Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Detailed instructions for applying to Singapore. Everything about requirements, preparatory programs, tuition fees and student visas.
Free consultation





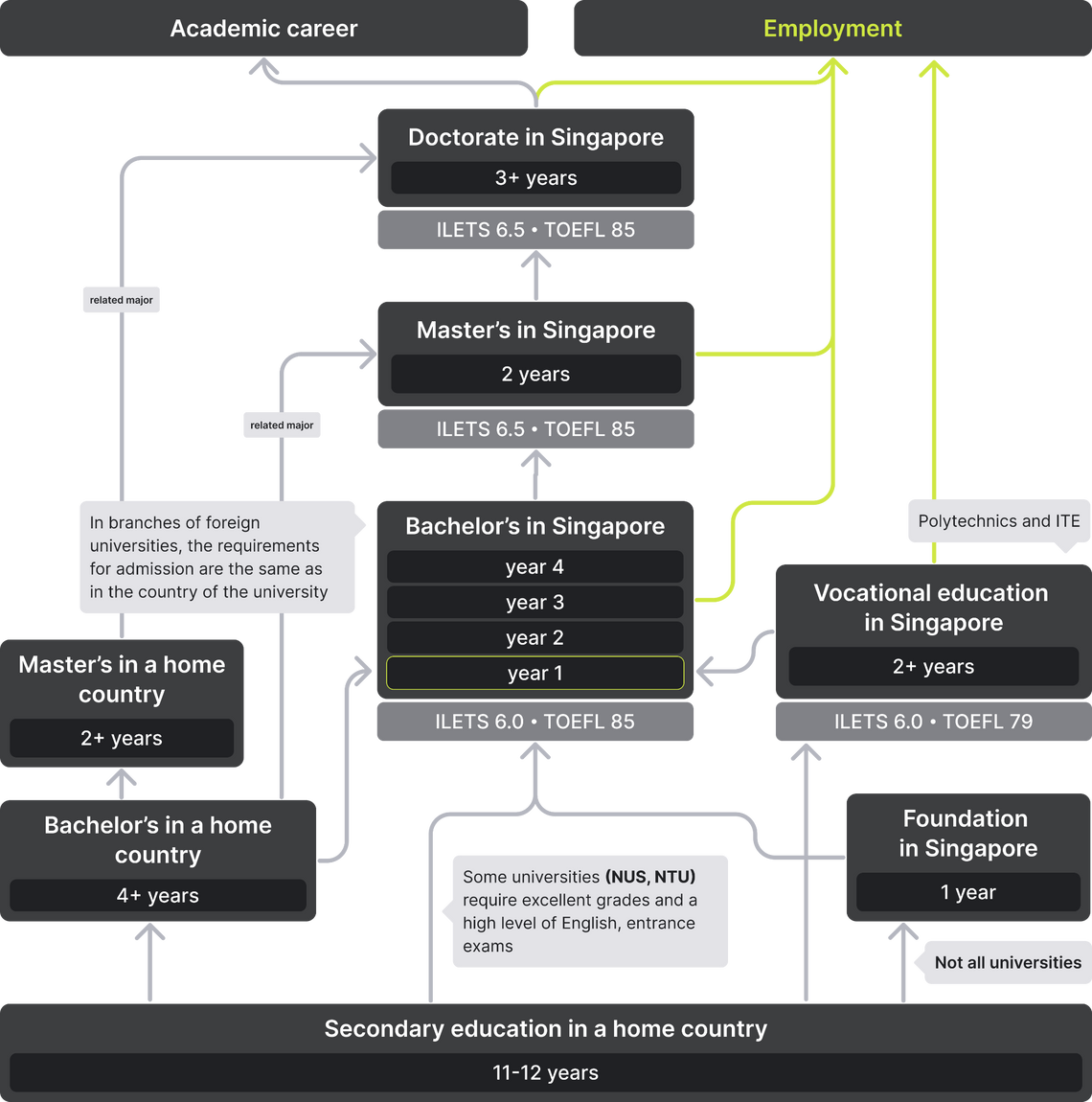
Applying to a university in Singapore is possible after the 11th grade, provided you have a strong academic record. This typically involves taking entrance exams and an English language proficiency test. However, certain universities may require completion of a preparatory program or one year of bachelor’s studies in your home country as a prerequisite. Further details regarding other requirements, costs, available scholarships, and visa procedures are discussed below.
For more information about higher education and universities in Singapore, refer to our separate articles on these topics.
| Program | Age | Duration / year | Min. cost / year | Avg. cost / year | Min. English level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | 16+ | 1 | 3,035 USD | 8,345 USD | B1 |
| College | 17+ | 1-3 | 4,173 USD | 18,966 USD | B2 |
| Bachelor's | 17+ | 3-4 | 11,380 USD | 28,828 USD | B2 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-2 | 22,759 USD | 34,139 USD | C1 |
| Medical programs | 17+ | 5+ | 31,863 USD | 53,105 USD | B2 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 | 22,759 USD | 53,105 USD | C1 |
| PhD | 20+ | 2-5 | 10,621 USD | 27,311 USD | C1 |
| Expense | Average cost / month |
|---|---|
| Rent | 2,655 USD |
| Communal fees | 152 USD |
| Registration fees | 11 USD |
| Visa | 30 USD |
| Medical insurance | 531 USD/year |
| Food | 275 USD |
| Public transportation | 41 USD |
| Internet | 55 USD |
All prices and requirements should be specified on the websites of universities.

