
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Article score: 4 out of 5 (1 review)
Turkey is a member country of the Bologna Process. Therefore, bachelor's, master's and doctoral programs are presented at universities. We tell you about the features of training and admission.
Free consultation




Education in Turkey seems a rather non-standard choice for a foreign applicant because most foreigners come here for a vacation, but since the beginning of the 2000s, the number of international students in the country has doubled. In 2019, their number reached 154505 people, and the state plans to increase this number by 2023[1]. This is due to low tuition and living costs, European quality standards, and generous grants. Moreover, thanks to government funding of education, it is becoming better and more affordable by the year. Warm climate, a unique interweaving of Eastern and Western cultures, and friendly local people increase the attractiveness of Turkish education in the eyes of students.
First table contains information for studying in Turkish, the second — in English.
| Type of training | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language proficiency | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer camp | 6+ | 1-10 weeks | 350 USD/week | 450 USD/week | - | - |
| Language schools | 6+ | 1-52 weeks | 160 USD/week | 400 USD/week | Temel 1 (A0) | Conducted at schools |
| Language courses at the university | 16+ | 2 weeks - 2 years | 68 USD/semester | 192 USD/week | - | - |
| Secondary education | 6+ | 1-12 years old | Free | 20,500 USD/year | Orta (B1) | School exam 70/100 |
| Foundation | 16+ | 1-2 years | 100 USD/month | 200 USD/month | Orta (B1) | Placement exam |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 4-6 years | 300 USD/year | 4,000 USD/year | Yüksek 1 (B2) | TÖMER / TYS |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-3 years | 300 USD/year | 5,000 USD/year | Yüksek 2 (C1) | TÖMER / TYS |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 4,000 USD/year | 18,000 USD/year | Yüksek 2 (C1) | TÖMER / TYS |
| Doctoral | 20+ | 2-4 years | 300 USD/year | 500 USD/year | Yüksek 2 (C1) | TÖMER / TYS |
| Type of training | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language proficiency | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer camp | 6+ | 1-10 weeks | 350 USD/week | 450 USD/week | A1 | - |
| Language schools | 6+ | 1-14 weeks | 200 USD/week | 600 USD/week | A1 | Conducted at schools |
| Secondary education | 6+ | 1-12 years | 20,000 USD/year | 20,500 USD/year | B1 | TOEFL IBT — 65 |
| Foundation | 16+ | 1-2 years | Free | 8,100 USD/month | A1 | Placement exams |
| Bachelor's | 18+ | 4-6 years | 450 USD/year | 7,000 USD/year | B2 | TOEFL IBT 75 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-3 years | 600 USD/year | 8,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL IBT 92 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 year | 2,000 USD/year | 15,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL IBT 92 |
| Doctoral | 20+ | 2-4 years | 500 USD/year | 9,000 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL IBT 92 |
Students from Turkic republics (Bashkortostan, Dagestan, Karachay-Cherkessia, Tatarstan) and countries (Azerbaijan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Macedonia, Mongolia, Moldova, Nakhchivan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Ukraine) in many state universities pay tuition as Turkish citizens.
| Expenses | Average cost |
|---|---|
| Registration fees | 120 USD |
| Visa | 100 USD |
| Accommodation | 2,400 USD/year |
| Insurance | 50 USD/year |
| Meals | 2,200 USD/year |
| Public transportation | 600 USD/year |
All prices and requirements must be specified on the websites of universities.
