
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Article score: 5 out of 5 (1 review)
The complete information about education in Hungary: universities, academic programs, tuition fees, admission requirements.
Free consultation
Secondary education system of Hungary consists of several steps:
| The level of education | Title in Hungarian | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Preschool | óvoda | 3-6 years |
| Primary school | általános iskola | 6-14 years |
| Secondary school | Gimnázium / szakközépiskola | 14-18 years |
In Hungary secondary education includes two types of schools:
However, the system is flexible, as graduates of vocational schools can choose to receive higher education.
In Hungary, the predominant language of instruction is Hungarian. However, in southern Hungary (a region of Croatian and Serbian ethnic groups) and in the northeastern region, bilingual education is widespread. Learning English and German usually begins at the age of ten, but in schools with in-depth linguistic learning, this happens already in the third grade or at the age of eight. International students can also study in private and international schools. In the latter, the main language of instruction is English and the number of students in classes is less.
Higher education in Hungary has a rich history. The first university in the country was founded in 1367. Today in Hungary there are 28 state universities, 11 private and 26 religious institutes. There are also branches of leading English and American universities that offer grants and discounts to students. The academic legacy, reputation, a large selection of programs and directions, affordable living costs, and financial support attract foreign students to study in Hungary.
| Type of studies | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language proficiency | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer camp | 6+ | 1-2 weeks. | 531 USD/week | 678 USD/week | A1 | - |
| Language schools | 6+ | 1-52 weeks | 226 USD/week | 452 USD/week | - | - |
| Language courses at the university | 2 weeks - 1 semester | 68 USD/semester | 192 USD/week | - | - | |
| Secondary education | 6+ | 1-12 years | Free | 6,780 USD | B1 | School English Test B1 |
| Foundation | 16+ | 1-2 semesters. | 3,842 USD/year | 5,650 USD/year | B1 | IELTS 5.5 |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 3 years | 3,390 USD/year | 8,475 USD/year | B1 | IELTS 5.5 |
| Master's | 20+ | 2 years | 3,390 USD/year | 10,170 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1 year | 5,650 USD/year | 16,950 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 |
| Doctoral | 20+ | 3+ years | 2,260 USD/year | 14,690 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 |
| Expenses | Average cost |
|---|---|
| Exams | 226 USD |
| Registration fees | 113 USD |
| Visa | 68 USD |
| Accommodations | 169 USD/month |
| Insurance | 271 USD/year |
| Meals | 136 USD/month |
| Public transport | 16 USD/month |
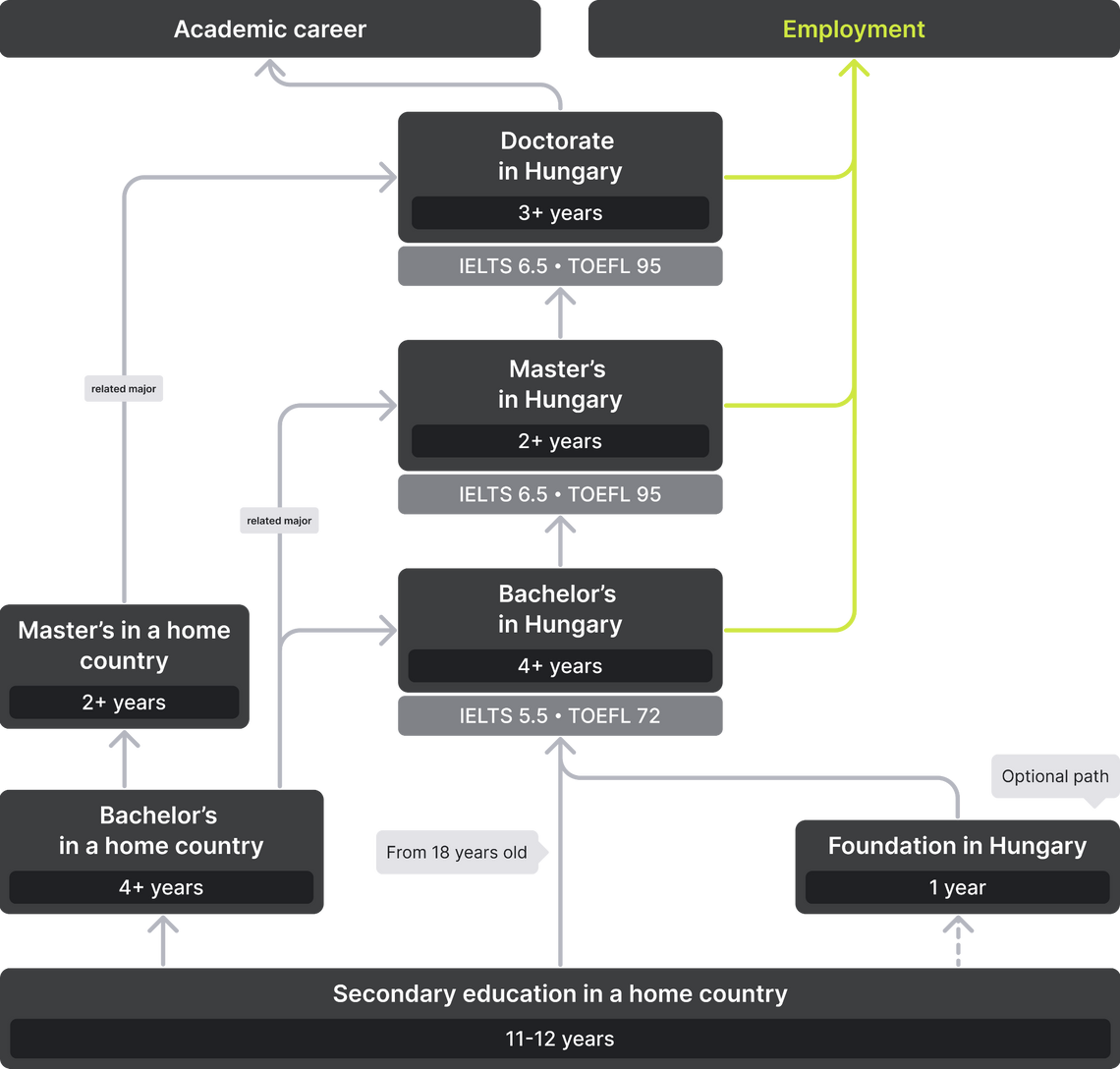

