
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Are you planning to study in Latvia? We recommend that you learn more about the pros and cons of education in this country.
Free consultation
Secondary education in Latvia begins with the compulsory pre-school level, attended by children of ages 5-6. Then there comes a 9 year period of compulsory schooling. State and municipal schools in Latvia are free. In private schools, the cost of training is about 1,130-1,356 USD/year. After graduating from primary school for the next 3 years a student can get a full secondary education. This may be a gymnasium, the main task of which is academic preparation for a university. Or, a student can go to a vocational school or college and get a diploma of secondary specialized education in such fields as art, business, medicine, etc. This document allows you to immediately start working or continue education at a university.
A large Russian diaspora lives in Latvia (about 40% of the total populace), thus the country has many Russian-language schools. Nevertheless, according to educational reform of 2019, all of the schools should switch to Latvian-only programs until 2021.
Education in Latvia is increasingly oriented towards the international market. Universities are moving away from post-Soviet standards and are developing English-language programs that attract applicants from abroad with high European quality and affordable prices. And the leisurely pace of life amid stunning architecture and nature captivates every foreigner who has visited Latvia.
| Type of training | Age | Duration | Min.cost | Avg. cost | Min. language proficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer camp | 6-17 | 1-8 weeks | 282 USD/week | 452 USD/week | Beginner |
| Language courses | 5+ | 1-8 weeks | 136 USD/week | 260 USD/week | Beginner |
| Secondary education | 12+ | 9-12 years | 904 USD/year | 1,243 USD/year | Intermediate |
| Foundation | 17+ | 1-2 years | 2,034 USD/year | 3,390 USD/year | IELTS 4.5 / TOEFL IBT 56 |
| College | 16+ | 2-3 years | 1,582 USD/year | 2,260 USD/year | VVPP B1 |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 3-4 years | 1,695 USD/year | 3,390 USD/year | IELTS 5.5 / TOEFL IBT 72 / VVPP B1 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-2 years | 2,260 USD/year | 2,825 USD/year | IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL IBT 80 / VVPP B2 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 3,390 USD/year | 7,910 USD/year | IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL IBT 80 / VVPPdegree B2 |
| Doctoral | 20+ | 3-4 years | 2,373 USD/year | 2,599 USD/year | IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL IBT 80 / VVPP B2 |
Please note that all prices are approximated and depend on the particular educational institution, the chosen specialty, and the year of enrollment.
| Item | Average cost |
| Language exam | 271 USD |
| Student visa | 68 USD |
| Registration fee | 17 USD |
| Accommodation | 226 USD/month |
| Transport | 18 USD/month |
| Meals | 158 USD/month |
| Insurance | 45 USD/year |

Latvia actively seeks to integrate into the international community and get rid of traces of the Soviet past. This could also be seen in the education system. Earlier, training in many institutions of Latvia was bilingual (teaching was conducted in Latvian and Russian), but after the reforms in 2019, the country began to pay much more attention to education in its native (Latvian) language, as well as attract foreign students from the EU countries with the help of a large the number of English-language programs. For students from abroad, this is a great opportunity to get a world-class diploma at a relatively low price.
Most major universities, such as the University of Latvia and Riga Stradiņš University are targeting their fully English-language programs specifically at international students. The required level of language proficiency is low and starts at IELTS 5.5. Some universities do not even require an applicant to have a language certificate and conduct their own entrance testing. Nevertheless, English-language education is not a guarantee of employment within Latvia: this requires at least basic knowledge of Latvian. That is why foreign students studying in Latvia in English often use it as the transit point before they go to live and work somewhere else, for example, the UK.
If the student plans to study in the Latvian language, most universities require the Valsts valodas prasmes pārbaude exam. You can read more about this test on the website of the State Educational Center of Latvia (Valsts izglītības satura centrs).
Upon admission or employment in Latvia, foreigners may be required to undergo the legalization of educational documents. If your country is a part of the Hague Convention, to legalize a diploma or certificate an apostille must be placed on them.
If the university or the employer asks you to go through the procedure of academic or professional recognition of foreign qualifications in addition to legalization, you should contact the Academic Information Center (Akadēmiskās informācijas centrs).
Academic recognition is required to continue studies in Latvia or to carry out labor activities in a profession not regulated by national legislation. In this case, you will need to provide a document of education and an identity card, as well as pay a fee of 46 USD.
Professional recognition is necessary if a foreigner plans to work in Latvia in a regulated profession. Most often this applies to medical professionals. A complete list of regulated specialties can be found here. The fee is 271 USD.