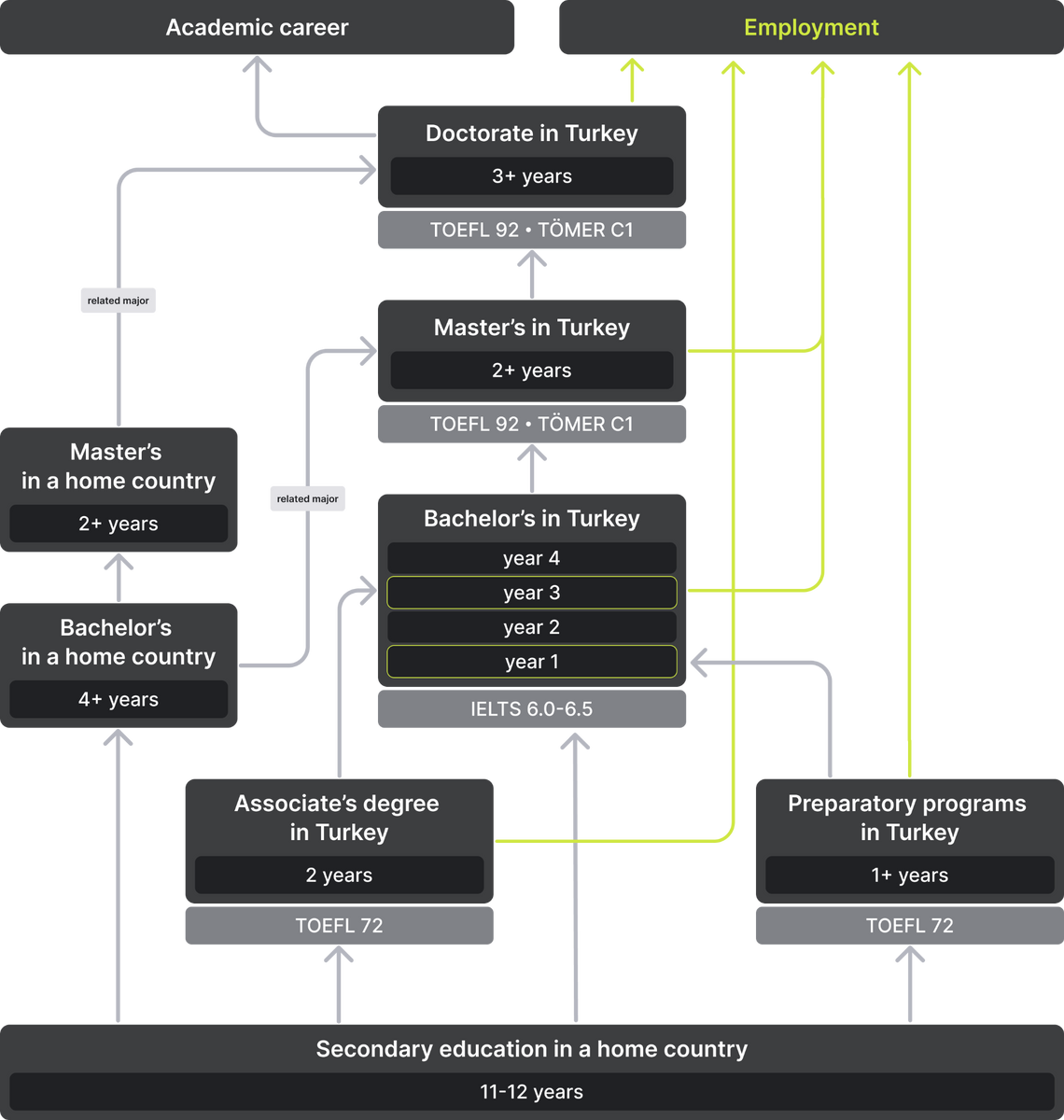

Turkish education system follows the Bologna process, therefore universities offer bachelor's, master's and doctoral programs. After graduating from secondary school, students enter universities and study for 4 years at bachelor's programs or go to vocational colleges for 2 years to obtain an associate degree. The master's program lasts for 2 years, doctoral studies — 3-5 years.
The academic year in universities is divided into two semesters and two-week winter vacation: the autumn semester most often begins in mid-September or early October and lasts until the end of December, and the spring semester — in February and lasts until May or early June. Some universities add an extra year for an in-depth study of English or Turkish.
For admission to Turkish universities, foreign students must receive a diploma of secondary education or a bachelor’s/master’s degree. Documents are submitted directly to universities.
Turkey is a part of the Hague Convention, which established simplified legalization of documents. To enter a university, it is enough to translate a diploma or certificate into English and notarize the translation. However, for further registration at the university, the documents must have an apostille. For each country, the apostille procedure varies. Citizens of countries that are not members of the Hague Convention, may be required to undergo consular legalization, except for the cases when countries have a mutual agreement.
