses | 76 USD |
| Registration fees | 23 USD |
| Visa | 30 USD |
| Health insurance | 531 USD/year |
| Meals | 607 USD |
| Public transport | 152 USD |
All prices and requirements must be specified on the websites of universities.
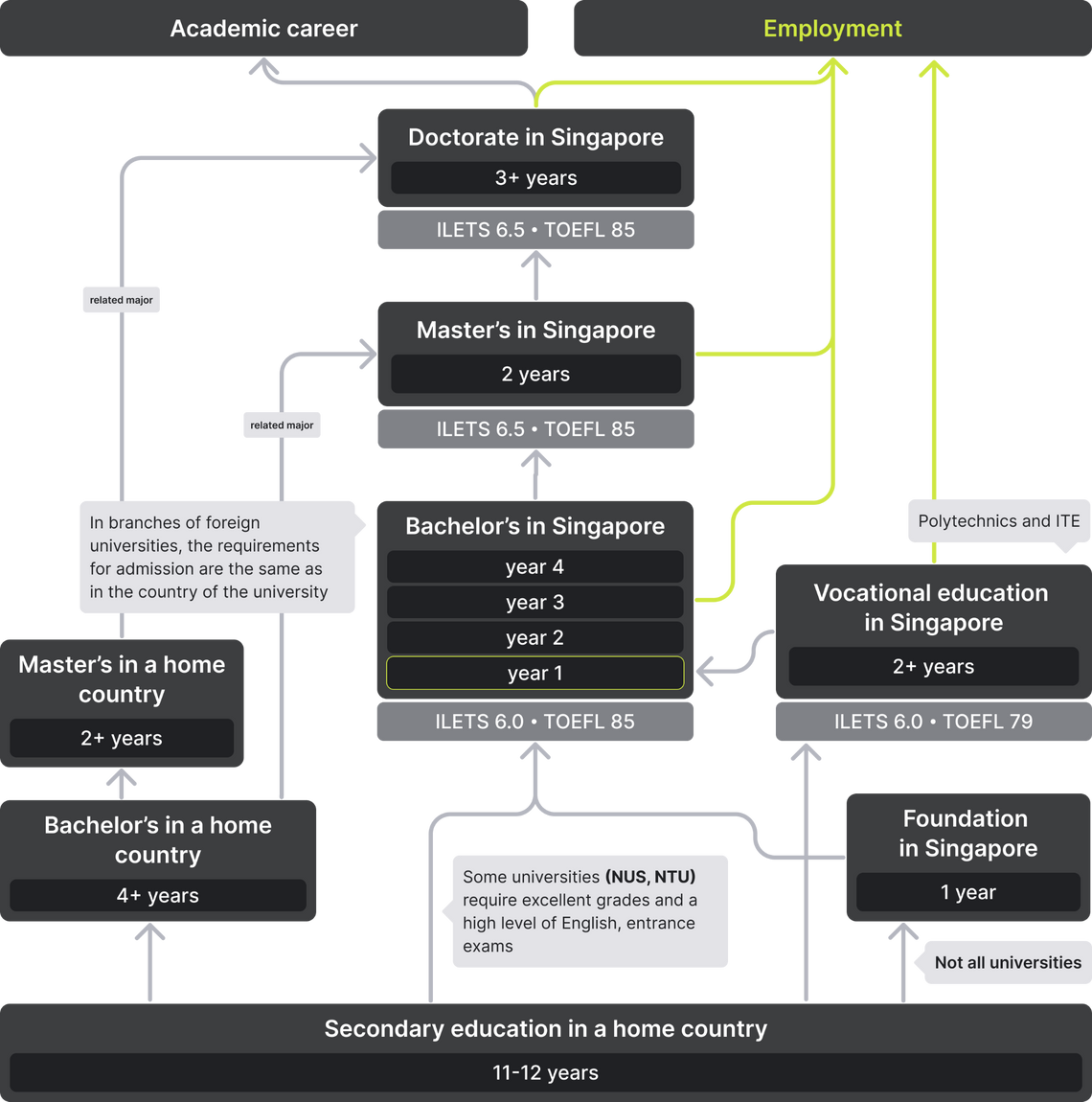

Admission of students to universities in Singapore is based on academic performance, exam results, achievements and the statement of purpose. It’s not easy to enter Singapore’s top universities. Motivation and exam results must be very high in order to pass fierce competition. Since the training is conducted in English, foreign applicants must provide the language certificate and translate all documents into English. Before applying, it is recommended to check the sites of universities, as each university and specialty has its own requirements.
Most programs also request the results of international exams (GRE/GMAT/SAT) and conduct interviews. For international students, application happens online: it starts in October and ends in March. The exact dates should be specified on the websites of the universities. You should carefully monitor the deadlines, as there are programs that start early, for example, in July.