Foreign students can enter a Hungarian university after 11 years of school at the age of 18, but there is one condition: you must know the language. Programs are conducted in Hungarian, English, French, German. Most often, international applicants choose to study in English, since universities have more specialties in this language than others. And the Hungarian language is rare and complex and chosen mostly by the local students.
List of documents for admission to a Hungarian university:
All documents must be translated into English or Hungarian and notarized.
After applying, the student will be appointed an interview or exam. Themes and assignments depend on the program. Tests are conducted locally, at partner institutes, or online. There are no unified tests in Hungary, each university has its own examination procedure.
Admission to Hungarian universities is carried out twice a year — in January and September. To start studies in the fall, documents must be submitted in January, and in winter — in December. Foreign citizens must pay entrance fees and pay for taking exams.
The legalization of educational documents is the responsibility of the institution in which you want to study. But it is worth considering that a foreign diploma recognized by a university upon admission does not give the right to work in a specialty in Hungary[3]. To be able to find a job, you must contact the Hungarian Center for Equivalence and Information (MEIK). The center is responsible for the recognition of professional qualifications and the localization of academic degrees. The cost of recognizing a qualification level is 42 USD, recognition of qualification is 125 USD, recognition of the qualification level and qualification itself is 166 USD. You can submit documents on the spot or via mail. Recognition of diplomas of specialists in medicine and pharmaceuticals is done by the National Healthcare Service Center.