Singapore boasts a total of 34 universities, with six of them being public institutions. Compared to other Asian countries — such as China, with over 2000 universities and India, with more than 1000 — Singapore offers a relatively smaller selection. To make an informed choice when selecting a university, pay attention to several key criteria.
Singaporean universities consistently rank among the top 30 in the world according to QS rankings. The National University of Singapore (NUS) holds the 8th position, while Nanyang Technological University (NTU) secures 26th place[1].
In the 2024 Times Higher Education rankings, NUS ranks 19th globally, with NTU following at 32th place. These same institutions excel in the Asian university rankings, with NUS ranking first and NTU taking the third position[2].
It is also worth considering their performance in subject-specific rankings. Singaporean universities excel in engineering fields. In the Shanghai ranking, particularly in Telecommunication Engineering, aside from NUS and NTU, the Singapore University of Technology and Design ranks 23rd[3].
Studying in Singapore tends to be pricier compared to other Asian countries. On average, a bachelor's program costs around 28,828 USD per year, though at prestigious universities, this figure can soar to 91,037 USD annually. For example, pursuing a bachelor’s degree in Music at NUS can amount to 97,182 USD per year. To put this in perspective, the average cost of a bachelor's program in China is approximately 4,000 USD per year.
While tuition fees are not waived, you do have the opportunity to secure scholarships if you enroll in one of the 13 publicly funded universities. Scholarships typically cover up to half of the educational expenses, but they are highly competitive. To stand a good chance, you will need outstanding grades and notable achievements in the field of science, such as published scientific articles, monographs, involvement in book translations, or textbook authorship.
Read more about: universities in SingaporeSingapore is home to some of the most prestigious MBA institutions in the world. In the Financial Times ranking, these leading institutions include: INSEAD, ranked 2nd globally; NUS, securing the 25th position; NTU, standing at 38th place; and Lee Kong Chian School of Business, positioned at 61st place. On average, an MBA graduate in Singapore can expect an annual salary of 159,000 USD[4].
MBA programs in Singapore encompass various types, including Executive MBA, Double Master's, Professional MBA, MSc in Accounting, MSc in Analytics, MSc in Finance, MSc in Sustainable and Green Finance, among others.
To be eligible for admission to MBA programs, you will need a bachelor's degree, at least 2 years of work experience, and language proficiency certificates — TOEFL 90 or IELTS 6.5.
Not all universities in Singapore admit students directly after the 11th grade. For those seeking admission to NUS, applicants are required to take standardized tests, such as the ACT with a minimum score of 29, or the SAT with at least 600 points. A high GPA and demonstrated excellence in national and international arenas, including participation in specialized subject Olympiads and sports competitions, can provide a competitive advantage during the admission process[5].
Items 1-6 of 84
Advanced search
Specific admission requirements can vary from one university to another in Singapore. Many universities do not admit students directly after the 11th grade. Instead, some universities may require students to pass entrance exams or complete a Foundation program.
The National University of Singapore admits students after the 11th grade, but only those with excellent grades and SAT exam results. Nanyang Technological University enrolls students based on internal examinations and does not offer Foundation programs.
In branch campuses of foreign universities, admission rules correspond to those of the parent country. For instance, Australian and British universities generally accept students after the successful completion of their respective Foundation programs.
To apply to a Singaporean university, you need to provide your high school certificate, along with a grade transcript translated into English.
Since instruction in Singapore is conducted in English, universities often require English language proficiency test scores, such as IELTS 6.0 or TOEFL 80. Additionally, many programs may request results from standardized tests like GRE / GMAT / SAT / GATE, and some may conduct interviews.
The minimum GPA for admission to Singaporean universities is typically set at 3.0 out of 4. However, at prestigious institutions like NUS, NTU, and SMU, the GPA requirements tend to be higher — often above 3.5 out of 4.
Application documents can be submitted through the official website or application portal of the university, with some universities also accepting applications via email or regular mail.
Singaporean universities admit students twice a year, in January and August.
All documents must be translated into English and certified by a notary.
Starting in 2021, some universities may also require an apostille on educational documents. We recommend checking with the admissions office in advance to confirm their specific requirements.

