
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
What is a higher education in India and what it consists of? We have a detailed explanation on how to enter, get a visa and what to do after graduation.
Free consultation



| Type of study | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Level of language proficiency | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer camp | 7+ | 1-10 weeks. | 200 USD/week | 250 USD/week | A1 | - |
| Language courses | 9+ | 1-12 weeks | 150 USD/week | 400 USD/week | A1 | - |
| Secondary education | 8+ | 12 years | - | - | B1 | - |
| Vocational education | 18+ | 0.5-3 years | 99 USD/year | 350 USD/year | B2 | TOEFL 78+ |
| Undergraduate | 18+ | 3-5 years | 150 USD/year | 1,400 USD/year | B2 | TOEFL 78+, SAT 1200+ |
| Master's | 21+ | 1-2 years | 292 USD/year | 3,320 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL 95+, GRE 300+ |
| MBA | 21+ | 1-2 years | 2,240 USD/year | 12,466 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL 95+, CAT 205+ / GMAT 600+ |
| PhD | 22+ | years 3-5 | 852 USD/year | 12,899 USD/year | C1 | TOEFL 95+, RET 122+ |
| Language exam | 260 USD |
| Registration fee | 233 USD |
| Flight | 200 USD |
| Accommodation | 82-134 USD/month |
| Meals | 82 USD/month |
| Transport | 7 USD/month |
| Visa | 40 USD/year |
| Insurance | 50 USD/year |
| Study materials | 400-600 USD |

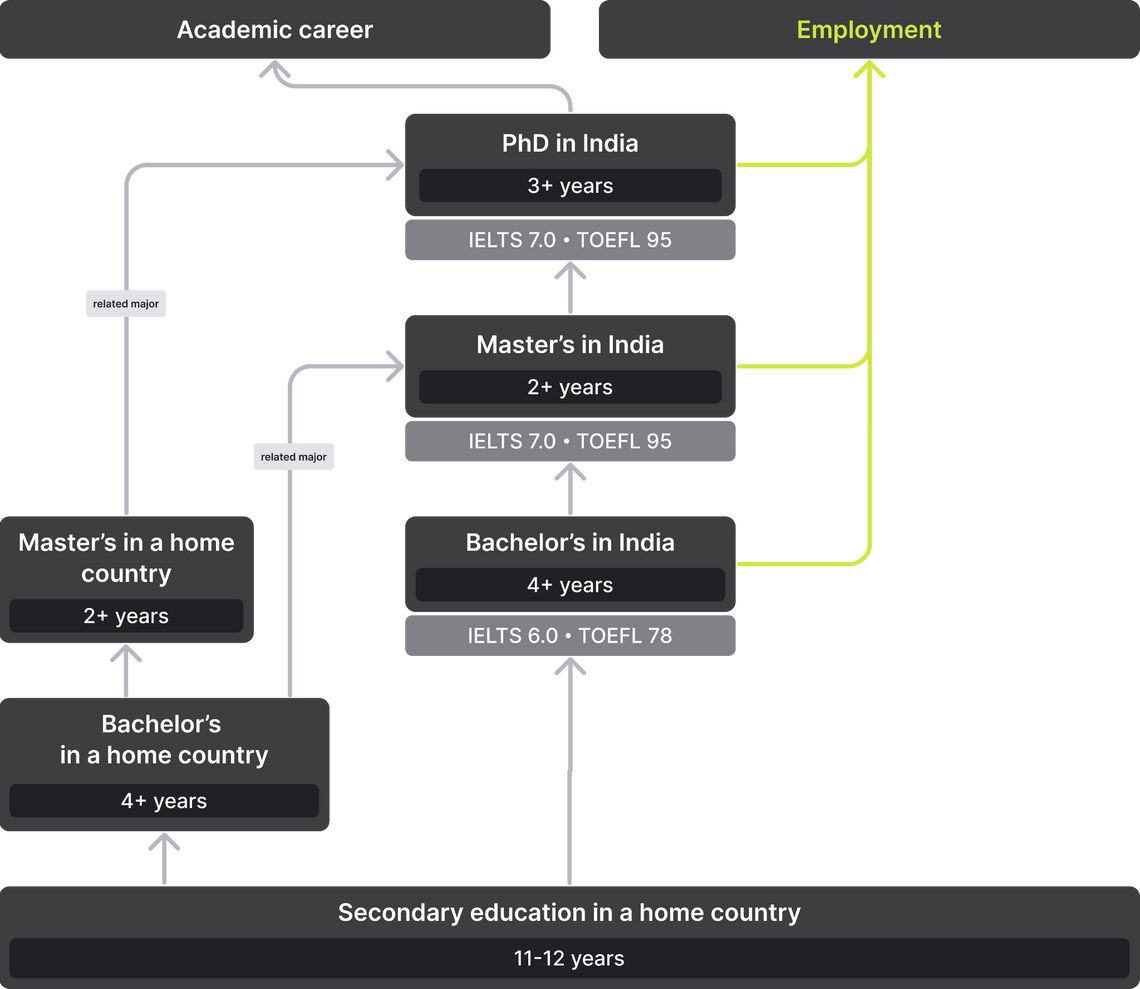
Indian higher education system is built on the Anglo-Saxon model and consists of three stages: Undergraduate, Postgraduate and Doctoral studies. For admission to most universities in India, the following documents are required:
Deadlines for submission of documents are usually from June to July and from January to February, but in some universities, admission is open throughout the year.
An application for admission can be submitted on the official website of the selected university. Also, for admission to universities with centralized funding, there is a service for submitting applications to more than one Indian university at the same time — DASA. Applications for undergraduate programs are accepted from 17-25 years old students, there is no age limit for graduate and doctoral studies. In most universities, the applicant must pay a registration fee of 300 USD and the tuition fee for the first semester — 4,000 USD[9].