Recognition of foreign documents is done by the Higher Education Council[7] (Denklik Belgesi) either before arriving at the Turkish Embassy/Consulate in your country or after arriving in Turkey. Students are advised to go through the procedure in advance since in this case the process will take less time (up to several weeks) and the likelihood of approval is high. However, not every Turkish consulate issues a certificate of equivalence. If the applicant does this in Turkey, then he needs to contact the Directorate of National Education of his city of study. Recognition of a diploma is required for registration in Turkish universities. However, many universities allow students to start their studies without a certificate of equivalence while documents are being prepared. Diplomas of graduate and doctoral applicants received outside Turkey are recognized by the Higher Education Council (YÖK).

Preparatory programs can be both language and specialized. Language courses are intended for students who do not meet the language requirements for admission. And specialized ones are for students applying for a master's or doctoral degrees and wanting to enhance knowledge in certain areas. For example, pre-MBA programs, pre-Law, or pre-Medicine.
Knowledge of Turkish is required for training in Turkish-language programs, but not for admission. If the student does not know the language, he can take preparatory Turkish courses before bachelor’s or master’s programs. Classes last for 4-6 hours a day. To successfully complete the program, it is important to attend classes regularly, do homework, and successfully pass midterm exams. At the end of the course, students take the final exam and begin their studies at the university.
Many universities in Turkey also offer pre-university programs in English. Proficiency levels presented range from beginner to advanced. To move from one level to another, students must attend at least 90% of the classes and successfully pass the exams. Programs at universities are designed so that all students, regardless of the initial level of language proficiency, can complete the program in one academic year. After completing the course, applicants enter universities.
Vocational colleges (Meslek Yüksek Okulları) award associate degrees (On Lisans Diplomasi). They are mainly part of state universities. However, there are 8 schools attached to private universities (founded by large funds of wealthy Turkish families).
Meslek Yüksek Okulları put great emphasis on the conversion of theory into skills and experience. Higher vocational schools collaborate with leading enterprises and companies. Thus, students combine practice and study. Upon graduation, students have real experience in the specialty and an understanding of what the employer needs. Colleges implement the following disciplines: foreign trade, logistics and transport, computer technology and programming, graphic and fashion design, trade and administration, accounting and taxation, translation and interpretation, tourism, culinary arts.
For admission the following documents are required:
All documents must be translated into English or Turkish.
After higher vocational schools, graduates can enter the 3rd year of bachelor’s studies or seek employment. To continue education, associates must pass the national DGS exam (Dikey Gecis Sinavi) and have a sufficient GPA for the bachelor's program of interest.

To enter a bachelor’s program in Turkey, an applicant must graduate from high school or a similar secondary educational institution. Universities accept applications online and post-admission requirements on the websites. Bachelor’s programs usually require:
Despite the fact that at some universities the minimum IELTS scores are still indicated, from 2019 Turkish educational institutions can no longer take the results of this exam. Some universities allow applicants to present their results in an application for admission. However, in case of successful admission, the applicant will still need to pass TOEFL or an internal university exam. Nevertheless, information regarding IELTS must be confirmed with the admission committee of each university. Also, the results of the SAT or any other exam conducted in English are sufficient to confirm English proficiency. In this case, there is no need to provide a language exam.
If a student does not have an official confirmation of English proficiency, then universities are allowed to conduct an internal exam upon the applicant’s arrival in Turkey. If the applicant fails to obtain the required score, he can take pre-university preparatory language courses.
To study in Turkish, you must have level C1 according to the results of the TÖMER or Yunus Emre Institute Turkish Proficiency Exam.
Candidates can also be interviewed via skype or phone, especially for medical programs that last for 6 years.
YÖS is a Turkish entrance exam for foreign students. It is held in many universities in both English or Turkish languages. Dome state universities require YÖS instead of SAT/ACT for admission to certain specialties, for example, medicine. As a rule, YÖS consists of 80 questions, half of which are general questions, and the rest are in mathematics.
Master’s in Turkey usually last for two years, but there are also shorter studies. For example, programs that do not require a defense of a thesis last only for a year and a half. In order to enroll in a master's program in Turkey, you must provide a bachelor’s diploma. Among other things, most applicants must pass an entrance exam or interview. Full-time master's programs most often begin in October.
For admission you must provide:
If you plan to study in Turkish, then as a foreigner you need to provide proof of language proficiency. Usually, the level required for higher education is C1 or 60 points according to TÖMER.
