
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Article score: 4.13 out of 5 (8 reviews)
The Spanish degree is recognized worldwide. The relatively low cost of tuition and accommodation makes education here more accessible for students than in other European countries. Find out more about Spanish higher education in our article.
Free consultation





Secondary education in Spain is compulsory for all children between ages 6 and 15. Schooling can be divided into two stages: Primaria — primary school (6-11 years old) and Educación Secundaria Obligatoria — high school (12-15 years old). Two years of high school, or Bachillerato, are not required for students: this is preparation for the university. In public schools, instruction is in Spanish or one of the dialects. Children learn the first foreign language from the age of 8, the second from 13 (optional). Foreign students usually prefer private boarding schools. They are often taught in English. Also, many private institutions collaborate with American and British universities. This allows students to choose which final exam to prepare for: Spanish Selectividad, British A-Level, or American SAT. Compared to other European countries, secondary education in a private school will not cost too much: primary — from 3000 to 7,910 USD/year, secondary and senior — from 8000 to 22,600 USD/year.
Education in Spain is rapidly gaining ground in Europe and the world. Studying here attracts more and more foreigners every year: in some educational institutions, the proportion of students from abroad reaches 20%. More than 25 universities in Spain are included in the QS world ranking of the best universities, which indicates the high quality of the educational standards. The Spanish degree is recognized worldwide and the relatively low cost of tuition and accommodation makes education here more accessible for students than in other European countries.
| Type of training | Age | Duration | Min.cost | Avg. cost | Min. language proficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer camp | 5-18 | 1-8 weeks | 384 USD/week | 791 USD/week | Beginner |
| Language courses | 4+ | 1-15 weeks | 203 USD/week | 418 USD/week | Beginner |
| Secondary education | 12+ | 1-4 years | 3,390 USD/year | 13,560 USD/year | Intermediate |
| Foundation | 17+ | 1-2 years | 4,520 USD/year | 11,300 USD/year | DELE B1 / IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 80 |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 4 years | 520 USD/year | 13,560 USD/year | DELE B1 / IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 80 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-2 years | 814 USD/year | 2,407 USD/year | DELE B2-C1 / IELTS 6.0 / TOEFL 80 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 20,340 USD/year | 42,940 USD/year | DELE B2-С1 / IELTS 6.5, GMAT 600 |
| Doctoral studies | 20+ | 3 years | 678 USD/year | 2,260 USD/year | DELE B2-С1 / IELTS 6.5 |
The number of educational programs conducted in English in Spain is constantly growing. Some of the bachelor's specialties are being taught only in English: marketing, tourism, economics, communications, journalism. Examples of the universities conducting studies in English are Global Business School in Barcelona and Marbella University in Malaga.
Among the master's programs, there are way more English than Spanish ones. The country is trying to focus on the global market and attract foreign students. This is especially true for private business schools and MBA programs.
Also in Spanish universities there are quite many bilingual programs, where some of the courses are taught in Spanish, and some in English. The minimum knowledge of English for most universities is IELTS 6.0 or TOEFL 80.

Applicants that are 17 years and older can undergo a Pre-Bachelor Foundation Program in many major universities in Spain. This helps to equalize the level of knowledge of foreign students who completed less than 12 years of school to local standards since Spanish students have to study for 12 years. Students can take a preparatory course in specialized subjects or tighten up the Spanish. ECTS (up to 60) received during training will be taken into account upon admission to the university. Classes are held in both English and Spanish, depending on the chosen study program.
Vocational (special) education, or La Formación Profesional, is an analog of a college or trade school. This path in Spain can be chosen instead of the senior classes, which are aimed at preparing for university entrance. After graduating from a Spanish technical school, it is impossible to immediately enter the university. To do this, you will have to go through a high school program or university preparatory courses. Therefore, among foreigners, this type of education is not very popular.
Professional education lasts from 18 months to 2 years and includes an obligatory stage of employment at the enterprise (Centro de Trabajo) lasting 300 hours. Upon completion of training, students receive a diploma of secondary education and can begin to work. It is also possible to continue education to specialized levels and receive the title of Ténnico (technician).

