
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Article score: 5 out of 5 (1 review)
In Estonian universities, there are many programs in English, and most of all foreign students are from Finland and Russia. More about education in Estonia in the article.
Free consultation
| Type of education | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Language requirements | Exams |
| Summer Camp | 7+ | 1-12 weeks | 130 USD/week | 226 USD/week | Beginner | - |
| Language schools | 7+ | from 1 month | Free | 1,356 USD/course | Beginner | - |
| Secondary education | 6+ | 1-12 years | Free | 5,650 USD/year | Intermediate (B1) | School Testing |
| College | 15+ | 1-4 years | Free | 2,825 USD/year | Intermediate (B1) | IELTS 5.5 / TOEFL IBT 72 / EKT B1 |
| Bachelor's | 18 | 3-4 years | Free | 4,520 USD/year | Intermediate (B1) | IELTS 5.5 / TOEFL IBT 72 / EKT B1 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-2 years | Free | 4,520 USD/year | Intermediate (B1) | IELTS 5.5 / TOEFL IBT 72 / EKT B1 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 5,650 USD/year | 7,345 USD/year | Upper-Intermediate (B2) | IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL IBT 75 / EKT B1 |
| Doctoral | 20+ | 4 years | Free | Free | Upper-Intermediate (B2) | IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL IBT 75 / EKT B1 |
The table contains approximate prices. More accurate information can be found on the websites of educational institutions.
| Item | Average cost |
| Language exam | IELTS — 240 USD, EKT — free |
| Student visa | 113 USD |
| Insurance | 339 USD / year |
| Registration fee | 113 USD |
| Flight | 113 USD |
| Rent | 169 USD/month |
| Transport | Free |
| Meals | 226 USD/month |
| Study materials | 79 USD/month |

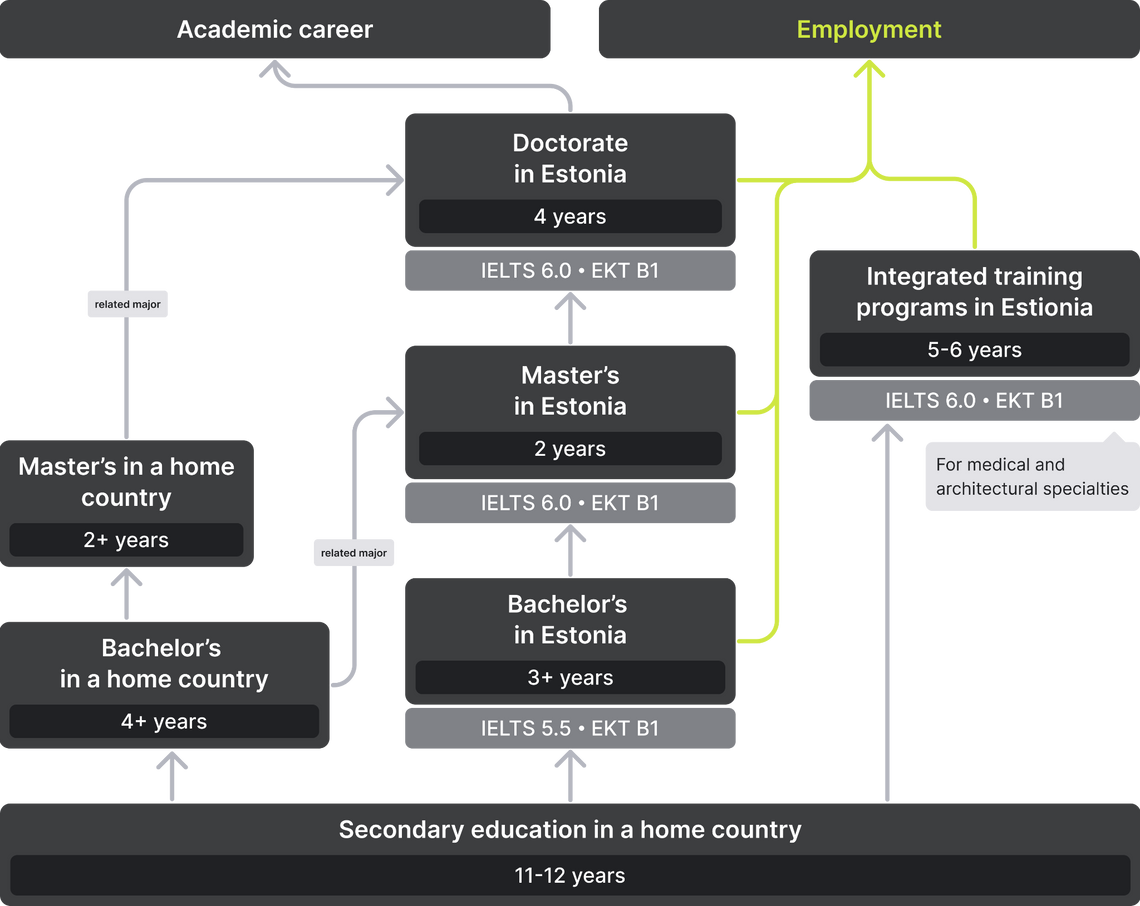
You can enter Estonian universities after graduating from high school (including schools in countries with 11-year secondary education). The average score of the certificate must be at least 60% of the maximum. A high GPA will increase your chances for admission and scholarship.
Enrollment takes place once a year from April to July. A more accurate deadline depends on the specific university and the applicant's citizenship. First, an applicant must submit an online application on the Dream Apply portal, attach scans of the necessary documents and a motivation letter. You can apply to a maximum of 5 universities, and 2 programs in each. Everything is done via a single form. This is followed by an interview via Skype and/or online tests in subjects from the field of the future profession.
If you manage to pass all the steps and the admission committee gives you a positive response, certified paper copies of all documents and their translations into English or Estonian must be sent via mail.
There are many programs in English in Estonia. To study in English you will need an IELTS or TOEFL certificate. Those who decide to study in Estonian must pass the Eesti keele tasemeeksam exam at a level not lower than B1. Testing is free and is carried out 4 times a year in major cities of Estonia.
For bachelor's programs:
Additionally for master's and doctoral studies:
The digital application must be accompanied by scans of original documents and their translations into English or Estonian. Translations must be certified in ONE of the following ways:

Estonia has concluded agreements on the mutual recognition of education documents with Latvia, Lithuania, China, and Ukraine. Students from these countries do not need to confirm their certificates and diplomas — a translation into Estonian or English is enough. Some institutions also accept documents in Russian, as it is the second most common language in the country.
Students from other countries outside the EU must certify the translations of their documents in one of three ways:
Further, the receiving institution makes a decision on the equivalence of qualifications. In controversial situations, the selection committee has the right to contact the organization responsible for the recognition of foreign documents ENIC/NARIC. Here the consideration of the application can take up to 30 days.
Students of all nationalities can study in Estonian at state universities for free with a workload of at least 30 ECTS per semester. To do this, you need to pass the Eesti keele tasemeeksam exam with a level B1 or higher. It is free and is held 4 times a year in Tallinn, Narva, Jõhvi, and Tartu. In addition, upon successful passing of the exam, you can request a refund of your Estonian language courses that were taken at educational institutions of the country.[6]
You can prepare for the exam at one of the many language schools or by taking courses at the University of Tartu. There is a year-long Estonian preparatory course that costs 1,356 USD per semester, as well as shorter summer and online courses. The workload for a one-year course will depend on the student's initial knowledge. Students who learn the language from scratch must gain 60 ECTS per year, which is equal to the full workload of a university student.

In Estonia, in addition to higher education institutions, there are more than 30 colleges of various kinds, where you can get vocational education and training (VET). These include vocational schools (ametikool) and vocational education centers (kutsehariduskeskus / kutseõppekeskus). A complete list can be found here. Most establishments accept foreigners. There are programs in Estonian and Russian, less often in English. When studying in Estonian, an additional year before the beginning of studies is often devoted to an intensive language course. There are both paid and grant programs.
You can enter Estonian colleges after grade 9 or 11. After grade 9, there are two options:
If you go to a vocational college after graduating from high school (grade 11 or higher), the program will be slightly shorter or less intense than in case of entering after grade 9. But these can vary depending on the specialty (from one year to 2.5 years). The level of the certificate issued after graduation will be higher: Certificate of Vocational Education Level 5. But such a qualification is still lower than a bachelor's degree at a university (Level 6).
In Estonia, as in most countries of the European Union, higher education is based on the Bologna system. The first stage is bachelor's studies (bakalaureuseõpe). Normally training lasts 3 years, some applied specialties can take 4. During this time, students gain 180-240 ECTS and receive a bachelor's degree (bakalaureus). There are also "integrated training programs" (integreeritud õpe), which last for 5-6 years. As a rule, these are medical and architectural specialties. In this case, graduates immediately receive a master’s degree.
There are almost as many bachelor's programs in English as in Estonian. During bachelor’s studies, students have 3 types of subjects, for each of them you need to collect the required number of ECTS:
Also, some universities, in addition to the main specialization (major), offer an additional one (minor). The combination can be anything: for example, engineering + psychology. This tradition is borrowed from American universities.