Due to the multidisciplinary secondary education, students graduate with different qualifications, therefore, the rules for admission for each individual case are indicated on the websites of universities and colleges. In order not to get confused, when looking for a program, a foreign student should choose the option Direct Admissions Exercise (DAE).
For entering Singapore universities it is enough to translate a certificate or a diploma and notarize it.
In turn, a diploma issued in Singapore can be used in your country only after its legalization by the Singapore authorities and the consular department of your country's embassy in Singapore[8].
Those who want to legalize documents submit an application online and are set with an appointment. You can legalize a diploma through a third party. Laminated documents are not accepted. This costs 8 USD (online payment only). Details about the legalization of documents in Singapore can be found here.

In the best universities, such as NUS, NTU, SMU, there are no Foundation programs. Therefore, students who do not meet the requirements, can enter these universities only after colleges, polytechnics, ITE, A-Level programs. A-Level is taught in specialized schools, elementary colleges and the centralized institute[-].
Some other universities offer Foundation programs. It should be noted that such programs, for example, in MDIS, allow students to continue education only at the same university, while courses taken at colleges are recognized by some universities and exempt students from examinations and the study of certain subjects.
Pre-university courses will help you to tighten the English language and specialized subjects. They can be found in some colleges and universities. The curriculum includes:
There are also short module courses. They can be taken individually or together.
Application to preparatory courses happens online on the websites of universities and colleges. The requirements depend on the nationality of the applicant. Usually this is a school graduation certificate and proof of language proficiency (IELTS/TOEFL).
In addition, there are training programs for postgraduate education, for example, pre-MBA, pre-Law or pre-Medicine and others. Requirements for applicants and all the details can be found on the websites of universities.
College — Vocational education in Singapore
Today, vocational education is a key link in the further development of the country. Over the past 20 years, the state has spent a lot of effort and resources on its improvement and promotion. For a long time, vocational education was not considered prestigious, moreover, the public agreed that only stupid, losers and those who simply have no other choice go to such educational institutions. A large-scale rebranding campaign was launched, and competent professionals were attracted to the teaching staff. Already in 1995, the initiative bore fruit, doubling the number of students in applied specialties, and now it already attracts 65% of the total number of applicants. Schools have acquired impressive modern campuses and offer more than 150 different types of programs[9].
Foreign students need a secondary education diploma to enroll in college but diploma requirements vary. For example, NAFA requires at least 10 years of school, in Singapore Polytechnic diploma should be equivalent to the examination GCE level "O" (complete secondary education — minimum 11grades), and in Republic Polytechnic each case is considered individually if your country is not listed on the website. Some colleges also need to take entrance exams in English and specialized subjects.
In order to enter bachelor’s programs in Singapore, students must complete 12 years of school. Some universities, such as NUS, accept students with 11 years of education, but these students are subjected to compulsory SAT examinations and have to have an excellent secondary education certificate. In many other universities, it is necessary to contact the admission committee and specify whether your prior education is sufficient. Universities will gladly answer your questions when it comes to the application process.
If the diploma is not accepted, the foreign applicant has a few options:
Basic requirements for admission are as follows: an English language certificate, ACT with the writing module or SAT with specialized SAT Subject Tests, to which each university presents its own criteria. For humanitarian specialties, the requirements for language proficiencyб test writing sections and critical reading are usually higher. Whereas for technical specialties it is expected to have higher scores in math. Some specialties also include written exams and interviews. In addition to the minimum requirements, the admission committee puts great emphasis to academic and extracurricular achievements.
The submission of documents is done through the website of a selected university. There you can find all the deadlines and requirements. Universities recommend that students check the information often, as it is frequently updated. Depending on the chosen specialization, training lasts 3-4 years, except for medical specialties.
Universities of Singapore do not set minimum scores for standardized tests. The average score for ACT is 29 (Writing — from 2 to 12); for SAT it is 600 in writing and reading, 650 in mathematics; SAT Subject tests — 650.

Master's programs in Singapore last for 1-2 years, and MBA programs — 1-1.5 years. However the duration may vary depending on the university. For example, the National University of Singapore is quite flexible: there is no set time frame and only the minimum number of credits for each semester is established. And at Nanyang University of Technology, a master's program in engineering lasts for a year and consists of 30 credits.
Master’s programs can be full-time and part-time. Study includes lectures, seminars, group and individual work on the final project or dissertation. Work on the dissertation can take the whole duration of study or the last semester. There are also master's programs that do not require a dissertation or a final project: it is enough to attend classes and pass exams. Upon completion of training, the average GPA is calculated — a maximum of 5 and a minimum threshold of 2.5 needed to pass.