Usually, educational documents must go through a legalization procedure in order to be valid abroad, which vary from country to country. There are certain countries that have mutual agreements with India to skip this step, so check if your country is among them.
For high school graduates and high school students[10] who want to get blue-collar jobs, there are vocational programs in India. They are offered by institutes and colleges. Such programs do not prepare students for academic pursuits. You can get education in Architecture, Engineering, Hotel Management, Infrastructure, Pharmacy, Urban Services, etc. Among the most popular areas of training are the programs by Industrial Training Institutes in Engineering, as well as specialties that prepare to work in the industries of service and tourism.
The conditions for admission depend on the chosen educational institution. First of all, universities take academic performance into account. Studies last from a month to three years, graduates receive a certificate or a diploma of vocational education. This option is suitable for those who want to acquire applied knowledge in a shorter period of time and at a more affordable price: the average cost will be about 350 USD per year.
At the same time, colleges in India are not very popular — both among international students and among citizens. Vocational education has the reputation of an option for students from lower classes of society without outstanding academic abilities[11]. There are far fewer such educational institutions than universities. Many colleges suffer from a lack of qualified teachers and the necessary resources[12]. However, in the future, the Indian government plans to integrate vocational education institutions into the higher education system. This is stated in the New National Education Policy, adopted in 2020[13].

Universities in India have the European system of credits, students are evaluated on a 10-point scale, and the programs themselves are interdisciplinary. Unlike many Western universities, initially studying in a general direction is impossible: upon admission, you must choose a specialization. Graduation requires 120-140 credits.
The duration of studies depends on the field:
A three-year program can be completed in a shorter period of time once you get a sufficient number of credits. It is also possible to complete training earlier and still receive a diploma: after the first year, a certificate is issued, after the second — a diploma, and after the third — a Bachelor's degree[14].

Admission conditions vary by state and university. Standard conditions for submission of documents for undergraduate programs are:
Some universities conduct their own entrance tests, as well as organize interviews for candidates who have passed the initial selection. You will also need to pay a registration fee. Information must be specified on the official website of the university.
Each university in India sets the date of beginning of the academic year independently. It is important to take this into account in order not to miss the application deadline. You can start studying from the fall or spring semester, and submit documents no later than three months before the start of classes. As soon as the application is accepted, it will be possible to proceed to the registration of a student visa.
Master’s programs in India last 1-2 years. The longer option is more suitable for those who are planning to enter doctoral studies. Master's students write course papers, take exams, and at the final stage of studying they prepare a thesis or another research project together with the supervisor. The academic year usually begins in July, the dates are set by the universities themselves and vary from state to state.

Indian universities generally set their own standards for admission to graduate programs. When preparing an application for admission, it is important to check the website of a specific university. A Bachelor's degree will be required, and in most institutions it is a necessity that the applicant's degree is related to the specialization of the Master's degree. You will also need to attach a transcript of all completed courses and assessments.
The choice of university for a Master's degree depends on the field of research interests of the student. Medicine, science and technology are usually studied in Institutes of National Importance. They are considered the most prestigious and advanced research centers in the country, with a high competition for admission. A Master's degree in the humanities and social sciences or an MBA can be obtained from public and private universities.
Before admission, you can take preparatory courses organized by universities for beginners in postgraduate educational programs.
Some universities offer additional entrance tests. This often applies to Institutes of National Importance, where competition among applicants can be very high. If your documents are not in English, you will need a notarized translation.