Certain master's programs are taught partially or entirely in English: a similar trend can be seen in new private universities and in some state universities that seek to attract more foreign students. The strongest master's programs in Turkey are biotechnology, IT, medicine, and the natural sciences.
Most Turkish master's programs include the writing of a dissertation, work on which begins in the second half of the second year of study. The defense of scientific work takes place orally. There are also master's programs that require a professional project instead of writing a dissertation.

Obtaining a doctorate (PhD) will take a master’s graduate from two to four years. Bachelor’s graduates who want to fully immerse themselves in science can immediately go to doctoral studies. Then the training course can last for a total of up to seven years.
Doctoral students write term papers and pass intermediate qualification exams while studying. In Turkish universities, there is a system in which the student is supervised by several teachers at once: they help in writing a final work and carry out pre defense of dissertations in order to assess the student's progress.
To obtain a scientific title, a PhD candidate must defend a dissertation in front of the dissertation council. It consists of supervisors and experts from other universities. The candidate will be allowed to defend the dissertation only if the work passes the plagiarism check.
To enter the doctoral program, students must choose a suitable program, apply online, and pass all the necessary exams and interviews. Universities rarely require hard copies of documents and written statements, so you need to check the information on the sites. Documents and exams that are required for admission to doctoral studies are most often the same as for master’s studies:
Some programs recommend that applicants contact a research supervisor of a planned dissertation before entering a university. The student can independently contact the teacher of interest and discuss a research project. This is mainly recommended for candidates in science, engineering, and health.
College faculties evaluate the applications of each applicant. If necessary, universities can conduct interviews.
Universities compete with each other, attracting leading foreign researchers. Therefore, both in state and private universities, the staff consists of local and foreign teachers. Foreign specialists are needed in English-language programs and departments, and even in some research institutions where training takes place in French and German. In all these cases, employees do not need to know Turkish.
The state annually determines the number of academic positions for each university. However, universities independently appoint and promote academicians, in accordance with the requirements of the Council of Higher Education and a senate of a university. According to the Higher Education Act 1981, the following academic positions are defined in Turkey: Research assistant, Lecturer, Instructor, Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, Professor.
To obtain an academic position, you must have a PhD. Universities recruit staff themselves, so openings can be found on their websites. Associate Professor and Professor positions are awarded by UAK and YOK. To do this, the candidate must have a good grade/report, pass a specialized oral and/or practical exam in front of 3-5 experts (not for all disciplines) and make several articles for prestigious scientific publications.
At public universities, full-time teachers are state employees. The Assistant Professor is a temporary position, while Professor and Associate Professor work on the basis of a permanent employment contract.
Teaching, research and administrative responsibilities vary from one position to another. But basically, all professors conduct research, supervise scientific work and do paperwork. Higher education institutions independently determine the number of hours and teaching methods.
Terminations of academic staff are extremely rare, usually in cases of proven plagiarism[8]. The average salary of a Professor ranges from 1,863 USD to 3,307 USD[9].
Turkiye Burslari. State-funded scholarship program. It is awarded to outstanding foreign students who wish to obtain bachelor’s, master’s or doctoral degrees. The scholarship is also awarded for short-term PhD studies. A prerequisite for participation in the consent to a free one-year study of the Turkish language before the start of the main program. Scholarships are not awarded for a two-year associate degree and specialties in the field of medicine.
Turkiye Burslari covers:
Scholarships are awarded on a competitive basis, and it is not easy to receive them. Each year, the commission receives more than 100000 applications and issues about 5000 scholarships[10]. The selected candidates are interviewed in their countries of residence, online or via phone.
| Degree | Scholarship | Duration | Academic performance | Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bachelor | 21 USD | 1 year of Turkish + 4-6 years | 70% | Under 21 |
| Master | 29 USD | 1 year of Turkish + 2 years | 75% | Under 30 |
| Doctor | 42 USD | 1 year of Turkish + 4 years | 75% (for medicine 90%) | Under 35 |
Detailed information and a list of universities can be found on the website scholarship.
Scholarship for winners of international scientific Olympiads. The Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK) provides scholarships for foreign students, winners of international scientific olympiads in:
Financial assistance is given for bachelor’s programs related to the subject of the Olympiad. The grant provides a monthly scholarship of 26 USD and covers the cost of training of up to 52 USD for 4-6 years. A nice bonus is the extension of the grant for the next step of education. This happens if the student successfully completes the bachelor’s studies and enters the master’s/doctoral program at a Turkish university. Here you can apply for a grant and find more detailed information.