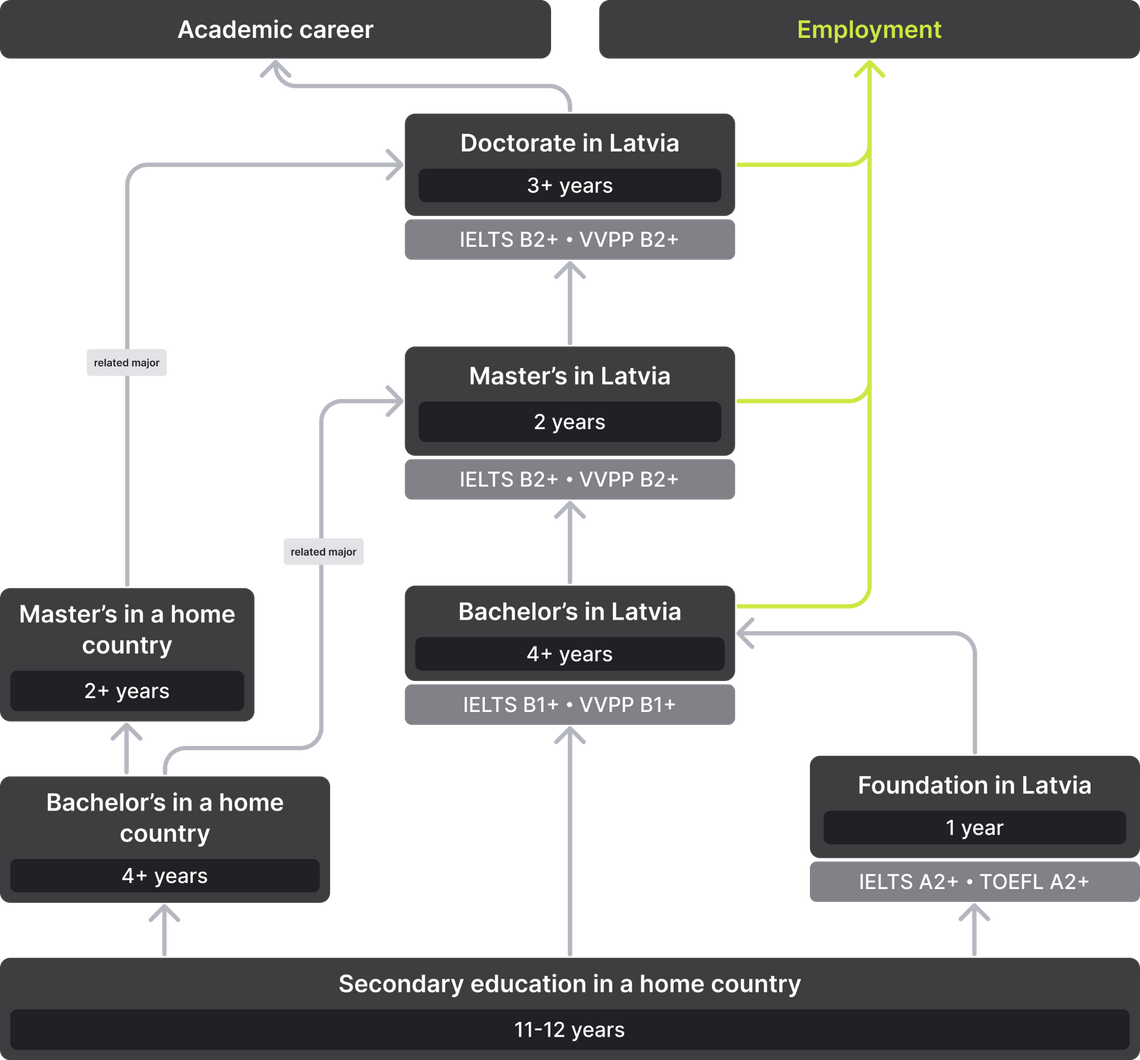
International students can enter Latvian universities immediately after graduating from high school, even if their education was shorter than 12 years of secondary school. Nevertheless, if a foreign applicant wants to improve his knowledge of English and Latvian, as well as specialized mathematical disciplines before starting his studies at the university, some universities offer this opportunity. Such courses, as a rule, last from three months to a year. Prices range from 500 to 3,390 USD per course, depending on the duration and number of academic hours. Teaching is conducted in English, so you will need to provide proof of a minimum level of language proficiency: IELTS 4.5 or TOEFL iBT 56. There are also online training courses, for example, at the Riga Transport and Telecommunication Institute.
Colleges in Latvia are rarely an attractive educational option for international students, as they teach mainly in Latvian: they train specialists for the domestic market. In college, you can get a secondary vocational or applied higher education. Training lasts 2-3 years. The received diploma of higher education will have a lower level than a bachelor's degree at a university or higher school, and a graduate will not be able to immediately continue studying at a master’s without studying for another 1-2 years.
Colleges can exist as independent institutions or be part of larger universities. Training is focused primarily on practical skills. It gives qualifications such as junior medical personnel, firefighter, accountant, mechanic, police officer, preschool teacher, children's trainer, etc. Graduates can quickly find work in Latvia.
Bachelor’s programs (bakalaurs) in Latvia are divided into standard academic and professional. In general, this division is formal, but there are still differences in the curricula. The duration of the bachelor's studies is 6-8 semesters (3-4 years), depending on the chosen specialty.
The purpose of academic education is to prepare graduates for research, as well as to provide them with a solid theoretical foundation for further professional activities. Examples of academic specialties are lawyer, teacher, translator.
Academic bachelor’s degree covers 120-160 Latvian credit points or 180-240 ECTS and includes the following:
The purpose of professional education is to provide students with in-depth knowledge in a specific field of applied science, to prepare graduates for the creation and improvement of various systems, products, technologies. Examples of specialties would be logistics specialist, engineer, etc.
Professional bachelor’s programs cover a minimum of 160 CP (240 ECTS) and include the following:
The process of admission to universities in Latvia is not centralized. Each university determines a list of entrance tests and the necessary documents individually. Below is the standardized list of documents for admission for foreigners to the English-language bachelor’s program.