Master's degree (magistriõpe) is the second level of higher education in Estonia. Education here usually lasts for 2 years. However, if before that the student graduated after 4 years of bachelor’s studies, it can be done in a year. The master's degree (magistrikraad) is awarded after earning between 60 and 120 ECTS. It is not necessary to have a bachelor's degree in an identical specialty to enroll in a master's program in Estonia. The main thing is to show that you have the basic knowledge necessary for further training during the interview.
At the end, students can either write a thesis or create a group or individual project and test it. The type of the final work depends on the orientation of the program, theoretical or applied. The main universities of the country work closely with research centers and commercial companies, where master’s students can take an internship.
All PhD programs in Estonia are free in both Estonian and English. Training lasts for 4 years. 180 out of 240 ECTS are dedicated to writing a dissertation. The number of places in universities is limited, as the research process is fully sponsored by the state. Moreover, PhD candidates often receive a scholarship of 226-678 USD.
Such generous conditions have a downside: when entering a doctoral program at an Estonian university, a person can choose only one of the proposed topics for a thesis on the university's website. The list is compiled according to the topics' relevance to the scientific community and the country. Thus, young researchers are guaranteed to make their contribution to solving socially important issues. Having decided on the topic, the future doctoral student chooses a potential supervisor and then submits an application.
To work in academic positions in Estonian universities, it is highly desirable to know the Estonian language. However, there are many English-language programs and courses in the country that invite foreign lecturers. It should be noted that salaries in the academic field are low compared to most Western countries.
While studying for a PhD at an Estonian university, young scientists can already start teaching junior students. Then their careers will follow these steps:
For those who graduated from the master’s and want to engage in scientific activities exclusively, research positions are also available:

To study in Estonia, students from non-EU countries need a visa. For short-term courses up to 3 months, a type C visa is enough. For studies of up to 12 months, a long-term type D visa will be required. Those who plan to stay in the country for more than a year must, upon arrival, exchange their D visa for a temporary residence permit (TRP). You must apply for a long-term visa and get it in person at one of the embassies or consulates of Estonia. A complete list can be found here. The fee is 113 USD. You can only pay by debit/credit card. The application is usually reviewed within 10 business days.
Important! If you are going to spend more than a year in Estonia and there are more than 4 months left before the trip, you can apply for TRP at the embassy or consulate in your country. It will cost 73 USD. The issuance procedure takes 3-4 months. If there is not enough time, a D visa is obtained, and TRP is issued immediately upon arrival in Estonia at the Police and Border Guard Board (Politsei- ja piirivalveamet). In this case, TRP is valid for the entire period of study and costs 40 USD.

Foreign students with a temporary residence permit can work while studying without an additional permit. There are no strict restrictions on the number of work hours — the main requirement is that there are no serious problems with academic performance and the timely passing of exams. According to statistics, almost 50% of foreign students in Estonia combine study and work.[5] To find a permanent job in Estonia, it is advisable to know the national language, therefore, the choice of positions for students of English-language programs is usually limited. However, in large cities like Tallinn and Tartu there are many opportunities for side jobs in tourism and services, where knowledge of English and other languages will be useful. The average salary in the country is 9 USD per hour or 1,469 USD per month. However, students often work part-time or in low-ranking positions, so the rate may vary.
All foreign students without EU citizenship can stay in Estonia for another 9 months (270 days) from the date of expiry of the TRP. You do not need to carry out any additional procedures with documents for this. During this time, you can find a job, conclude a contract, and apply for a new work TRP. This document is issued for the period specified in the contract with the employer, but not more than 2 years. In the future, it can be extended for up to 5 years.
After 5 years of continuous residence in Estonia, a foreigner can obtain a long-term residence permit. To do this, you need to have a permanent official job, registration at the place of residence, insurance, and also pass an exam for knowledge of the Estonian language (at least B1). More information about the immigration process can be found on the website of the police department.

In Estonia, there are many young developing companies, especially in the IT sector. Newly graduated professionals can find jobs in them if they only speak English. However, it should be kept in mind that the Estonian government is very concerned about the problem of migrants, which compete with local residents for jobs. Most of them are from Ukraine and Russia. HR in a large company is more likely to hire a citizen of the European Union. Nevertheless, the number of foreign students who get a job immediately after graduating from a university in Estonia is constantly growing: in 2018, almost 60% of graduates of master's and doctoral studies were employed in the country[5]. In order to increase their chances, visitors should definitely learn Estonian.
In Europe, diplomas from Estonian universities are recognized on an equal basis with others, so graduates can find work in any country of the European Union.
It is much easier to build an academic career at an Estonian university with knowledge of the Estonian language, but you can try yourself in numerous English-language programs. Students can start teaching while pursuing a PhD, and research positions are available already at the master's cycle.
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got