Help from universities. Turkish universities receive financial support from large corporations, which allows them to provide scholarships to students. But it is rather difficult for foreigners to receive such grants.

Student visas are issued at the Turkish Embassy or Consulate in the country of residence. It usually takes about eight weeks from the moment of application to issuing a visa. Therefore, it is necessary to apply for a student visa as soon as the university sends an invitation. The earliest application is 60 days in advance. You can schedule an interview and a date for submitting documents on the website of consular services in Turkey.
The documents required when applying for a visa vary from country to country. The package usually consists of:
The questionnaire and detailed information can be found on the website of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Turkey. The cost of a visa depends on the country of the candidate, on average — 200 USD.
Upon arrival in Turkey, students must register at the nearest local police station and apply for a residence permit in the migration department within 30 days. To do this, fill out the form on the site.
After obtaining a residence permit (ikamet), you can live in Turkey, open a bank account, and use the ikamet card when entering or leaving Turkey. Six weeks before the expiration of the residence permit, you must apply for its extension.
Foreign bachelor’s students are not eligible for official employment in either public or private institutions. However, Turkish universities provide their students with the opportunity to work at the department, in libraries, or engage in scientific activities on campus. And foreign master’s and doctoral students, in accordance with the new Law on the international workforce, can now obtain a work permit. The Turkish Ministry of Foreign Affairs regulates their employment.
Often, universities fully finance master’s and doctoral studies. In return, foreign students help professors in teaching, conducting research, or preparing statistics. For this, students are not required to know the Turkish language, because many universities offer English-language programs. Examples of public universities with an international focus: Boğaziçi University (Istanbul) and Middle East Technical University (Ankara). Private universities include Sabanci University, Koç University, Istanbul Bilgi University (all in Istanbul), and Bilkent University (Ankara).
In addition, for students under thirty, there are many different paid internships, after which you can get a job in one of the Turkish companies. Detailed information on internship conditions can be found in educational institutions. For example, at Bosphorus University there is a Career Center, where any student or graduate can seek professional advice.
Opportunity to stay and immigration to Turkey
Graduates have the right to apply for a work permit. This should be done within one year after graduation. After applying, the decision will be made by the International Labor Policy Advisory Council. It is important to note that bachelor’s students who have studied under a state scholarship in Turkey are not eligible for a work permit. This ban applies even after graduation or in the presence of a short-term residence permit.
Work permit (PermitsCalisma Izni) is issued by the Ministry of Labor. The contracting company must send the application. Most work permits are initially issued for one year, extended for three years, and then for six years. If you have lived in Turkey for eight years and you had a work permit for six of them, you will be able to obtain a permanent work permit.
Here is a list of documents that must be provided by the employer. The applicant will need to provide:
Documents must be scanned and sent online.
| Type of permit | Cost |
|---|---|
| Temporary (up to 1 year) | 24 USD |
| Permanent | 245 USD |
| Independent | 245 USD |

Turkey has been a participant in the Bologna process since 2001, as well as a candidate for accession to the European Union. This means that, firstly, all students can continue their education in other countries using the credit system ECTS, and secondly, a Turkish diploma is recognized by European employers.
For non-Turkish graduates, there are not many job opportunities in the country. Much depends on qualifications. If you are a specialist in tourism and hotel business, then there are more chances to find a job. Some of the highest-paid and prestigious positions are located in embassies, consulates, and non-governmental organizations. There you can try to apply for an internship and subsequently gain a foothold in the workplace. Another possibility is teaching at a language school.
The youth unemployment rate in the country for 2020 is 24.4%, and the general level is 10.4% in 2019[12]. In the same year, the minimum employee salary per month was 67 USD[13]. The state economy has been actively developing since 2000: employment and wages are increasing. Thanks to government reforms and programs, poverty has more than halved in 2002–2015, and extreme poverty has declined even faster. However, inflation, reduced investment, the external situation, vulnerability in the financial sector, and the impact of the COVID-19 crisis can weaken the country's economy[14]. The main industries in Turkey are agricultural production, tourism, food, textile, chemical and pharmaceutical industries, mechanical engineering, electronics, mining and construction[15].
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got