The duration of a doctoral program varies from university to university and can be between 3-5 years. The academic year lasts from July to May. The studies often begin with a course paper. This allows the student to dive deeper into the subject area and acquire the necessary research skills. The course paper can be completed by the end of the first year of study, or earlier if the student already has acquired a relevant qualification at the Master's level. After that, the PhD candidate prepares a synopsis of the future dissertation and begins to work with the academic advisor.
To obtain a degree, you must go through several stages. First, a student submits a dissertation at their educational institution. In India, this stage of doctoral studies is more significant than in some other countries. The reviewing is done by several faculty members who may request corrections and resubmissions before admitting a student to an external exam.
After the dissertation is approved at the university level, the work is handed over to one or more external examiners who review it orally. In India, this procedure is called "open defense." The procedure is held in a festive atmosphere in front of an audience that includes fellow students, teachers, family and friends of the student.
In addition to the dissertation, PhD candidates must publish the work in a peer-reviewed scientific journal.
An important feature: in India, not only standard PhD degrees are issued, but also specialized ones. For example, a Fellow Program in Management (FPM) or a Doctorate in Pharmacy (Pharm D).
The candidate needs to hold a Master's degree in the relevant subject area and prove fluency in English.
The admission process usually looks like this:
Some Indian universities follow a three-tier American-style academic system (Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, Professor) with strict requirements for entry-level positions. In order to take up the position of Assistant Professor, you must have at least 3 years of postdoctoral work. Candidates with less experience take up a "contract" position, akin to a non-tenure track at American universities.
Promotion to the position of Associate Professor is possible in the fourth year of work, although more often this does not occur until the sixth. For this position, the candidate must have a certain number of publications in scientific journals, recommendations of reviewers in India and abroad, and outstanding teaching results. Further promotion to the position of Professor requires less effort.
Other Indian universities offer two ways to enter academia. One of them is through direct selection by the university, the second is through selection by a centralized commission. The competition is based on the points that the candidate received in the Master's degree program, as well as the results of the National Eligibility Test (NET) and an interview.
Tuition-free seats in Indian universities are not available to foreigners, but there are opportunities to study for free or get partial coverage of the costs:
For a more complete list of scholarships and grants to study in India, including grants for doctoral programs, see the University Grants Commission website.

Visa is issued for a period of 1 to 5 years. A prerequisite is an invitation from a university with state accreditation. In addition, the following documents will be required:
The visa fee is from 100 USD, the request is processed within 5 working days.
All foreign students must undergo a medical examination and obtain a health certificate upon arrival in the country. You must also register with your local Foreigner Regional Registration Office (FRRO) within 7-14 days. After registration, students must obtain a residence permit within 90 days.
Students residing in India with a student visa are not allowed to work while studying. The only option is internships if they are part of the curriculum, but in most cases they are not paid. However, India's Ministry of Education is preparing a bill that will ease conditions for international students. The bill might allow a limited work permit in certain areas where there is a lack of qualified specialists[15].

Government policies to control overpopulation make it difficult to obtain a residence permit in India. For a university graduate, the most convenient option would be an invitation to work, which will allow you to apply for a work visa. In this case, the residence permit will be valid until the end of the contract, which is usually concluded for a period of 1 to 5 years. Preference is given to highly qualified personnel in managerial positions. The requirements also include a fixed salary of at least 25,000 USD. Required documents for a work visa:
The cost of a work visa varies from 102 USD to 142 USD.
India is a country with an explosive economic growth. According to experts, by 2024 it will rank fifth in the world with a GDP of 3.7 trillion USD[16]. Agriculture, mining and the service industry are the largest sectors of the national economy[17].
Geographically, major northern cities such as the political capital of New Delhi and the financial center of Mumbai provide the bulk of jobs. In turn, the southern metropolis of Bangalore is the center of the country's high-tech industry. Retail and hospitality businesses are better developed in coastal tourist areas such as Goa.

Highest salaries are received by IT employees and engineers with a doctoral degree[18]. They have the highest employment rates among university graduates[19]. The easiest way to build a successful career in India is to receive a degree in one of these areas. The rest should take into account that the overall unemployment rate in the country remains high[20]. Moreover, about half of the country's population earns less than 120 USD per month[21]. However, representatives of less popular professions also stay to work in India, as they see a number of advantages for themselves:
As Indian higher education is renowned for strong programs in technical and scientific fields, such a degree can be highly regarded by employers in the US and European countries.
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got