Following the 11th grade, applicants have the option to enroll in a Foundation program. However, prestigious universities like NUS, NTU, and SMU do not offer such programs. Instead, admission to these universities can be based on entrance exam results or after completing programs at colleges, polytechnics, ITEs, A-Level school programs. A-Levels are typically offered in specialized schools, junior colleges, and centralized institutes.
Branch campuses of foreign universities in Singapore usually require certificates from their own Foundation programs.
To apply for preparatory programs, you can visit the websites of universities and colleges. Requirements may vary depending on your nationality, but you will generally be asked to provide a high school diploma and a language proficiency certificate, such as IELTS 5.5 or TOEFL 60.
For specific requirements, check the websites of universities.

In Singapore, admission requirements for bachelor’s programs can vary significantly between universities. For instance, institutions like NUS and NTU may admit students after the 11th grade, but they typically require candidates to pass entrance exams. Other universities may only admit students after the 12th grade, necessitating the completion of a Foundation program. This requirement is more common in European branch campuses of universities in Singapore.
The main prerequisite for admission is a high school diploma, which must be translated and notarized. If the university mandates completion of a preparatory program, applicants must provide the corresponding certificates.
Singapore sets relatively high GPA requirements. To enhance your chances of admission, you should aim for a score of 3.5 out of 4. Top-tier universities may require a perfect 4.0 GPA.
Furthermore, universities in Singapore often request additional documents such as a motivation letter, resume, recommendation letters, and a portfolio for creative fields.
Additional requirements:
Singaporean universities admit students twice a year, offering intake opportunities in both January and August.
For master's programs, a higher level of English proficiency is typically required compared to bachelor’s programs — IELTS 6.5 or TOEFL 85.
Admissions committees primarily consider a candidate's bachelor's degree, academic performance, recommendation letters, and exam results (GRE or GMAT). The minimum GPA requirement is generally set at 3.0 out of 4.
Additional requirements:
Additional requirements:


Singaporean universities welcome applications for PhD programs in two intakes, occurring in January and August. The application can be submitted online through the respective university websites.
Candidates can apply for a PhD program after receiving a master's degree. The field of study must be closely related or align with their previous level of education.
To secure a spot at a top university, applicants typically need to hold an honors degree or demonstrate notable achievements in the field of science — published scientific articles, monographs, involvement in book translations, or contributions to textbook authorship. Many universities offer scholarships to exceptional students[12].
Additional requirements:
In Singapore, scholarships are available from various sources, including the government, universities, and private organizations.
As a rule, these cover up to 50% of the total educational expenses, with only a few larger scholarships that fully fund education. To be eligible for such scholarships, academic excellence and exceptional achievements are often required.
The Singaporean Ministry of Education offers scholarships that contribute to up to half of the educational expenses, excluding other costs.
One of the prominent government scholarships is the Tuition Grant, which supports 13 universities — including the National University of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University, and Singapore Management University. This grant covers 50% of tuition fees.
Singaporean citizens are automatically eligible for the Tuition Grant upon admission, while international students must submit an application. The application deadlines for the grant coincide with university enrollment deadlines. The primary condition is full-time enrollment. Applicants can submit an online application through the MOE TGonline system, and detailed instructions are provided by the Ministry of Education.
Scholarships are awarded to students who demonstrate exceptional academic achievements and maintain outstanding grades.
The majority of scholarships are accessible to Singaporean citizens and permanent residents, making the competition more intense for international students. To enhance your chances, meticulous preparation of your resume is crucial. Detailed information regarding available scholarships can be found on university websites within the "Scholarships" section.
Additionally, universities often offer financial aid in the form of social stipends to students facing financial hardship. Information about these stipends can be located on university websites within the "Bursary" or "Need-based scholarship" sections.
To qualify for such benefits, evidence of low income is required, typically up to 759 USD per month per family member. In cases where documents are not in English, translation and notarization are necessary.
Several prominent local and international organizations offer scholarships to exceptionally talented international students. Notable examples include the Association of Commonwealth Universities, Evolve Warrior Scholarship, Singapore Airlines Open Overseas Scholarship.


A student visa is required to pursue studies in Singapore, and the processing time for this visa is typically four weeks. However, several nuances can potentially extend this processing period.
To initiate the visa application process, it is crucial to apply promptly after securing admission to a university through the Student’s Pass Online Application & Registration (SOLAR+) portal. The registration fee is 23 USD. After completing the online form, applicants must print and present it to the Singapore Immigration Service upon their arrival. Only then will a permanent visa be issued. The cost of the Student Pass card is 46 USD.

Required documents for a student visa:
All documents must be translated into English and certified by a notary.
If your travel document is issued by one of the countries or regions listed below, you will require a visa to enter the Republic of Singapore:
Afghanistan, Algeria, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, Belarus, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Egypt, Georgia, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (Identity Certificate), India, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Libya, Macao Special Administrative Region (Travel Permit), Mali, Morocco, Moldova, Nigeria, Pakistan, People's Republic of China, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Tunisia, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Yemen, South Sudan.
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got