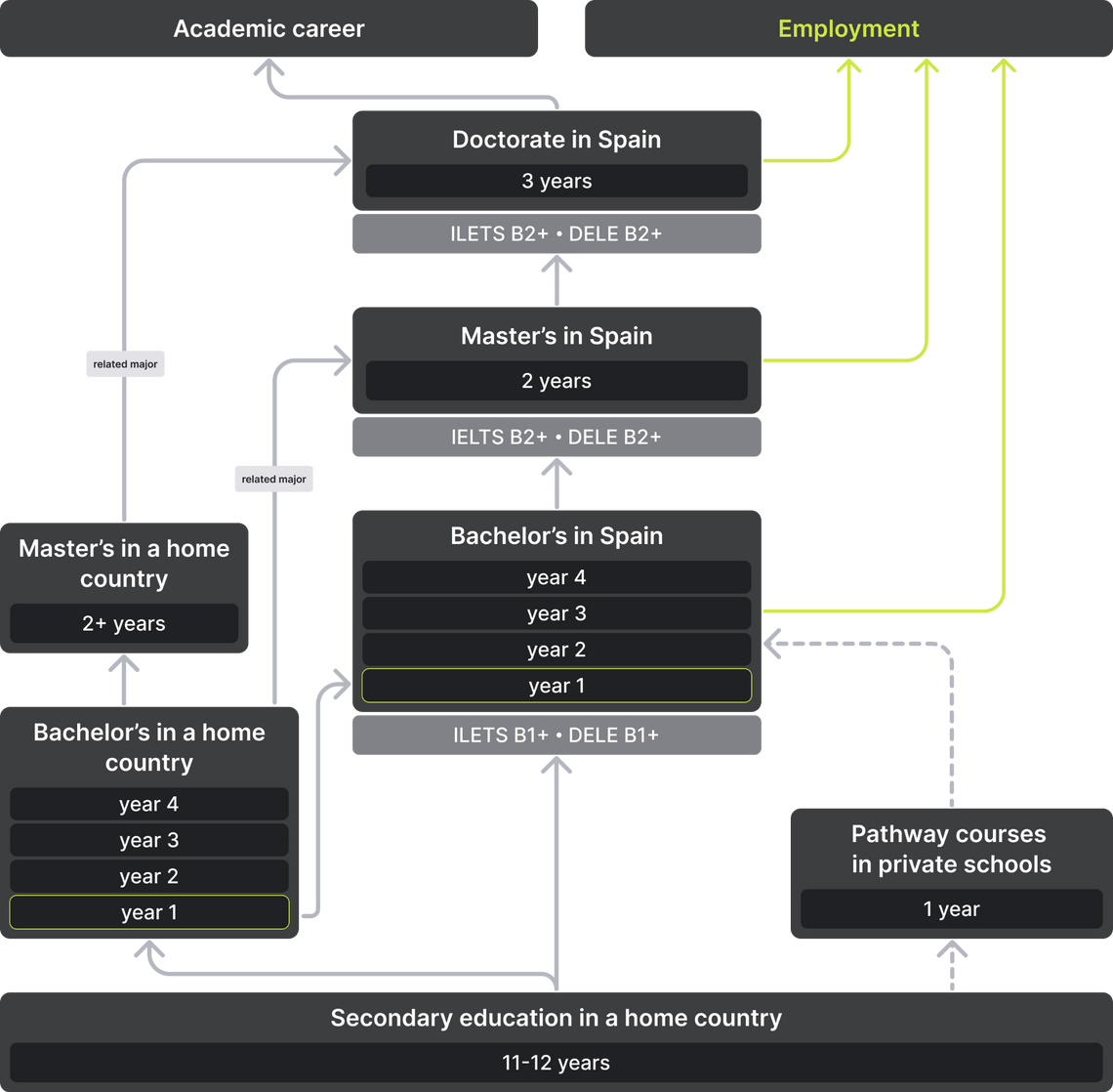
Obtaining a Bachelor’s degree typically takes 4 years. This corresponds to 240 ECTS. The exception is medicine and architecture programs that last for 5 years or longer. Each year, the student is required to gain 60 ECTS. Students annually write term papers, and in the last year, they graduate with a thesis, which is estimated at 30 ECTS. The dissertation is defended publicly before the commission. Additional credits can be obtained for electives and participation in university events. There are a lot of elective courses, but still they are less in numbers compared to compulsory subjects.
Master’s programs in Spain usually last 1-2 years and equal 180 ECTS. At the end of the second year of study, students publicly defend a master's thesis, which is rated at 30 ECTS. There are three types of master's degree programs:

A PhD will take 3 years to acquire. Doctoral studies are divided into two stages: the first stage is theoretical, that is, attending lectures and seminars for which the student receives 60 ECTS, the second is research and involves the writing of a doctoral dissertation. In the end, the student must defend his study in front of the commission. There is no official time limit for writing a doctoral dissertation; on average, it takes students 3-4 years to do this. Doctoral programs are usually taught in special colleges (doctoral colleges). They may be part of universities or individual research institutes.
To write a doctoral dissertation, you must first find a suitable program and a potential academic supervisor on the website of the university of interest. After that, universities offer to fill out an online application on their website, where the future doctoral student reports on his scientific interests and academic success. The main formal condition is the presence of at least 300 ECTS for the previous stages of student education, 60 of which could be transferred from the master's program.
Doctoral students can work on research grants. In Spain there are quite a lot of them. They are provided by both the government and independent funds. There are several stages in an academic career:
The salary of an academic staff member is fixed and determined by the Spanish government. The researcher receives 2,226 USD per month, lecturer — 2,825 USD, associate professor and professor — from 3,051 USD to 4,068 USD[2].
EU students can work while studying in Spain without serious limitations. However, you still have to check with the local authorities whether you need to provide any documents. Sometimes even EU students are required to sign a contract and apply for a work permit valid for the duration of the contract.
Those staying in the country on a student visa can work for 20 hours per week. These hours should not overlap with studies. Full-time work (40 hours a week) is possible only during summer and holidays. For official employment, you must first receive an invitation from the employer, and then a work permit: form AUT05a. You can apply to the migration office (Oficina de Extranjeria) of each city. Documents are reviewed within 5 weeks.
Finding a job for a student in Spain is quite difficult. Employers prefer full-time employees. Also, few want to spend so much time on the official registration of a foreigner in the state. Most students choose freelance, which allows them to work at a convenient time from home.

Foreign students in Spain have a special NIE number (Numero de Identificacion de Extranjero). It is necessary for all formal procedures within the country. But it expires 30 days after graduation along with a TIE student ID. To be eligible to stay in the country and find work, the most convenient way is to apply for a job search visa (estancia por estudios superiores que cesa, para búsqueda de empleo). This can be done 60 days before and 90 days after the expiration of the TIE. Such a visa gives the right to stay in Spain for another 12 months. If during this time the graduate gets a job, later he will receive a resident card with the right to work, which he will be able to renew in the future. After 5 years of living in Spain, a resident has the right to apply for permanent residence and citizenship.
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got