Master’s programs (maģistrs) in Latvia are also divided into academic and professional. The duration of the master's is 1-2 years.
Academic master’s program covers a minimum of 80 CP (120 ECTS) and includes the following:
Professional master's program covers at least 40 CP (60 ECTS) and includes the following:
Below is the standardized list of documents for admission for foreigners to the English-language master’s program.
Doctoral studies are the final, third stage of higher education in Latvia. This degree enhances the competitiveness of graduates in the labor market. In the process of writing a doctoral dissertation, primarily research skills are improved. Holders of PhD may in the future be invited to the position of a teacher at your university or other universities. Doctoral students usually spend 3 years training. An average number of credits: 120 CP (180 ECTS). The program may include:
Documents for admission:
When searching for positions in the academic field in Latvia, one may come across the designations R1-R4, which are used in other EU countries as well. They reflect the career stages of researchers. This classification applies to scientists from both private and public educational institutions. Each career level has certain characteristics. You can read more about the rights and obligations of a representative of each step here.
Salaries in academic positions start from 508 USD/month and can reach up to 3,955 USD/month for leading high-class researchers. The average salary in the field of education is very low for the EU — 1,073 USD/month.

Latvian universities have few state-funded places, and only citizens of the country can apply for them. The cost of education for third-country nationals is much higher than for immigrants from the EU and EEA. Doctoral programs may have a cost that is three times higher. Universities often offer students discounts for excellent studies (up to 20%) and the possibility of paying by installments. You can also apply for funding for your research projects.
The most prestigious (and actually the only) scholarship for which foreign students in Latvia are fighting is the Latvian State Scholarship from the State Agency for Educational Development (Valsts izglītības attīstības aģentūra). Citizens of 25 countries that have signed an agreement with Latvia on cooperation in education and science can apply for it. The list of countries can be found on the site.
EU, EEA, and Swiss citizens do not need any visa to stay and study in Latvian register institutions. However, if the duration of an academic program exceeds 1 year, they are supposed to apply for a residence permit within 3 months upon arrival. Check the details here.
Non-EU citizens may be required to obtain a long-term national category D visa at the visa center depending on the country (countries are subdivided into visa and non-visa ones). The average consular fee is 68 USD, and the application takes 2-4 weeks, but these figures may vary depending on the place of application.
A student visa is valid for 90 days from the moment of entry to Latvia. However, no matter if you are a national of a visa or non-visa country, in case the period of your stay in Latvia is more than 90 days, you must obtain a temporary residence permit (TRP). You can apply for TRP both upon arrival in Latvia through the Citizenship and Migration Affairs Office (Pilsonības un migrācijas lietu pārvalde — PMLP), and at the Latvian Embassy in your country of residence. If the student submits documents through PMLP, this should be done no later than 30 days after entering the country, since the examination of the application may also take up to 30 days. The list of required documents is the same in both cases.
TRP is valid for 1 year, then it must be renewed. It is necessary to apply to the PMLP for a new TRP no later than 3 months before the expiration of the document. If the application is submitted later than 45 days before the TRP expiration date, the student is required to pay a fine of 322 USD.

Foreign students in Latvia with a student visa (and then TRP) can be employed part-time (20 hours a week), provided that the part-time job does not overlap with the time of study at the university. During holidays and study breaks, students have the right to work a full day (40 hours a week). In the presence of TRP, additional documents for a work permit in Latvia are not required for foreign students.
Most often, students without a good knowledge of Latvian can only get low-skill jobs. Salaries in this position are only enough to cover pocket expenses even with the low cost of living. For example, working as a waiter half-time will bring 226-282 USD / month[1]. Nevertheless, large universities are sure to send their students for internships, which is a good chance to get an invitation to work after graduation.
If a foreign student of a Latvian university is not an EU or EEA citizen, after graduation he does not have free access to the labor market in Latvia: he cannot stay in the country with the goal of finding work. Staying in Latvia after graduation is only possible with an invitation from an employer before completing education. But getting the contract is also not easy: the Latvian government is preoccupied with the issue of unemployment in the country, therefore, local residents have an advantage over foreigners when they apply for the same vacancy. The employer is obliged to place a vacancy in the database of the State Employment Agency (Nodarbinātības valsts aģentūrā) and can hire a foreigner from a non-EU country only if no responses from citizens of Latvia, EU or EEA are received within 30 days.
Nevertheless, if a foreign student manages to get a job, after 5 years of living in Latvia (including the time of the study), he has the right to change his temporary residence permit to a permanent residency. And after 10 years in the country, a person can apply for Latvian citizenship. However, it should be borne in mind that Latvia does not recognize dual citizenship and you will have to refuse a native passport in this case.

60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got