Universities and private educational institutions organize one-year preparatory courses for foreigners. During the courses, students learn the language and prepare for their upcoming studies — they study the introductory subjects of their future specialty. The duration is 1-2 semesters.
Types of preparatory courses:
For future engineers, preparatory courses are held at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics (BME) and at the College of Dunaújváros. Business courses are held here as well as at the University of Pécs, Szolnok University College, and Tomori Pál College. Science and music training is offered at the University of Debrecen. Preparation for medical programs is conducted at Debrecen and Pécs, at the University of Szeged and McDaniel College in Budapest.
At the end of the courses, a final exam is held. Based on its results, the College of Dunaújváros accepts students for undergraduate studies. But in many other universities, students still have to take entrance exams.
You can browse courses here.
Higher education in Hungary includes higher education VET programs (felsöoktatási szakképzés, FSZ). They provide students with a higher level of professional qualifications than in technical schools, but they are not higher education. To enter them, you need a secondary education diploma and, depending on the specialty, certain professional and medical indicators.
The study is full-time or part-time, paid or funded by the state. Classes should be held at colleges and universities. However, in reality, half of the time they are held in secondary vocational schools (szakközépiskola) under the supervision of a partner university. Programs last 4-5 semesters and consist of 60 credits[4]. The curriculum includes basic education and at least 25% of compulsory professional practice. Thanks to the credit system, students can transfer from FSZ to higher education in the same field. In this case, 30-60 credits of the program reduce bachelor’s studies by 1-2 semesters.
Despite the fact that the number of participants in FSZ programs has been growing since its inception, the labor market does not particularly favor them, if at all is informed about such programs. Graduates with higher education and degrees have a greater chance of getting a good job with a higher salary[5].

Most bachelor’s programs last for 3 years (180 credits ECTS), some last 3.5 years (180 + 30 ECTS) or 4 years (240 ECTS). The student acceptance rate at many universities in Hungary is quite high (Eszterházy Károly University of Applied Sciences has 90%, Adventist Theological College — 87%, Kodolányi János University of Applied Sciences — 80%, University of Pécs — 60%, Corvinus University of Budapest — 55%[6]).
General documents for submission to undergraduate:
Documents that are not in English or Hungarian must be translated and notarized. Some programs also conduct entrance exams. Business programs can take SAT results instead of entrance exams in mathematical, creative specialties require a portfolio and conduct interviews, and medical programs will ask for written and oral examinations.
The state sets requirements for the learning process (subjects, hours, recommendations for dissertations, etc.), but universities are given freedom in the actual construction of the process. Teachers can independently choose the teaching methodology, study guides, and books since there are no standardized approaches. However, in reality, it turns out that the training is based on traditional and established methods, and the list of teaching materials is reviewed during the accreditation process.
Most bachelor’s programs provide compulsory internships.
Master's degree is the second level of qualification after a bachelor's or college degree.
To accept students, universities evaluate candidates according to a 100-point system. Points are compiled on the basis of grades, language skills, and other requirements of each university. Some conduct oral and written exams, practical exams (for students of arts, sports), and interviews. Additional points are given for foreign languages, high GPA, work experience, etc.
Documents can be submitted online via the FEVLI system (in Hungarian) or directly to the university by e-mail or on the website.
Documents:
The list of documents varies by program and university.
Master's programs last 1-2 years. For admission for a 2-year program, an applicant must have a three-year bachelor's degree, and for a 1-year master's degree, a four-year bachelor's degree is required. Teaching in master’s programs is based on lectures, seminars, study guides, and practical exercises. Students write term papers and dissertations.

The academic year in Hungary begins in September/October. Application deadlines are indicated on the websites of universities. To enter a doctoral program you need:
Doctoral programs present general and subject-oriented training. The learning process includes compulsory and optional courses, and credits are obtained through research. Doctoral students study on an individual schedule, in accordance with the work plans made by their supervisors. Thus, the progress of doctoral students is closely monitored.
Doctoral candidates do not only conduct personal research but also participate in cooperative research projects. This way they contribute to the reputation of their institutions and to the academic community. Doctoral students also teach which develops them professionally and personally.
Academic vacancies can be found on the websites of the universities themselves.
The selection for academic positions is held through an open competition, sometimes — invitation. In Hungary, there are no perpetual contracts between universities and professors. Promotion depends on teaching experience, and especially research. The working time of professors is 40 hours a week, of which at least 25% of the time the teacher is engaged in research work[7].
Habilitation is the second major post-doctoral study in the academician’s career. It is required to obtain a professorship. University professors are appointed by the President of the Republic of Hungary, college professors are appointed by the Prime Minister.
Foreign students can study in Hungary for free under the program Stipendium Hungaricum and bilateral state scholarships.
Stipendium Hungaricum is based on bilateral cooperation between the Ministry of Education of Hungary and other states.
Documents for submission:
Additionally, for doctoral candidates:
All documents must be translated into English or Hungarian.
The program fully covers the cost of training, dormitory, and medical insurance, and also provides a monthly scholarship. The application deadline for the program in 2020-2021 is January 15, 2020. Here you can submit documents online, clarify deadlines, and find out more information.
Bilateral state scholarships are based on educational and scientific cooperation between states. Students study for free and receive a scholarship. Accommodation and other expenses may also be covered depending on the type of scholarship.
Types of scholarships:
Documents for applying for a scholarship:
If the documents are not in English or Hungarian, they must be translated and, if they are not printed, notarized. You can submit documents to the national office or leave an individual application in the online system Tempus Public Foundation.
Deadlines for the academic year 2020-2021 (full bachelor’s, master’s, doctoral degrees) — March 24, 2020. Here you can submit documents, specify the deadlines, and contact the scholarship representative in your country.
However the list of available scholarships is not limited to the abovementioned. Check the government’s and universities’ websites for more opportunities.