Most educational institutions accept students twice a year: in January and in August. An applicant needs to carefully study the requirements of his program, which vary depending on a university and specialty. Most often, the commission admits applicants on the basis of a bachelor’s diploma, letters of recommendation, results exams (GRE/GMAT) and work experience. The minimum GPA is 3.0. Since English is the language of instruction, applicants must provide TOEFL/IELTS certificates. Compliance with the minimum requirements does not guarantee admission, since Singapore universities have high competition.
Average scores for GRE are 320 (verbal & quantitative) and 3.5 (analytical), GMAT — 650+.
Doctoral studies at many universities in Singapore are divided into two types:
At some universities in Singapore Joint PhD programs are offered. They are based on the cooperation of Singaporean and foreign universities (Europe, Israel, India). Upon successful completion, students receive a doctorate with a seal of both partner universities. For example, NTU offers programs with full funding for medical and technical fields.
Many programs conduct PhD Qualifying Examination during their studies to confirm the student’s readiness to work on a dissertation. Its delivery takes place in two stages: the oral defense of the project and topics in the form of a presentation and the oral defense of an already written dissertation in front of the academic commission. After fulfilling all the requirements and, possibly, correcting the scientific work, the university assigns the PhD degree to the student.
The duration of doctoral studies is from two to five years. Like master’s programs, PhD does not have uniform requirements for admission, each university has its own standards.
Almost all programs are available full-time or part-time. Documents are submitted by means of the websites of universities. Some faculties require physical copies that can be mailed or delivered in person. The full list of documents must be checked on the websites of the departments and programs you are interested in. Selected candidates, especially those who applied for a research scholarship, often have to go through the interview process (if possible in the applicant’s country). The admission periods are: March/April for admission in August, and August/September for admission in January.
Average scores for GRE are 320 (verbal & quantitative) and 3.5 (analytical), GMAT — 650+.
The academic community in Singapore is rapidly developing and expanding. Since the universities of Singapore have a good research base, you can find many opportunities and vacancies for academic positions. The main recruiters are National University of Singapore and Nanyang University of Technology, their affiliated research institutes and other independent research centers. The number of vacancies has increased in recent years thanks to new government research initiatives, especially in the field of biomedical sciences.
Each university offers its own positions (Lecturer / Senior Lecturer / Assistant Professor / Associate Professor / Professor), and selection of candidates takes place directly at the university. Applications are accepted online. Interviews are conducted with selected candidates.
Working conditions depend on the laboratory, the supervisor and the nature of the study. Typically, employees are assigned specific projects with one or more assistants. Work is offered on a full and part-time basis or one can be hired as a temporary employee. All positions are based on contracts, so employees do not have guarantees for direct promotions.
The salary of a researcher depends on academic education, the level and relevance of his experience. A random sample by Next Wave in Singapore shows that the annual salary ranges from 39,601 USD to 57,201 USD[10].

Tuition Grants. The Ministry of Education of Singapore offers grants to students. Applications are open to all nationalities. The main condition is that the student must be enrolled in a full-time bachelor’s or diploma program at a university or polytechnic institution. Singaporeans automatically receive a grant on the basis of citizenship, while foreign students and residents apply for funding upon admission to the university.
Since applications for a grant and a university are accepted simultaneously, the deadlines for submitting documents are the same. After approval by the state, the student must register in the MOE TGonline system and sign the contract. This obliges the grant recipient to work in the country for 3 years after graduation. The amount of financial assistance depends on the university, specialty and citizenship. The grant only partially covers the cost of training and accommodations. For example, in NUS, a business program without a grant costs 24,466 USD, and with a grant — 15,552 USD.
A list of universities and all application details can be found here.
Service obligation. In the Nanyang Technological University and National University of Singapore there is financial support for foreign master’s students and doctoral students. Here you can find information on programs that do not fall under the NUS grant. The list of subsidized programs at NTU for 2019-2020. Make sure to check the websites of universities, as the information is updated every year.
Such a grant obliges graduates to work in a Singaporean organization for 3 years after the completion of the program. Applications are submitted online through the MOE TGonline system: the submission process starts in January/February and lasts for several weeks. The detailed information can be found on the website of the Ministry.
Aid from universities. Universities offer financial assistance to international students. You can view the list of available opportunities on the official website of your chosen university. Such scholarships may partially cover tuition. Universities select scholarship holders on the basis of a transcript, knowledge of the language, motivation, achievements and personal qualities of the applicant.
In general, getting scholarships is rather difficult due to high competition and strict requirements. Meeting the minimum criteria does not guarantee the reception of a grant or scholarship. A large number of various grants and scholarships are also indicated on university sites, but they are mainly intended for residents of Singapore and Asian countries.
A*STAR. Agency for Science, Technology and Research — A*STAR — provides scholarships and grants that allow novice scientists to develop in science and prepare for their upcoming careers. Financial assistance is offered at all levels of higher education in the best universities and laboratories in the country and abroad. The conditions are the adoption of Singapore citizenship for foreigners and compulsory work for Singaporean companies for two years after graduation. More information about grants and the agency can be found on the website.
Singapore international graduate award (SINGA). A*STAR Agency, together with Nanyang University of Technology (NTU), National University of Singapore (NUS), and Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD), offers grants to PhD candidates in the field of biomedical sciences, physics, and engineering. The recipients then study in English at one of the universities or at the A*STAR Research Institute. To receive funding, an applicant needs to have interest in research and excellent academic results; good written and spoken English skills; positive reports from academic reviewers.
The grant covers the full cost of tuition for up to 4 years, gives a monthly scholarship of 1,517 USD, a one-time payment of 1,138 USD for an airplane ticket and 759 USD for accommodation. To apply for SINGA, you must create a research project and prepare a package of documents: diplomas and transcripts of a master’s/bachelor’s, 2 letters of recommendation. Optional GRE/IELTS/TOEFL/SAT I&II/GATE results. However, it is worth noting that universities may request exams as a prerequisite for admission. Applications are submitted exclusively online and there are no extra fees. Accepting documents for the winter semester ends in June. To participate in the program, you do not need to take Singaporean citizenship or work in a local company. Here you can find more detailed information.
Scholarships of external organizations. Some major local and international organizations offer scholarships to talented international students. For example, Association of commonwealth Universities, Evolve Warrior Scholarship, Singapore Airlines Open Overseas Scholarship, Her Flowers Scholarship. Lists of other organizations can be found on university websites.
In 99% of cases, foreigners are given visas within four weeks, but there are a number of subtleties that are described in the article about applying for a student visa to Singapore.
The cost of a visa for many countries is 30 USD. The deadline for reception is about 4 weeks.

Students have the right to work without additional documents in Singapore if:
Also, the work must meet one of the following requirements:
Students may work during the holidays, subjected to the requirements specified above.
If a foreign student earns at least 2,959 USD/month, he/she must apply for an employment pass[11]. This rarely happens since the average hourly rate for part-time work in Singapore is 5 USD[12].
If a student graduates from a state-approved university and is waiting for exam or graduation results, he has the right to work until his student visa expires. After graduating, you must obtain a work permit to stay in Singapore. It is a responsibility of an employer to apply on your behalf.
Moreover, if a student studied under the government program Tuition Grant, then its condition is a mandatory 3 years of work in Singapore. In this case, the student must also change his legal status after graduation.
Most universities in Singapore offer students various services for finding work: career fairs, career counseling offices and consultant services, online job search portals. For example, NUS has its own mobile app that automatically recognizes your academic grades and creates a list of your skills. Based on the list, the app selects open positions in the labor market suitable for you[13]. Some universities place part-time vacancies in departments of the universities themselves, so that students can gain experience in their specialty during their studies.
To work, an international student must obtain permission. At the moment of writing, the following types are available:
| Permission | Qualification | Min. salary | Duration | Renewal | Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employment Pass | High | 2,959 USD | 2 years | Yes (up to 3 years) | Degree, managerial, executive, specialized work |
| S Pass | Average | 1,821 USD | 2 years | Yes | Degree/diploma, work experience |
| EntrePass | Entrepreneur | Innovative criteria[14] | 1 year | Yes (up to 2 years) | An established business no older than 6 months, or an intent to start a business. |
More information can be found on the Singapore Department of Labor website in the section of work permits.
People under these categories can apply for a Permanent Resident Permit:
Citizenship can be obtained by:
The cost of both types of applications is 76 USD. Details can be found on the website of ICA.
Keep in mind that dual citizenship is not allowed in the country, so you must give up your original passport in order to obtain a Singaporean one.

Singapore is a favorable country for expats. As of December 2019, approximately 1.5 million foreign workers are registered here, which makes up almost a quarter of the population[15]. Singapore's strong and rapidly growing economy needs a workforce. Therefore, the state attracts professionals from abroad, finances education and offers favorable working conditions for foreigners[16].
The main economic sectors are manufacturing (electronics, chemicals, biomedical sciences and transport engineering), financial, business and IT sectors[17]. Singapore is well located geographically: the waters surrounding the country and many seaports provide the development of trade and logistics in the country. The unemployment rate is very low — 2.4% for 2019[18].
The main tourists in the country are Chinese, Indonesians, Indians, Malays and Australians[19]. And the main trading partners are the USA, Japan, China and Hong Kong[20]. The graduate will need to use a good diploma, qualifications, experience and personal qualities to impress the employer.
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got