Nationals of EEA countries have the right of free movement and residence in Hungary while studying at the university. They are only required to register at the regional office of the Directorate General for Aliens Policing within 15 days after arrival.
Citizens of other countries must personally apply for a student long-stay visa "D" to the Hungarian Consulate in their home country prior to the departure. All applicants over the age of 6 have to submit fingerprints. The consular fee is 68 USD. The consideration takes up to 15 days (but no longer than 60 days).
The required documents are as follows:
You can download the application form on the website of the Hungarian Embassy branch of your country. Within 30 days after arriving in Hungary, the student must contact the regional migration office to obtain a residence permit card.
A registration card is enough for citizens of EEA states to work in Hungary during studies without any limitations.
A residence permit of non-EEA nationals gives a student the right to work during full-time and part-time studies up to 24 hours a week. During holidays — 90 days (or 66 working days).
Students will need knowledge of the Hungarian language at least at the elementary level: in everyday life, English is not widely spoken. The minimum wage in Hungary for 2020, including students, is 550 USD per month[8].

The most common type of immigration to the country is the work migration. Almost all universities have employment offices. The consultants take into account the demands of the labor market in Hungary and Eastern Europe and have connections in companies. Universities also regularly hold job fairs and events where students meet with employers. Prospects for working in local companies may be limited due to their knowledge of the language, but in Hungary, there are branches of international companies, where it is possible to get employed with the knowledge of English.
Also, one of the opportunities to find work for a student after graduation is dual programs at the university. Since September 2015, Hungarian education has introduced dual programs in engineering, IT, agriculture, science, and business[9]. They imply cooperation between universities and companies. Students combine work in these companies with studies and after graduation, they can get a permanent position there. As of February 2020, 37 bachelor’s programs are collaborating with 24 institutions and 417 companies. 1653 students are enrolled in these dual programs (58% in technical fields). Also, 22 master's programs are involved in cooperation. Under such conditions, 148 master’s students are studying[9].
To legally stay in the country after studies, EEA nationals do not have to obtain any additional documents. All the others can apply for a residence permit in order to find work. To do this, you need to confirm that you are indeed looking for a job. As evidence, you can provide a certificate of registration with a state employment agency or a statement from a commercial organization that employed you for at least three months.
Documents must be submitted in person and 15 days before the expiration of the current study permit. A residence permit for the purpose of seeking employment is issued for 9 months and is not extended. Application forms and additional information about documents can be found here.
If you already have a job, you can apply for a work visa.
Here you can download the application and find out detailed information.
The unemployment rate in the country is 3.7%[10]. This is a low percentage, but the difficulty is that in Hungary, according to the labor law, companies hire foreigners only if not a single Hungarian citizen is suitable for the position. In addition, hiring a foreigner involves a lot of paperwork, so the candidate should try to impress the employer.
One of the main sectors of the country is heavy industry (mining, metallurgy, mechanical engineering, and steel production)[11]. Hungary also actively produces cars, develops pharmaceuticals and medicine, agriculture and tourism.
Thanks to the Bologna credit system, diplomas of Hungarian higher education institutions are recognized all over the world: countries of the European Union and the CIS, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Great Britain, and the USA (including medical diplomas). The exception is Greece.
Here you can see the employment statistics of individual universities.




60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got